- Title
-
Analysis of transcriptional codes for zebrafish dopaminergic neurons reveals essential functions of Arx and Isl1 in prethalamic dopaminergic neuron development
- Authors
- Filippi, A., Jainok, C., and Driever, W.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
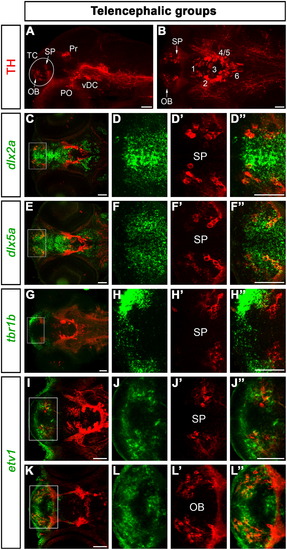
Expression of transcription factors characterizing DA neurons in the telencephalon. For orientation, a lateral (A, 43 μm projection) and a dorsal (B, 30 μm projection) overview of a 96 hpf zebrafish brain immunostained for TH are shown. The telencephalic DA groups are framed by a circle in A and indicated by arrows in B. In this and in the following figures, TH-immunoreactive cells are always displayed in red and the analyzed transcription factors in green. The dorsalmost telencephalic DA cells express the subpallial markers dlx2a (C–D3) and dlx5a (E–F3), but not tbr1b (G–H3), which labels the dorsal telencephalon. etv1 is expressed only in a subset of subpallial DA neurons (I–J3), but it prominently labels DA cells in the olfactory bulb (K–L3). The images shown in C, E, G, I, and K are overviews of the head of 96 hpf larvae (15–30 μm projections), whereas D–D3, F–F3, H–H3, J–J3, and L–L3 are high magnifications (25 μm projections) of the areas framed in C, E, G, I, and K, respectively. Abbreviations: OB, olfactory bulb; PO, preoptic group; Pr, pretectal group; SP, subpallium; TC, telencephalic cluster; vDC, ventral diencephalic cluster; 1–6; diencephalic DA neuronal groups numbered according to Rink and Wullimann (2002). Anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
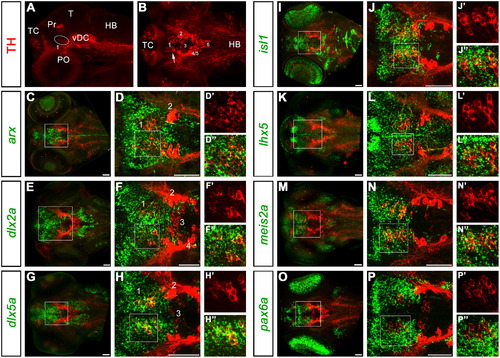
Expression of transcription factors characterizing DA neurons of the prethalamus (group 1). A and B: overviews are like in Fig. 1A,B. Here, group 1 is framed by a circle in A. For each analyzed transcription factor, an overview of the whole head of 96 hpf embryos is presented in C, E, G, I, K, M and O (20–35 μm projections encompassing the prethalamus). A high magnification of prethalamic group 1 within the framed areas is shown in D, F, H, J, L, N and P, respectively (5–20 μm projections). An additional enlarged view of the framed areas in D, F, H, J, L, N and P is shown for each transcription factor at the right side of each row. Abbreviations: HB, hindbrain; PO, preoptic group; Pr, pretectal group; T, tectum; TC, telencephalic cluster; vDC, ventral diencephalic cluster; 1-6; diencephalic DA neuronal groups. Anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
