- Title
-
Mib-Jag1-Notch signalling regulates patterning and structural roles of the notochord by controlling cell-fate decisions
- Authors
- Yamamoto, M., Morita, R., Mizoguchi, T., Matsuo, H., Isoda, M., Ishitani, T., Chitnis, A.B., Matsumoto, K., Crump, J.G., Hozumi, K., Yonemura, S., Kawakami, K., and Itoh, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
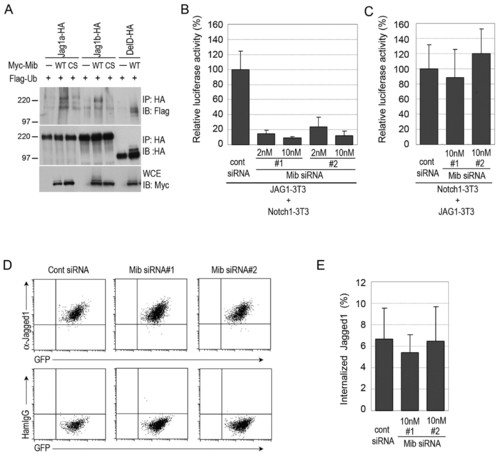
Mind bomb ubiquitylates Jagged 1 and is required for Jagged 1-induced Notch activation. (A) Jag1a and Jag1b were ubiquitylated by Mib. COS7 cells were transfected with HA-tagged Jag1a (Jag1a-HA), HA-tagged Jag1b (Jag1b-HA), HA-tagged DeltaD (DelD-HA), Myc-tagged wild-type Mib (WT), C1001S Mib (CS) and Flag-ubiquitin (Ub), as indicated. Cell extracts were then subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-HA antibody. The immunoprecipitated complexes were immunoblotted with anti-Flag (top) and anti-HA (top and middle) antibodies. Whole cell extracts (WCEs) were immunoblotted with an anti-Myc antibody (bottom). Molecular weight marker sizes in kDa are indicated on the left. (B) Mib was required for Jag1-induced Notch activation in Jag1-expressing cells. Jag1-3T3 cells were transfected with each Mib siRNA and then co-cultured with Notch1-3T3 cells. Notch activity was measured in Notch1-3T3 cells transfected with TP1, a Notch reporter plasmid. (C) Mib was not required for Jag1-induced Notch activation in Notch1-expressing cells. Notch1-3T3 cells were transfected with each Mib siRNA and the TP1 reporter plasmid, and then co-cultured with Jag1-3T3 cells. Error bars in B,C represent the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. (D) The expression of Jag1 on the cell surface was not altered by Mib knockdown. GFP-positive Jag1-3T3 cells were transfected with Mib siRNAs and, after 48 hours, the expression of Jag1 was examined by flow cytometry with an anti-Jag1 antibody. Hamster IgG was used as a control. (E) The Jag1 endocytosis rate was not dramatically altered by Mib knockdown. The surface proteins of Jag1-3T3 cells were labelled with Sulfo-NHS-SS-Biotin and incubated for 20 minutes at 37°C. The remaining cell-surface biotin was then stripped, and WCEs were prepared. Internalized biotinylated Jag1 and total Jag1 was measured by an ELISA. The values shown are mean ± s.d. (%). |
