Fig. S5
|
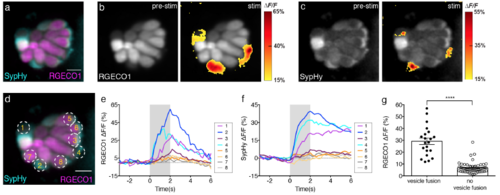
Hair cells with vesicle fusion correlate with strong cytosolic Ca2+ influx. (a) Double transgenic neuromast co-expressing RGECO1 (magenta) and SypHy (cyan) in hair cells. (b-c) RGECO1 and SypHy responses acquired from the same neuromast organ during a 2-s 5 Hz (anterior-posterior directed square wave) stimulus that activates all hair cells. Spatial patterns of RGECO1 Ca2+ activities (b, right panel) or SypHy vesicle fusion (c, right panel) during stimulation are colorized according to the ΔF/F heat maps and superimposed onto pre-stimulus baseline grayscale image RGECO1 (b, left panel) or SypHy (c, left panel) image. (d) Combined color image of SypHy (cyan) and RGECO1 (magenta), with 8 hair cells outlined with ROIs (3 μm). (e-f) Temporal curves of RGECO1 Ca2+ signals (e) and SypHy vesicle fusion signals (f) from the 8 ROIs drawn in (d). Hair cells (cells 1, 2, 4) with stronger Ca2+ influx (e) also have detectable vesicle fusion (f). (g) RGECO1 Ca2+ signal magnitude is greater in hair cells with (ΔF/F, 29.18 % ± 2.75, n = 21 cells) than without (ΔF/F, 6.70 % ± 0.58, n = 58 cells) detectable SypHy signals, p< 0.0001. A Mann Whitney test was used in (g), **** p < 0.0001. Scale bars = 5 μm. |