- Title
-
Transcription factor Meis1b regulates craniofacial morphogenesis in zebrafish
- Authors
- Psutkova, V., Nickl, P., Brezinova, V., Machonova, O., Machon, O.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
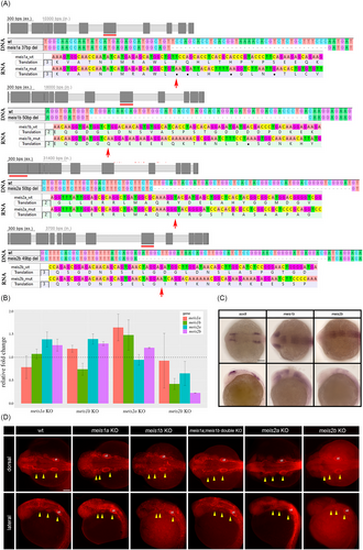
Meis1b and meis2b are expressed in midbrain and hindbrain and do not influence NC migration. (A) Top: Scheme of deletions in DNA generated by CRISPR/Cas9 in zebrafish meis genes. Red lines mark targeted exons. Meis1a mutants had 37-bp long deletion in exon 8/intron8, meis1b 50-bp in exon 8, meis2a 50-bp in exon2, meis2b 49-bp in exon 8. Bottom: Sequencing of RNA of mutated genes and protein translation sequences in mutated regions. Red arrows point at sites of shifted reading frames. (B) qRT-PCR analysis showing relative expression of meis transcripts in respective mutant line embryos at 24 hpf. Ct values were normalized to gapdh reference housekeeping gene. Relative fold change to calibrator wild-type controls (set to 1, dashed line). (C) Expression of NC marker sox9 relative to meis1b and meis2b in wild type embryos at stage 12 hpf. Dorsal views (top) and lateral views (bottom). Anterior to the left. (D) Migratory streams of NC at 24 hpf labeled by Sox9 (red) antibody, the first stream (mandibular) at the left, the second (hyoid) and the third stream. Dorsal views (top) and lateral views (bottom) with anterior to left. ot, otic, wt, wild type. Scale bar = 100 μm. |
|
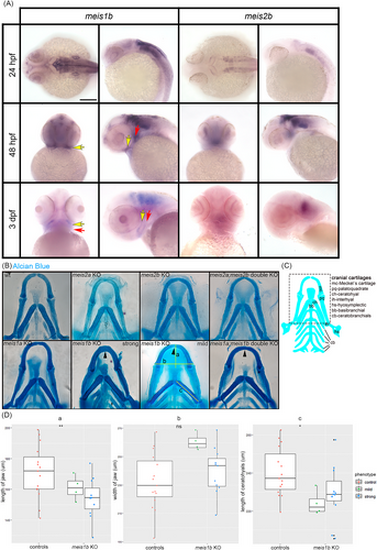
Meis1b affects the jaw and ceratohyal cartilages development. (A) Expression of meis1b and meis2b in wild type embryos during formation of NC derivatives. Meis1b is expressed in mandibular (yellow arrow) and hyoid arches (red arrow). Dorsal view (24 hpf, left column), ventral view (48 hpf, 3 dpf, left column), lateral view (right column in meis1b and meis2b). Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) Staining of cartilage with Alcian Blue at stage 8 dpf. Ventral views, anterior to the top. Meis1b and meis1ab mutants were separated into two groups by the level of morphological damages: mild (n = 8) and strong (n = 24). The yellow lines indicate distance measurements. The fusion of the Meckel's cartilage is shown by arrowheads. (C) Schematic drawing of cartilage at 8 dpf, the dotted frame corresponds to images in (B). D, Quantification of the jaw length (a), width (b) and the length of the ceratohyals (c). Two tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis, controls (n = 15), mutants (n = 15: mild = 4, strong = 11), *p < .05, **p < .01. Scale bar = 50 μm. |