|
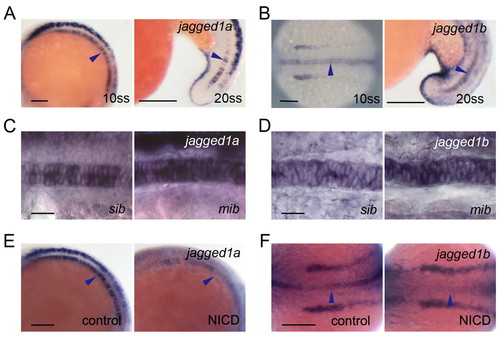
The two zebrafish jagged 1 homologues are expressed in spatially and temporally restricted patterns in the developing notochord, and their expression is controlled by Notch signalling. (A,B) Expression of jag1a (A) and jag1b (B) in the notochord cells at 10 and 20, ss. (C,D) jag1a (C) and jag1b (D) expression was increased in the mib mutants at 10 ss. sib, sibling control. (E,F) jag1a (E) and jag1b (F) expression was decreased at 10 ss in the notochord of embryos with increased Notch activity. Control siblings (control) or double transgenic Tg(UAS:myc-Notch1a-intra);Tg(hsp70:Gal4) embryos (NICD) were heat shocked at 3 ss. Arrowheads show expression in the notochord. (A-E) Lateral view with anterior to the left, except for 10 ss in B. 10 ss in B and F is a dorsal view with anterior to the left. Scale bars: 100 μm in A,B,E,F; 20 μm in C,D. |
|
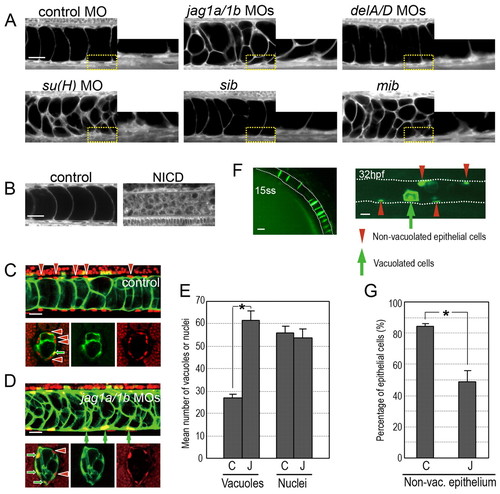
Jagged 1a and Jagged 1b regulate cell fates during notochord development. (A) Defects in Mib-Jag1-Notch but not DeltaA/D-Notch signalling led to increased vacuoles in the notochord. Enlarged views of the yellow-boxed areas are shown in each right panel. (B) Notch activation reduced the vacuolated cells in the notochord. Control siblings (control) or double transgenic Tg(UAS:myc-Notch1a-intra);Tg(hsp70:Gal4) embryos (NICD) were heat shocked at 3 ss. A and B are side views of the BODIPY TR methyl ester-stained notochord cells in embryos at around 34 hpf. (C,D) Vacuolated cells were increased at the expense of non-vacuolated cells in jag1a/1b knockdown embryos. Nuclei were visualized by nuclear-localized mCherry (red, upper panels in C,D) or by Ntl antibody (red, lower panels in C,D). Vacuolated cells were revealed by using a transgenic fish line (214A-GFP), in which the vacuolated cells are labelled with GFP (green). Red arrowheads indicate non-vacuolated cell nuclei. Green arrows indicate vacuolated cell nuclei. (E) Quantification of the mean number of vacuoles and nuclei. The vacuoles and nuclei were counted within the trunk region of the notochord (230 μm in width, as in the upper images of C,D). Control MO (C, n=20), jag1a/1b MOs (J, n=22). (F) Vacuolated cells and non-vacuolated epithelial cells are derived from notochord precursor cells. The GFP-positive cells at 15 ss were followed until 32 hpf in an embryo injected with Flh-GFP plasmid. (G) Quantification of the proportion of non-vacuolated cells. GFP-positive vacuolated and GFP-negative non-vacuolated cells were counted in embryos co-injected with Flh-GFP plasmid and the control MO (C, n=6) or jag1a/1b MOs (J, n=8). Asterisks in F and G indicate statistically significant differences relative to the control (P<0.005). Error bars indicate s.e.m. Scale bars: 20 μm in A-D,F. |
|
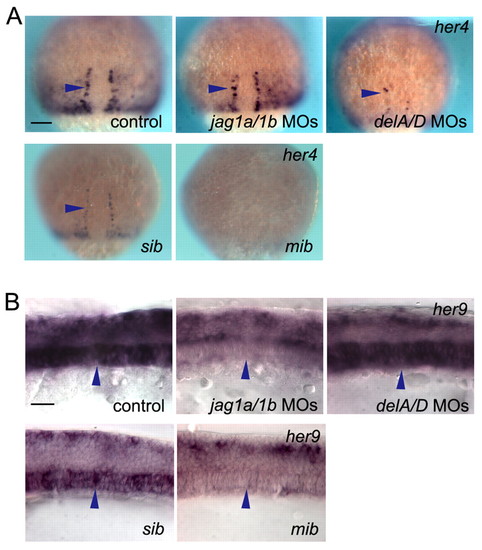
Jagged 1-Notch signalling regulates her9 but not her4 expression, independent of Delta-Notch signalling. (A) her4 expression was reduced in the hypochord precursor cells of deltaA/D (delA/D) knockdown embryos and mib mutants, but not in those of jag1a/1b (jag1a/1b) knockdown embryos. Arrowheads indicate the hypochord precursor cells. Dorsal views at 80% epibody are shown. (B) her9 expression was decreased in the notochord of jag1a/1b knockdown and mib mutant embryos, but not in that of deltaA/D knockdown embryos. Arrowheads indicate notochord cells. sib, sibling control. Side views at 10 ss are shown. Scale bars: 100 μm in A; 20 μm in B. |
|
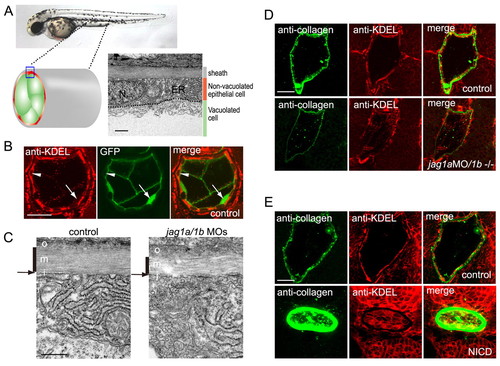
Jagged 1a/1b is required for notochord extracellular matrix sheath formation. (A) Non-vacuolated epithelial cells contained abundant rough ER compared with vacuolated cells. N, nuclei; ER, endoplasmic reticulum. Transmission electron micrographs (TEMs) of transverse sections of a wild-type embryo on day 2. (B) Non-vacuolated cells were rich in rough ER. ER was stained by an anti-KDEL antibody (red), and vacuolated cells were revealed by the 214A-GFP transgenic line (green). Arrowheads indicate anti-KDEL-positive non-vacuolated cells. Arrows indicate GFP-positive vacuolated cells. (C) The medial layer of the peri-notochordal basement membrane was thinner in the jag1a/1b knockdown embryos than in wild-type embryos. TEM of transverse sections. o, outer; m, medial; i, inner. Black vertical lines indicate the medial layer of the sheath. Arrows indicate the thin inner layer. (D) jag1a/1b knockdown resulted in