- Title
-
Knockout of dhx38 Causes Inner Ear Developmental Defects in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Ren, M., Chen, X., Dai, L., Tu, J., Hu, H., Sun, X., Luo, J., Li, P., Fu, Y., Zhu, Y., Sun, W., Tang, Z., Liu, M., Ren, X., Lu, Q.
- Source
- Full text @ Biomedicines
|
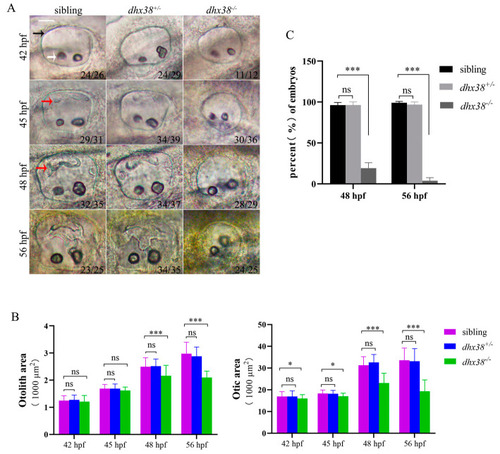
The deletion of |
|
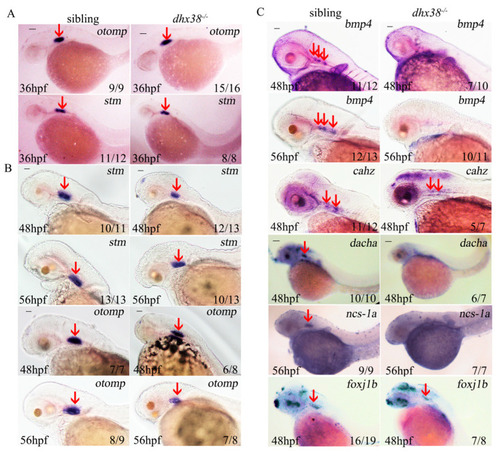
The expressions of some specification-related inner ear markers differed significantly between the sibling and |
|
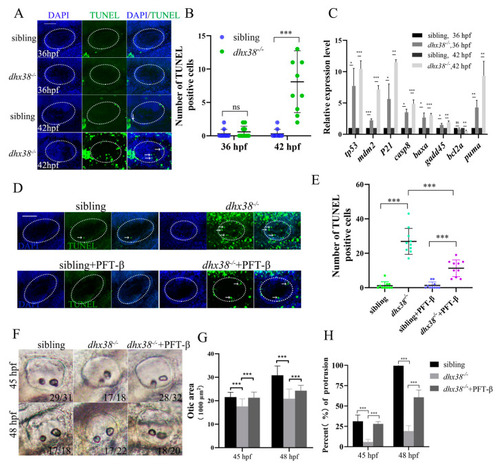
Apoptosis was increased in the inner ear epithelium cells of |
|
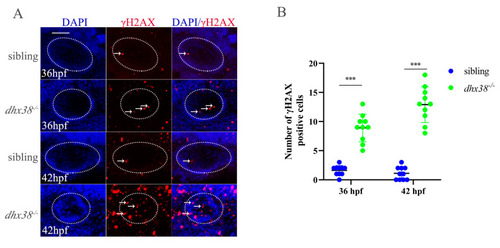
Analysis of the accumulation of DNA damage in inner ears of |
|
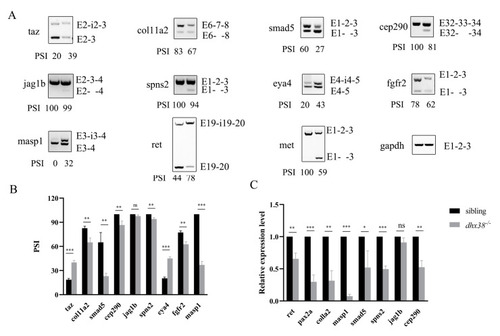
Dhx38 regulates the alternative splicing of some genes involved in DNA damage repair: ( |
|
The abnormal splicing of genes involved inner ear development at 42 hpf: ( |