|
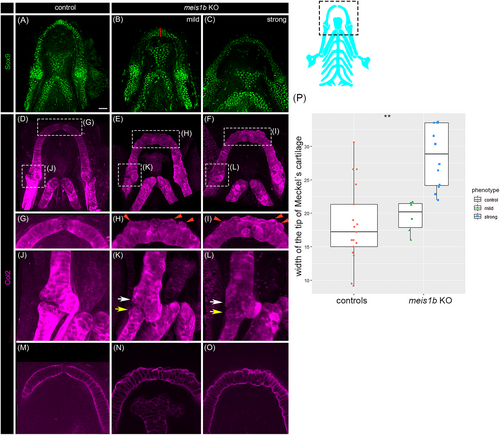
Chondrocytes of the Meckel's cartilage appear unaligned in meis1b KO mutants. (A–C) Whole-mount antibody staining of chondrocytes with Sox9 (green) and (D–O) Col2 (magenta) at 8 dpf. (A–I), (M–O), Ventral views; (J–L), lateral view; anterior to the top. The position of cartilage in images is displayed in a dotted frame in the scheme (right). (G–I) Magnification of dotted frame of (D–F), the border between Meckel's cartilages is missing in meis1b mutants (H, I). (H, I) Chondrocytes are misaligned which causes irregularities in the cartilage (red arrowheads). (J–L) Magnification of dotted frame of (D–F) from lateral view; The posterior end of the Meckel's cartilage (white arrows) and anterior end of palatoquadrate (red arrows) are deformed. The gap within the jaw joint is missing. (M–O) Optical section of the Meckel's cartilage from (D–F). (M) Chondrocytes are stacked in columns of columnar-shaped cells. (N, O) The shape of chondrocytes is uneven and chondrocytes are unorganized. The red line indicates the site of width measurement of Meckel's cartilage. (P) Quantification of the width of the tip of Meckel's cartilage. Two tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis, control (n = 17), mutants (n = 17: mild = 6, strong = 11), **p < .01. Scale bar = 30 μm. |
|
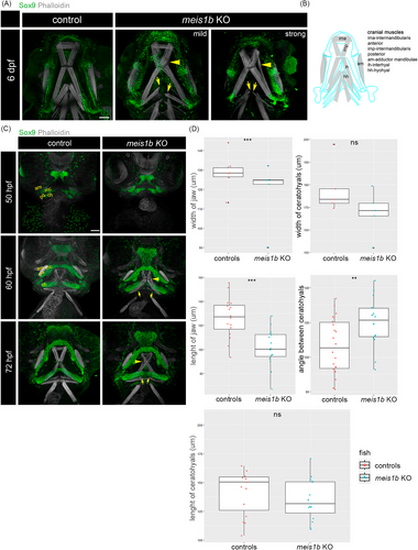
Muscle fiber structure is modulated by impaired cartilage in meis1b mutants. Antibody staining of cartilage (Sox9, green) and muscles (phalloidin, white). Ventral views, anterior to the top. (A) At 6 dpf, separated muscle fibers of the intermadibularis posterior (imp) are indicated by yellow arrowheads. Split ends of the hyohyal muscles in mutants are labeled with yellow arrows. (B) Schematic of cranial muscles (gray) and contours of adjacent cartilage (blue). (C) At stage 50 hpf, rudiments of the Meckel's cartilage (mc), palatoquadrate (pq) and ceratohyals (ch) start to form, the only visible muscle is the adductor mandibulae (am) at this stage. At 60 hpf, the separated intermadibularis posterior muscle fibers are already detected at this stage (arrowhead). The hyohyal muscle are underdeveloped (arrows). At 72 hpf, the intermadibularis posterior muscle fibers are unaligned (arrowhead) and the fibers of the hyohyal muscle appear separated even more (arrows). Scale bar = 30 μm. (D) Quantification of the width of the jaw and ceratohyals at 50 hpf (controls = 5, mutants = 5), length of the jaw and ceratohyals and angle between the ceratohyals at 72 hpf (controls = 16, mutants = 16). Two tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis, **p < .01, ***p < .001. am, adductor mandibulae; ch, ceratohyals; mc, Meckel's cartilage; pq, palatoquadrate. Scale bar = 50 μm. |