reduced type II collagen deposition and fewer cells with abundant rough ER in the notochord. (E) Notch activation increased type II collagen deposition and ER-positive cells in the notochord. Control siblings (control) or double transgenic Tg(UAS:myc-Notch1a-intra);Tg(hsp70:Gal4) embryos (NICD) were heat shocked at 3 ss. A-E are transverse sections of day 2 embryos. Scale bars: 0.5 μm in A,C; 20 μm in B,D,E. |
|
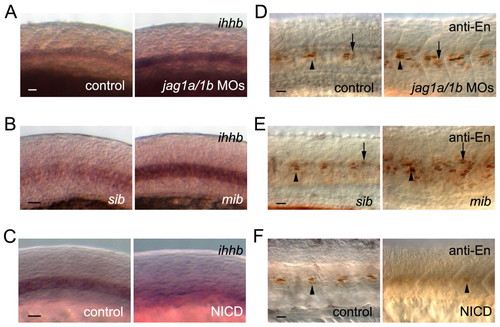
Mind bomb-Jagged-Notch signalling regulates muscle cell identities by altering ihhb expression. (A-C) ihhb expression was increased in jag1a/1b (jag1a/1b)-knockdown embryos and mib mutants, whereas Notch activation decreased ihhb expression at 18 ss. (D-F) Engrailed-positive (anti-En) MPs and MEFs were increased in jag1a/1b knockdown and mib mutant embryos, whereas Notch activation decreased the Engrailed-positive cells at 24 hpf. (B,E) sib, sibling control. (C,F) Control siblings (control) or double transgenic Tg(UAS:myc-Notch1a-intra);Tg(hsp70:Gal4) embryos (NICD) were heat-shocked at 3 ss. MPs and MFFs are indicated by arrowheads and arrows, respectively. Scale bars: 20 μm in A-F. |
|
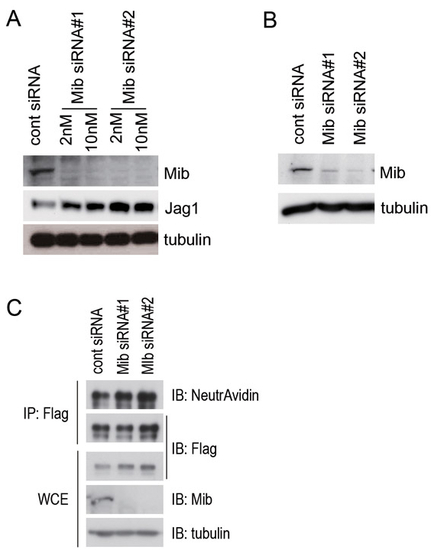
The expression of Mib is efficiently knocked down by two independent siRNAs, but Jagged 1 expression is not affected by the Mib knockdown. (A) Jag1-3T3 cells were transfected with two Mib siRNAs (#1 and #2) at 2 nM or 10 nM, and whole-cell extracts were immunoblotted with anti-Mib (Mib, upper panel), anti-Flag (Jag1, middle panel), and anti-α tubulin (tubulin, bottom panel) antibodies. (B) Notch-3T3 cells were transfected with two Mib siRNAs (#1 and #2) at 10 nM, and whole-cell extracts were immunoblotted with anti-Mib (Mib, upper panel) and anti-α tubulin (tubulin, lower panel) antibodies. (C) The surface proteins of Jag1-3T3 cells were labelled with Sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin for 15 minutes, and whole-cell lysates were prepared. Flag-tagged Jag1 was immunoprecipitated with a Flag antibody from the whole-cell extract (WCE). Immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with NeutrAvidin and the anti-Flag antibody. WCE was immunoblotted with anti-Flag, anti-Mib, and anti-α tubulin antibodies. α tubulin was used as a loading control. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblot. |
