- Title
-
Role of the 2 zebrafish survivin genes in vasculo-angiogenesis, neurogenesis, cardiogenesis and hematopoiesis
- Authors
- Delvaeye, M., Devriese, A., Zwerts, F., Betz, I., Moons, M., Autiero, M., and Conway, E.M.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Dev. Biol.
|
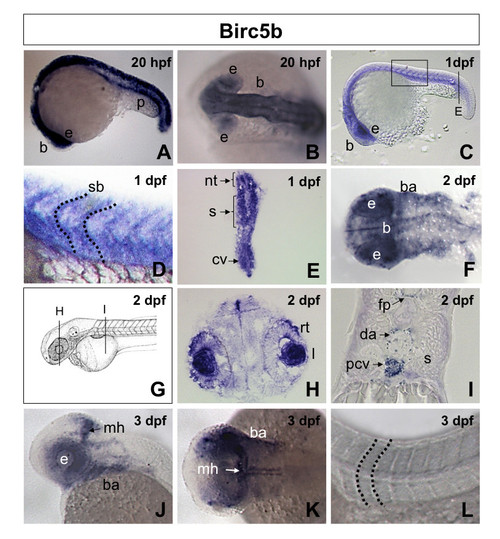
Birc5b spatiotemporal expression in zebrafish embryos. A, B. Lateral (A) and dorsal (B) views of 20 hpf (20 somites) embryos revealing expression of Birc5b in the neural tube, brain, pronephric duct and eyes. C. Lateral view 1 dpf (30 somites) embryo, showing Birc5b expression in brain, eye, neural tube, somite and intersomite boundaries, with higher magnification in D. E. Transverse section through 1 dpf embryo (from C), revealing expression of Birc5b in neural tube, somites and caudal vein plexus. F. Dorsal view of head region of 2 dpf embryo. Birc5a detected in brain, floor plate and branchial arches. G. Diagram of 2 dpf embryo with transverse sections in panels H and I. Transverse sections through 2 dpf embryo reveals expression in retina and iris (H), floor plate, dorsal aorta, posterior cardinal vein; not in somite (I). J-L. Lateral (J) and dorsal (K, L) views of 3 dpf embryo; expression of Birc5b at midbrain-hindbrain barrier, branchial arches and eyes; not in region of axial vessels, somites or intersomite boundaries (L). nt: neural tube, p: pronephric duct, b: brain, e: eye, rt: retina, I: iris, mh: midbrain-hindbrain barrier, fp: floor plate, ba: branchial arches, s: somite, sb: intersomite boundary, da: dorsal aorta, pcv: posterior cardinal vein, cv: caudal vein plexus. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
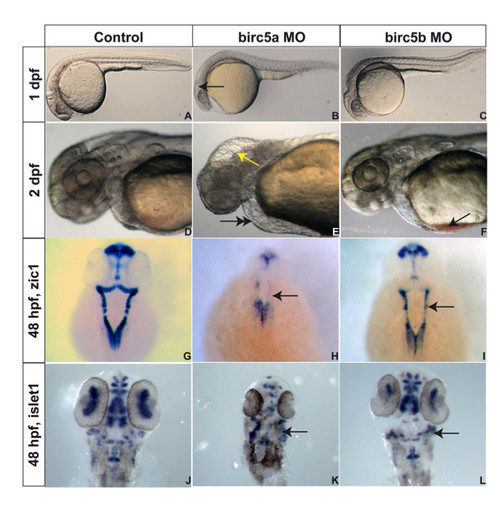
Birc5 in neurodevelopment. Brightfield microscopy of AB zebrafish embryos. A-F: Embryos oriented with head to left. Lateral views at 1 dpf (A, B, C) and 2 dpf (D, E, F), the latter being higher power views of head region. Depletion of Birc5a results in lack of brain development, revealed at 1 dpf (B, arrow) and 2 dpf (E, arrow), with fluid in 4th ventricle, compared to controls (A, D). At 2 dpf, Birc5a knockdown causes cardiogenic defects and pericardial edema (E, double arrow), not observed in controls (D). Majority of Birc5b depleted embryos do not exhibit phenotypic abnormalities under brightfield microscopy at 1 dpf (C) compared to controls (A). At 2 dpf, Birc5b knockdown embryos have smaller head and brain, and accumulate blood in the sinus venosus (F, arrow). Zic1 expression to detect neural tissue, is decreased by Birc5a depletion (H, arrow), compared to controls (G). A similar but less dramatic diminution of Zic1 expression is observed with morpholino knockdown of Birc5b (I, arrow). Depletion of Birc5a also induces disorganization of motor neurons, detected by expression of islet1 (K, arrow), compared to controls (J). Birc5b morphants exhibit less severe but still evident, suppression of islet1 expression (L, arrow). |
|
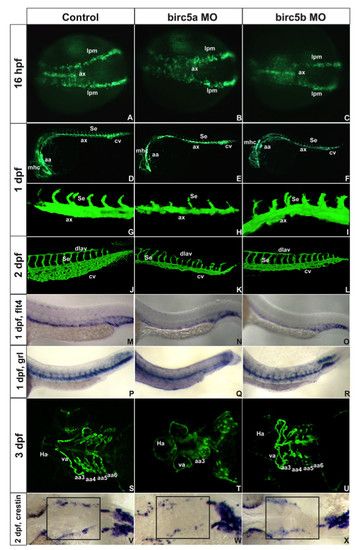