|
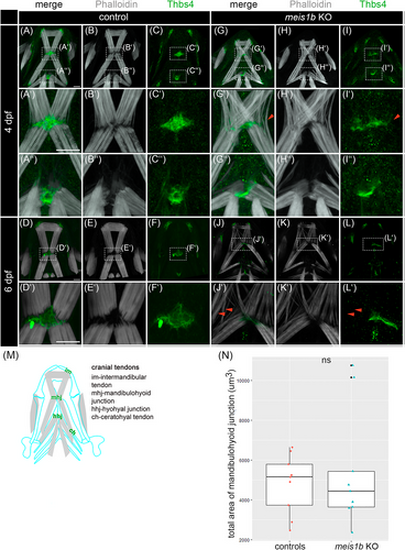
Tendons are disorganized together with muscles in meis1b mutants. (A–L′) Immunostaining of tendons with Thbs4 antibody (green) and muscles with phalloidin (white). Ventral views with the anterior to the top. (A′–C′, G′–I′) Detail of the mandibulohyoid junction at 4 dpf. (A″–C″, G″–I″) Detail of the hyohyal junction at 4 dpf. (G′, I′) Red arrowheads indicate affected muscle fibers without tendon. (D′–F′, J′–L′) Detail of the mandibulohyoid junction at 6 dpf. (J′, L′) Tendons and muscles are more disorganized, and some muscle fibers lacked corresponding tendons (red arrowheads). (M) Schematic position of tendons in the context of head muscles (gray) and cartilage (blue contours) at 6 dpf. (N) Quantification of the total area of the mandibulohyoid junction, color dots indicate individual animals (controls = 9, mutants = 9). Mann–Whitney U test was used for statistical analysis. Scale bar = 30 μm. |
|
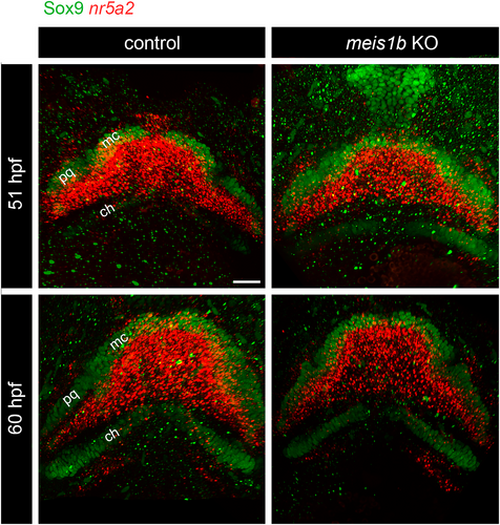
Expression of tenocyte precursor marker nr5a2 was not affected in meis1b mutants. Combined HCR FISH-antibody staining of nr5a2 mRNA (red) and immunostaining of cartilage (Sox9 antibody, green) at 51 and 60 hpf. Nr5a2 was expressed in whole area of the first PA demarcated by cartilage at both stages. At 60 hpf, nr5a2 was also observed in the area of the second PA. ch, ceratohyals; mc, Meckel's cartilage; pq, palatoquadrate. Scale bar = 30 μm. |
|
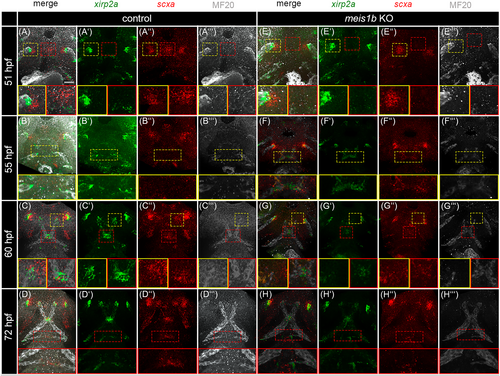
Tenocytes development is affected together with muscles in meis1b mutants. Tenocytes were analyzed by HCR FISH using probes for xirp2a (green, A′–D′, E′–H′) and scxa (red, A″–D″, E″–H″) and muscles were co-stained by MF20 antibody (white, A‴–D‴, E‴–H‴). Ventral views with the anterior to the top. (A, A″) scxa expression was localized in two lateral cluster (yellow dotted frame and insets) and one in the middle (red dotted frame and insets). In meis1b mutants (E–E″), expression of scxa is seen only in two lateral clusters (yellow dotted frame and insets) whereas the expression in the middle is missing (red dotted frame and insets). (A–A‴, E–E‴) Detail of the tip of adductor mandibulae in yellow insets, detail of the anterior scxa positive area in red insets. (B′, F′) xirp2a is expressed at the