|
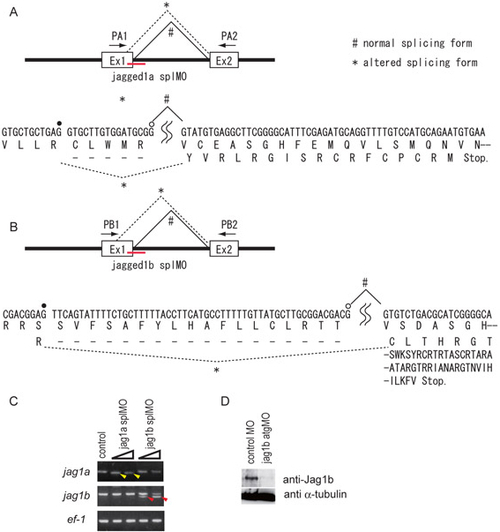
Morpholino-mediated knockdown of the Jagged genes in zebrafish. (A-C) The jag1a splMO (A) and jag1b splMO (B) were designed to target the splice donor sites of the first exon-intron boundary. These splMOs caused deletions of the mRNAs by altering the splicing donor sites (*; confirmed by DNA sequence analysis of the PCR products indicated by yellow and red arrowheads in C). The altered splicing forms of mRNA potentially produce premature truncated proteins (A,B). Open and filled circles indicate the normal and cryptic splice donor sites, respectively. (C) RT-PCR analysis of Jagged gene expression in jag1a MO (jag1a splMO)- and jag1b MO (jag1b splMO)-injected embryos. Yellow and red arrowheads indicate the shorter forms of jag1a and jag1b cDNA, respectively. ef-1 was used as a reference gene. (D) The jag1b atgMO reduced the protein level of Jag1b (Jag1b). α-tubulin was used as a loading control. |
|
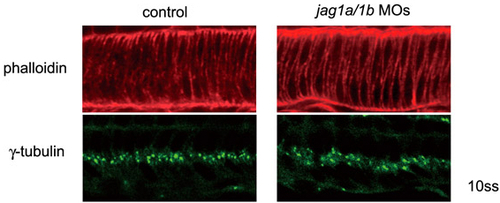
Normal cell morphology of the notochord is established in the jagged 1 knockdown embryos at 10 ss. Embryos were stained by Rhodamine-phalloidin or anti γ-tubulin. Normal intercalated cell morphology of the notochord was observed with phalloidin staining. Notochord cell polarities were well established, as assessed by the central localization (basal) of γ-tubulin in the notochord in the jag1a/1b-knockdown embryos (jag1a/1b MOs). Side views of the notochord cells in 10 ss embryos are shown. |
|
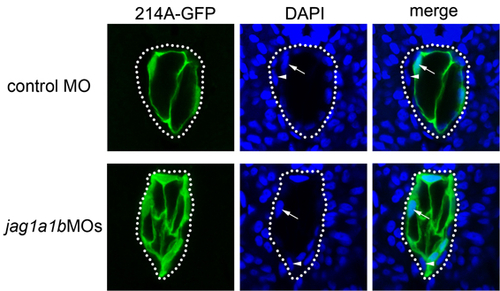
Vacuolated cells selectively express GFP in the 214A-GFP transgenic fish line. Control MO or jag1a/1b MOs were injected into 214A-GFP at the one-cell stage. Images were taken from transverse sections of embryos at 32 hpf. Arrows indicate the nuclei of GFP-positive cells (vacuolated cells), and arrowheads indicate the nuclei of GFP-negative cells (non-vacuolated cells). Note that the number of vacuolated cells increased in the jag1a/1b knockdown embryos (jag1a1bMOs). |
|
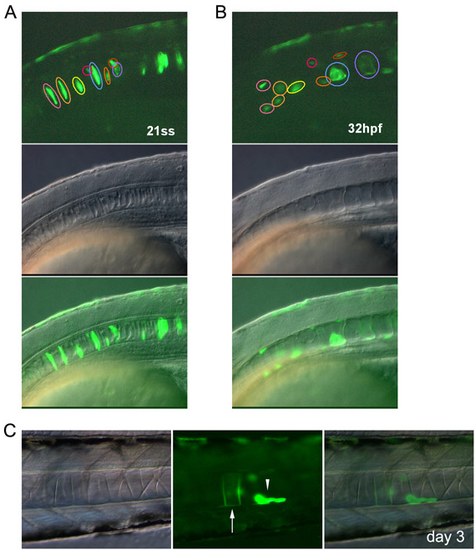