Birc5 in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Tg(Fli:eGFP) (A-L) and Tg(Flk1:GFP) (S-U) embryos. A-C: 16 hpf (14 somites), Birc5a morphants with angioblast migration defects from lateral plate mesoderm (B) which are minor in Birc5b morphants (C). D-F: 1 dpf, Birc5a (E, H) and Birc5b (F, I) morphants have thinner axial vessels and poor caudal vein plexus development. G-I: 1 dpf Birc5a depletion (H) delays intersomitic vessels; not with Birc5b depletion (I). J-L: 2dpf Birc5a morphants with abnormal dorsal longitudinal anastomic and intersomitic vessels. Both morphants have poorly developed caudal vein plexus. M-O: flt4 at 1 dpf is reduced in posterior cardinal vein in both morphants (N, O). P-R: gridlock (grl) at 1 dpf is reduced with Birc5a depletion (Q), but not with Birc5b (R). S-U: 3 dpf Birc5a morphants have hypoplastic aortic arches (T). Birc5b depletion at 3 dpf causes hypoplasia of aortic arches 5–6 (U). V-X: Birc5a depletion decreases neural crest cells that migrate to branchial arches, detected with crestin probe. Birc5b depletion (L) reduces neural crest cells. ax: axial vessels, mhc: midbrain-hindbrain channel, Se: intersomitic vessels, aa: aortic arch, cv: caudal vein plexus, pcv: posterior cardinal vein, da: dorsal aorta, dlav, dorsal longitudinal anastomic vessel, Ha: hypobranchial artery, va: ventral aorta, lpm: lateral plate mesoderm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
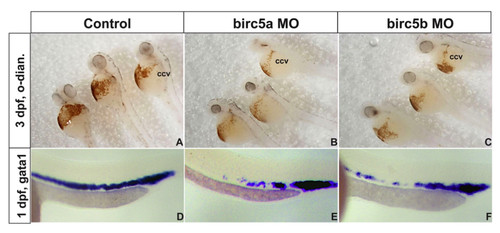
Birc5 in hematopoiesis. A-C: Depletion of Birc5a (B) or Birc5b (D) causes a reduction in erythropoiesis, shown by staining of erthrocytes with o-dianisidine (control, A). D-F: The preceding is consistent with decreased expression of gata1 by in situ hybridization in both gene knockdowns (E, F) as compared to control (D). ccv: common cardinal vein or duct of Cuvier, o-dian.: o-dianisidine. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
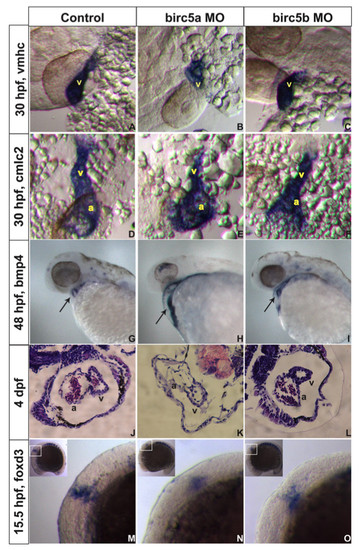
Birc5 in cardiogenesis. In situ hybridizations (A-I, M-O) and histologic sections (J-L) on AB embryos. A-C: At 30 hpf, expression of cardiac ventricle marker vmhc is reduced with Birc5a depletion (A, B), and to lesser extent in Birc5b morphants (C). D-F: cmlc2 staining shows Birc5a (E) or Birc5b (F) morphants with impaired development of atrium and ventricle, compared to controls (D). G-I: At 48 hpf, bmp4 normally localizes in heart to reveal a ring-like structure, representing endocardial cushions of the atrio-ventricular valve (G, arrow). With depletion of Birc5a, bmp4 staining remains diffuse and ring structure is absent (H, arrow). In Birc5b-morphants, bmp4 localizes normally (I, arrow), but the ring is smaller. J-L: H&E stained histologic sections of hearts of normal embryos (J), and those depleted of Birc5a (K) and Birc5b (L) at 4 dpf. Birc5a morphants have thin-walled heart chambers, and little evidence of a-v valve formation. Birc5b-depleted embryos have smaller ventricles. M-O: Premigratory cardiac neural crest cells contributing to heart development, were detected by staining embryos at 15.5 hpf (13 somites) with foxd3. Compared to controls (M), premigratory neural crest cells were barely detectable in embryos depleted of Birc5a (N), and reduced in Birc5b morphants (O). a:atrium, v:ventricle. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