muscle tips in the presumptive mandibulohyoid junction (yellow dotted frame and insets). (B–B‴, F–F‴) Detail of the mandibulohyoid junction in yellow insets. (C, G) xirp2a and scxa are co-expressed at the sides of attachment to the Meckel's cartilage (yellow dotted frame and insets). In meis1b mutants (G′), xirp2a expression is less condensed in the mandibulohyoid junction (red dotted frame and insets). (C–C‴, G–G‴) Detail of the presumptive intermandibular tendon in yellow insets, detail of the mandibulohyoid junction in red insets. (H) Loss of the hyohyal muscle led to an underdeveloped the hyohyal junction (red dotted frame and insets). (D–D‴, H–H‴) Detail of the hyohyal junction in red insets. Scale bar = 30 μm. |
|
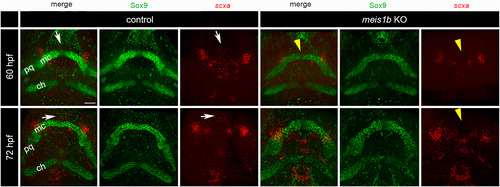
Expression of scxa in tenocytes surrounds the tips of the Meckel's cartilage. HCR-antibody staining of scxa mRNA (red) and cartilage (Sox9 antibody, green). Ventral views with the anterior to top. In controls at 60–72 hpf, the anterior tenocyte cluster in the midline was localized between and anterior to the tip of the Meckel's cartilage (arrows). In contrast, this scxa-positive cluster was missing in meis1b mutants (arrowheads). ch, ceratohyals; mc, Meckel's cartilage; pq, palatoquadrate. Scale bar = 30 μm. |
|
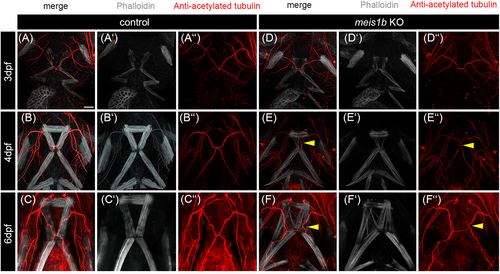
The position of the trigeminal nerve reflected misshapen muscles. Whole-mount antibody co-staining of nerves with anti-acetylated tubulin (red, A″–C″, D″–F″) and muscles with phalloidin (white, A′–C′, D′–F′). Arrowheads in (E–E″) indicate misshapen pattern of the trigeminal nerve which corresponds to disrupted intermandibularis posterior and hyohyal muscles. Malformation of the trigeminal nerve is even more apparent at 6 dpf in meis1b mutants (arrowheads in F–F″). Scale bar = 30 μm. |
|
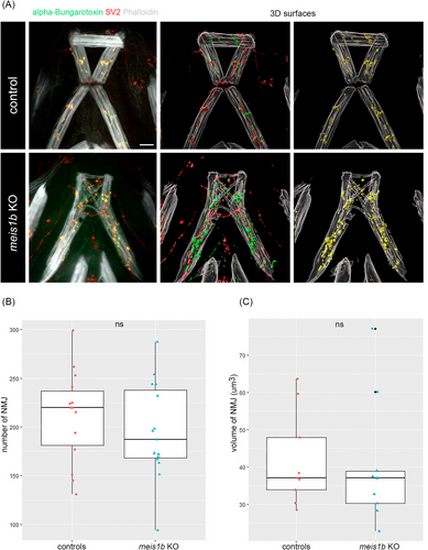
Neuromuscular junctions (NMJ) are developed and colocalized in meis1b mutants. (A) Left panels: Combined antibody staining of presynaptic receptors (SV2, red) and postsynaptic receptors (alpha bungarotoxin, green). Muscles are counterstained with phalloidin (white). Middle and right panels: 3D surfaces of images on the left generated in Imaris (n = 15), yellow indicates colocalization of SV2 and alpha bungarotoxin (NMJ). (B) Quantification of the number of NMJ, (C) volume of NMJ. Color dots indicate individual animals (controls = 9, mutants = 9). Two tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis. All images are ventral views, anterior on top. Scale bar = 30 μm. |