Intercalated notochord cells develop into vacuolated and non-vacuolated epithelial cells. (A-C) Notochord cells were tracked by GFP expression under the promoter of the floating head gene (Flh-GFP). (A,B) Time-lapse images of the notochord cells of an embryo at 21 ss and 32 hpf. Cells indicated by pink and yellow circles developed into non-vacuolated cells. The cell indicated by a blue circle developed into a vacuolated cell. (C) A non-vacuolated epithelial cell observed on day 3. Vacuolated and non-vacuolated cells are indicated by the arrow and arrowhead, respectively. Images are lateral views with anterior to the left. |
|
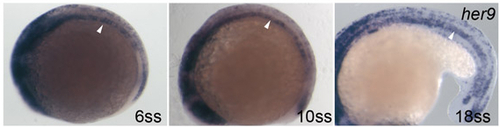
her9 is expressed in the notochord at the segmentation stage. Side views of embryos at 6, 10 and 18 ss. Arrowheads indicate the her9 expression in the notochord. |
|
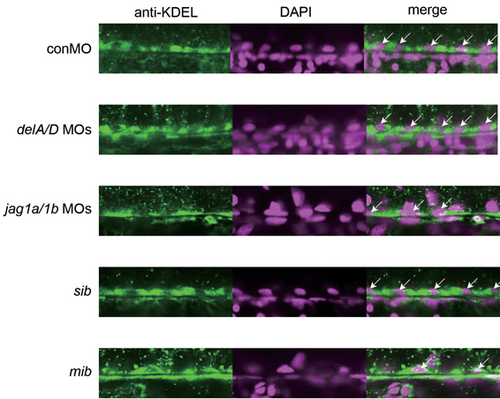
Mind bomb-Jagged 1 signalling is required for the development of non-vacuolated cells with abundant rough ER. The number of non-vacuolated cells stained by an anti-KDEL antibody was reduced in the jag1a/1b-knockdown and mib mutant embryos, but not in deltaA/D-knockdown embryos. The ER was stained with an anti-KDEL antibody (green), and nuclei were revealed by DAPI staining (magenta). Arrows indicate anti-KDEL-positive non-vacuolated cells. Side views of the ventral regions of the notochord in embryos on day 2 are shown. |
|
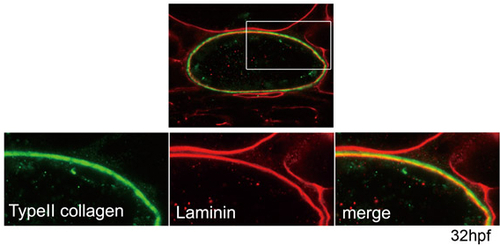
The medial layer appears to consist of type II collagen. Type II collagen was detected external to the laminin-rich inner layer. The boxed area is enlarged in the lower panels. Green, type II collagen; red, laminin; yellow, merged expression of type II collagen and laminin. Transverse sections through the trunk region of an embryo at 32 hpf are shown. |
|
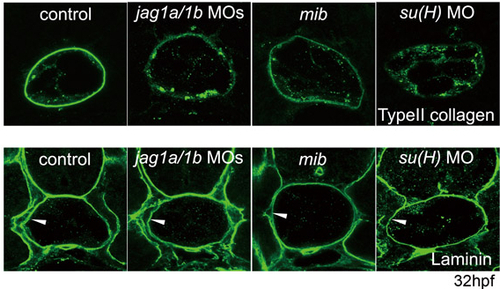
Collagen but not laminin protein in the PBM was reduced by the knockdown of Mind bomb-Jagged 1-Notch signalling. Arrowheads indicate laminin expression in the PBM. Transverse sections of the trunk region of embryos at 32 hpf are shown. |
|
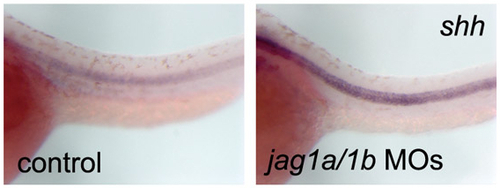
Expression of shh in Jagged 1-Notch signalling knockdown embryos. The expression of shh did not decrease as the notochord differentiated, in Jag1-Notch signalling knockdown embryos (jag1a/1b MOs). Side views of the trunk region of 32 hpf embryos are shown. |