- Title
-
Prpf31 is essential for the survival and differentiation of retinal progenitor cells by modulating alternative splicing
- Authors
- Li, J., Liu, F., Lv, Y., Sun, K., Zhao, Y., Reilly, J., Zhang, Y., Tu, J., Yu, S., Liu, X., Qin, Y., Huang, Y., Gao, P., Jia, D., Chen, X., Han, Y., Shu, X., Luo, D., Tang, Z., Liu, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Nucleic Acids Res.
|
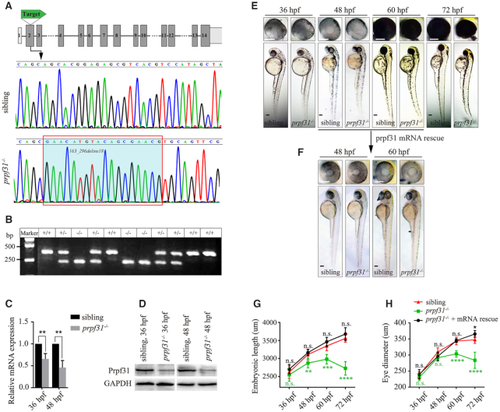
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of PHENOTYPE:
|
|
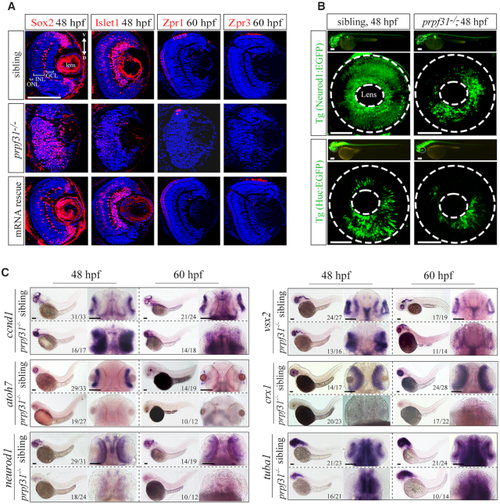
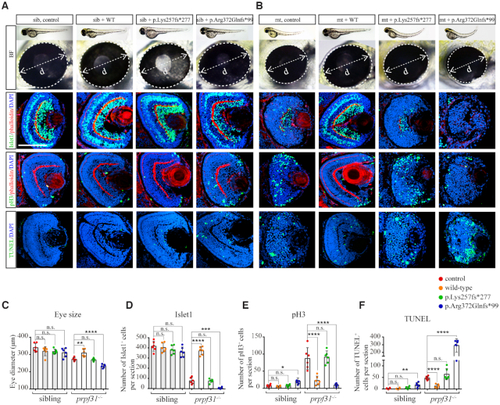
Deletion of Prpf31 impaired RPCs differentiation. ( |
|
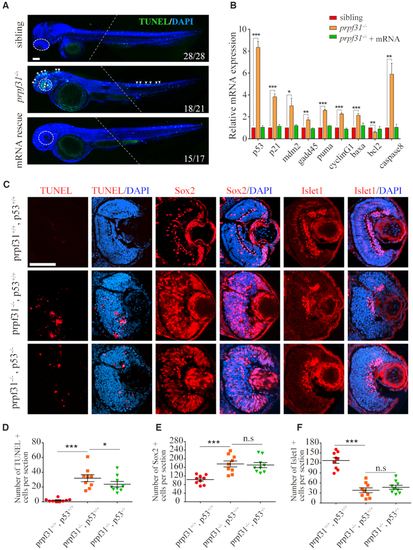
Increased apoptosis and activated |
|
Prpf31 deficiency causes abnormal spindle structure and mitotic arrest. ( |
|
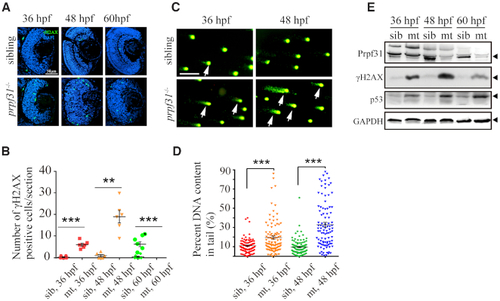
Accumulation of DNA damage in |
|
The defective retinal development in prpf31 mutants can be rescued by injection of wild-type but not RP mutant |
|
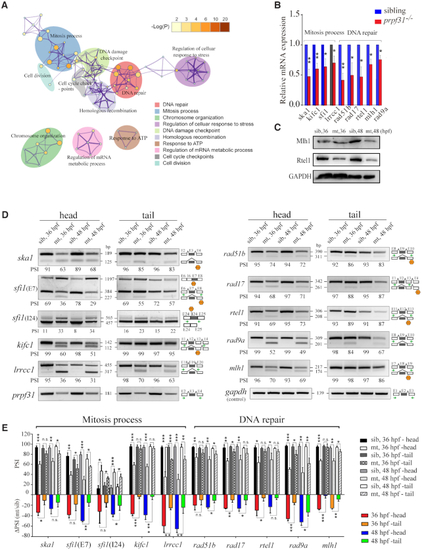
Prpf31 modulates the alternative splicing of a subset of genes involved in DNA repair and spindle assembly. ( |
|
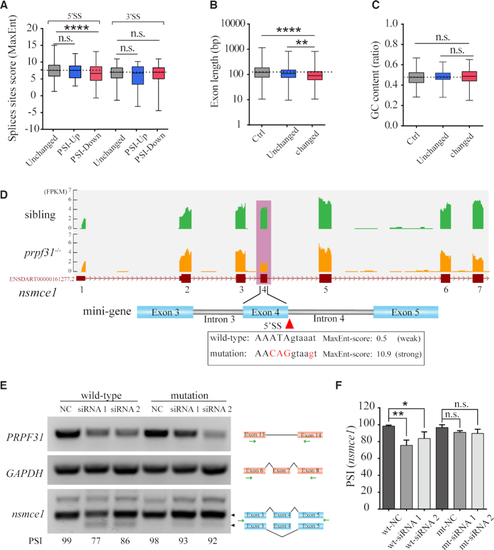
Prpf31 deletion is more likely to cause the skipping of exons with shorter length and weaker 5′ splicing site. ( |
|
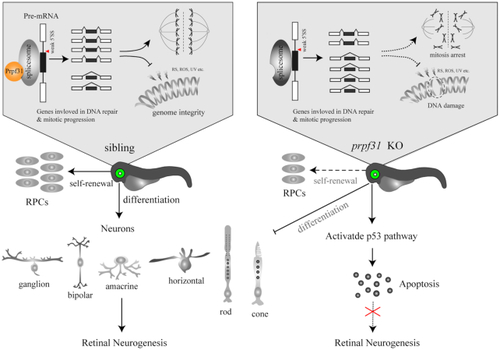
A schematic summary of the main findings. Prpf31 is required for the maintenance of RPCs and retinal neurogenesis in zebrafish. In the absence of Prpf31, the splicing of genes related to mitosis and DNA repair is compromised, resulting in decreased expression and abnormal functions of these genes. RPCs could not complete the mitotic progression and deal with DNA damages, and finally undergo apoptosis. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |

Unillustrated author statements |