- Title
-
Zebrafish disease model of human RNASET2 deficient cystic leukoencephalopathy displays abnormalities in early microglia
- Authors
- Weber, T., Schlotawa, L., Dosch, R., Hamilton, N., Kaiser, J., Schiller, S., Wenske, B., Gärtner, J., Henneke, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Biol. Open
|
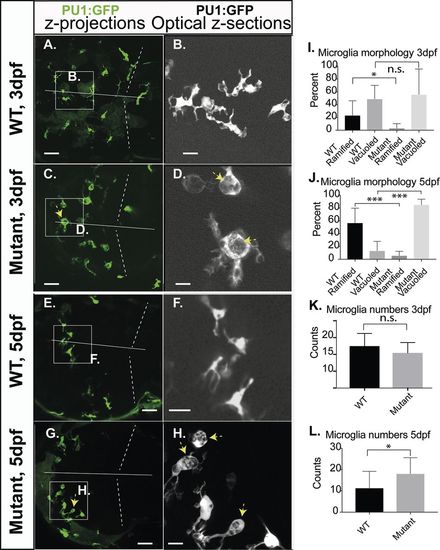
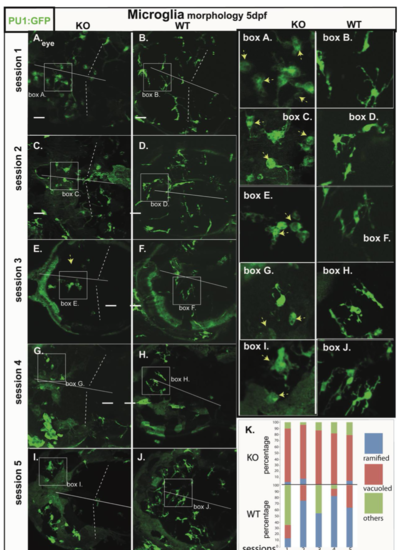
Microglia morphology of RNASET2-deficient embryos and larvae. Zebrafish of the transgenic reporter strain Tg:(PU1:GFP) were analyzed by in vivo CLSM. The morphology of microglia together with their total numbers was determined manually by going stepwise through the confocal z-stacks of individual larvae. These key figures were categorized, quantified and shown as averages in the respective graphs. Thus, the images shown here were selected to highlight the morphology of microglia and should not be used to deduce cell numbers or relative proportions. (A,C,E,G) Projections of confocal z-stacks through the brain showing microglia (green, arrows indicate abnormally vacuoled microglia). (B,D,F,H) Single optical sections at increased size as in the respective left panel, showing ramified and vacuoled microglia (arrows indicate abnormally vacuoled microglia). (I,J) Quantification of the morphological categories of microglia on 3 dpf (ramified mean: WT 23.2%; s.d.=22.8; n=14; mutants 3.2%; s.d.=7.0; n=9; P<0.5; vacuoled mean: WT 48.8%; s.d. 22.8; n=14; mutants 55.7%; s.d.=21.3; n=9; P>0.5) and 5 dpf (ramified mean: WT 56.9%; s.d.=23.0; n=12; mutants 5.8%; s.d.=6.6; n=14. Vacuoled mean: WT 13.3%; s.d.=14.8; n=12; mutants 85.2%; s.d.=8.7; n=14), respectively. (K,L) Averaged counts of microglia within the optical tectum on 3 dpf (mutants 10.4; s.d.=3.1, n=8; WT 12.5; s.d.=3.8; n=12; P>0.05) and 5 dpf (mutants 18.1; s.d.=7.9, n=14; WT 11.3; s.d.=8.2; n=12; P<0.05). Dotted lines, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; straight line, midline, separating left and right brain hemispheres. Scale bars: A,C,E,G: 40 µm; B,D,F,H 10 µm. n-numbers were generated from >7 individual litters and analyzed in seven independent CLSM-sessions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