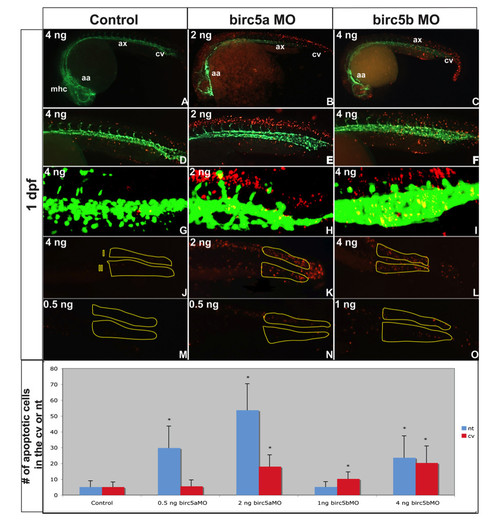
Apoptosis in Birc5-depleted embryos. Tg(Fli:eGFP) embryos reveal apoptosis (red) in relation to blood vessels (green) (A-O). A-I: Morphants at 1 dpf exhibit increased apoptosis, particularly in the brain (B) and along neural tube (E) in Birc5a morphants (morpholino dose 2 ng). Birc5b depletion with 4 ng of morpholino caused apoptosis in axial vessel region, caudal vein plexus, and neural structures (C, F). G-I: Confocal microscopy of 1 μm sagittal "slice" in region of caudal vein plexus and corresponding neural tube (excludes somites): Dose-dependent changes in apoptosis in caudal vein plexus region (J, region II) and corresponding neural tissue (J, region I) after Birc5 knockdowns was quantified at 1 dpf. High dose Birc5a morpholino (2 ng) or Birc5b morpholino (4 ng) causes significant increase in apoptosis in caudal vein plexus and neural tube (K, L). With lower Birc5a morpholino dose 0.5 ng), neural tube apoptosis remains significantly increased, but is almost absent in caudal vein plexus (N). Low dose Birc5b morpholino (1.0 ng) causes significant apoptosis in caudal vein plexus, but not in neural tube (O). Data presented in bottom panel. n = 30 x 3 independent experiments. * p < 0.05 relative to corresponding control. mhc: midbrain-hindbrain channel, aa: aortic arch, ax: axial vessels, cv: caudal vein plexus. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
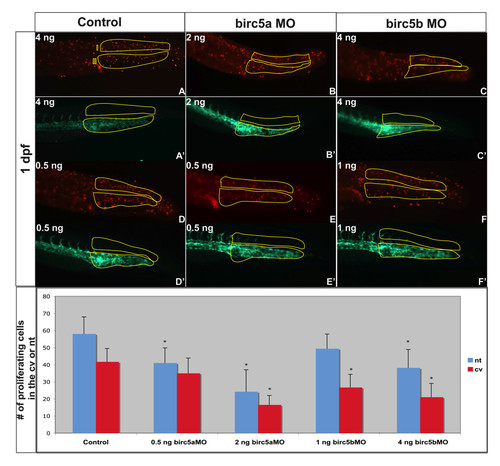
Cell proliferation in Brc5-depleted embryos. Tg(Fli:eGFP) embryos, were used to localize proliferating cells (red, A-F) in relation to blood vessels (green, A′-F′) after Birc5 morpholino knockdowns. Proliferating cells immuno-detected by whole-mount staining of 2 dpf embryos with anti-phospho-Histone H3 antibodies (red). The number of proliferating cells in the caudal vein plexus and neural tube (see Figure 6J for regions) was quantified in embryos after high dose (B, C) or low dose (E, F) morpholino knockdowns. With high dose Birc5a or Birc5b morpholino (2 ng or 4 ng, respectively), there is a significant decrease in cell proliferation in the caudal vein plexus and the neural tube (B, C) as compared to the control (A). When the Birc5a morpholino knockdown dose is lowered (0.5 ng) (E), there is still a significant decrease in cell proliferation in the neural tube, but not in the caudal vein plexus, compared to control (D). Conversely, low dose Birc5b morpholino knockdown (1.0 ng) results in a significant diminution of cell proliferation in the caudal vein plexus, but not in the neural tube (F). Quantitative data are presented in the bottom panel. n = 30 x 3 independent experiments. * p < 0.05 relative to corresponding control. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
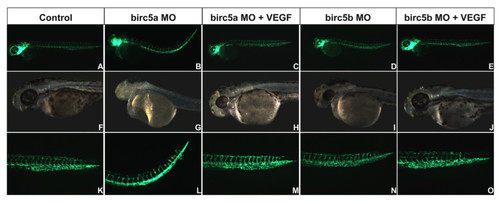
Rescue of Birc5 knockdown phenotypes with VEGF mRNA. Birc5a or Birc5b was depleted with 2 ng or 4 ng, respectively, of corresponding morpholino into Tg(Fli:eGFP) embryos, alone or with human VEGF mRNA. Embryos were evaluated at 2 dpf. Morpholino-induced angiogenic, cardiac and neurodevelopmental defects were reversed by VEGF. PHENOTYPE:
|