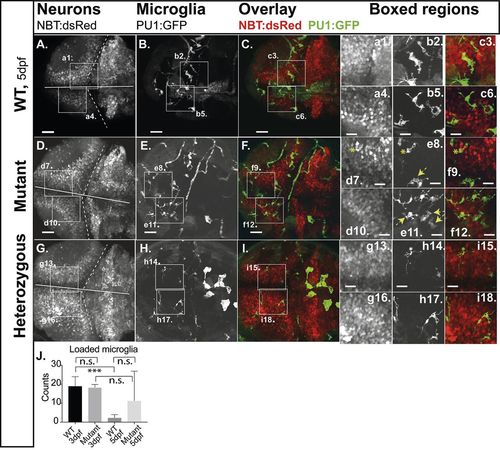
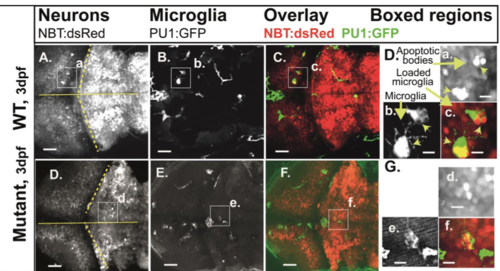
Engulfment of apoptotic neurons. Compound transgenic reporter strain zebrafish embryos Tg:(PU1:GFP)/Tg:(NBT:dsRed) were analyzed by in vivo CLSM at 5 dpf. Representative projections of confocal z-stacks through the brain: (A,D,G) NBT:dsRed (neurons); (B,E,H) PU1:GFP (microglia). (C,F,I) Overlays of the respective panels (A,B and C,D). Boxed regions, increased images: (a,d,g) neurons; (b,e,h) microglia; (c,f,i) microglia with engulfed apoptotic bodies of neurons (loaded microglia, asterisks; vacuoled microglia, arrows). (J) Quantification of loaded microglia (3 dpf, see Fig. S3: WT 19.0; n=5; mutants 18.3; n=3; P>0.5; 5 dpf: WT 2.3: s.d.=1.8; n=6; mutants 11.3; s.d.=15.6; n=7; P>0.5). Scale bars: 40 µm. E,F show expression of GFP in circulating cells as observed in about 20% of PU1:GFP-positive larvae. n-numbers were generated from one to three individual litters and analyzed in one to three independent CLSM-sessions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
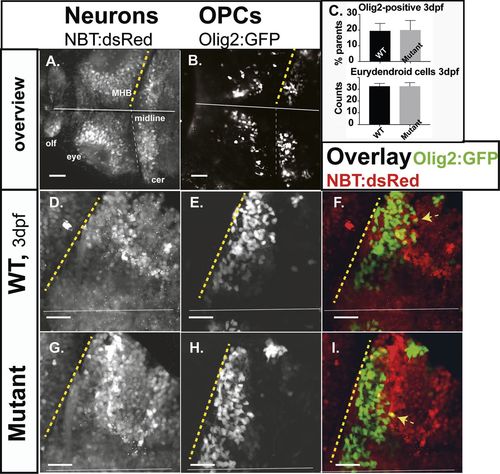
Neurons and oligodendrocytes in the developing hindbrain. Zebrafish larvae of compound transgenics Tg:(NBT:dsRed)/Tg:(Olig2:GFP) analyzed by in vivo CLSM. Projections of confocal z-stacks highlight neurons and OPCs at 3 dpf. (A,B) Overview; brain of a WT larvae, showing neurons (NBT:dsRed) and OPCs (Olig2:GFP). (C) Relative proportions of OPCs (average OPCs: WT 19.53%; n=7; mutants 20.8%; n=4; P>0.5) and counts of developing eurydendroid cells (average ECs: mutants 32.6; n=3; WT 32.6; n=3; P>0.5) in the right cerebellar hemispheres. Expression of both fluorophores in F and I is indicated by yellow arrows. Projections of representative confocal z-stacks through the cerebellum on 3 dpf (D,E,G,H). Scale bars: 40 µm. n-numbers were generated from one litter and analyzed in one CLSM-session. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Transgenic zebrafish lines and analyzed zebrafish brain regions |
|
Microglia morphology of RNASET2-deficient embryos and larvae in independent clutches. |
|
Images of engulfed apoptotic neurons at 3 dpf |