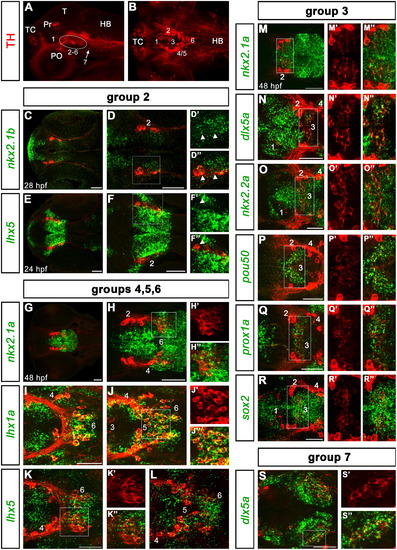
Expression of transcription factors characterizing DA neurons of the ventral diencephalon (groups 2–7). A and B: overviews are like in Fig. 1A,B. Here, the diencephalic groups from 2 to 6 are framed by a circle in A, group 7 in the caudal hypothalamus is indicated by an arrow. In B, group 7 is not comprised in the optical planes used to generate the z-projection, and the other groups are numbered according to Rink and Wullimann (2002). At the left side of each row the analyzed transcription factors are indicated (see results). Abbreviations: HB, hindbrain; PO, preoptic group; Pr, pretectal group; T, tectum; TC, telencephalic cluster; 1-7; diencephalic DA neuronal groups 1 to 7. All images from C to S are dorsal views, anterior is to the left. All larvae are shown at 96 hpf, unless specified. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
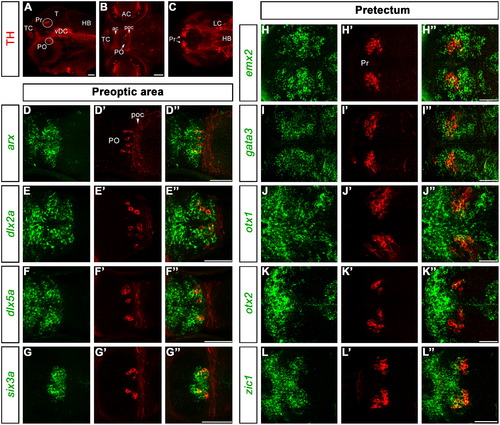
Expression of transcription factors characterizing DA neurons of the preoptic area and the pretectum. A: lateral overview is like in Fig. 1A. Here, the pretectal (Pr) and preoptic (PO) groups are framed by circles. B and C are dorsal z-projections encompassing the optical planes through the PO area (B, 34 μm projection) and the pretectum (C, 25 μm projection). D–G3 and H–L3 are higher magnified dorsal views of the PO (7–11 μm projections) and Pr (7–9 μm projections), respectively, at 96 hpf. The analyzed genes are indicated at the left side of each row. Abbreviations: ac, anterior commissure; AC, amacrine cells of the retina; HB, hindbrain; LC, locus coeruleus; PO, preoptic group; poc, postoptic commissure; Pr, pretectal group; T, tectum; TC, telencephalic cluster; vDC, ventral diencephalic cluster. Anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
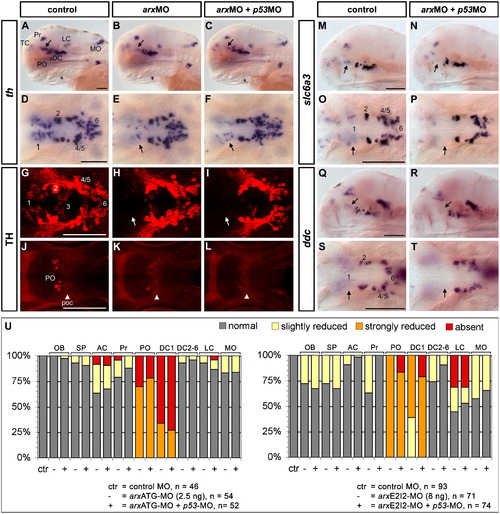
arx is required for the formation of DA neurons in the prethalamus and in the preoptic area. Morpholino-injected embryos were analyzed by WISH to detect th (A-F, 96 hpf), slc6a3/dat (M-P, 72 hpf) or ddc (Q-T, 72 hpf) expression, as well as by anti-TH immunofluorescence (G-L, 72 hpf). Arx knockdown by Morpholino injection results in a reduction in the number of prethalamic group 1 DA neurons (arrows in B, E, H) and of the preoptic group (K, arrowhead points to the postoptic commissure). This phenotype is not caused by Morpholino off-target p53-mediated cell death, as we obtain the same result when co-injecting p53-MO as a control (C, F, I, L). Moreover, the prethalamic expression domains of slc6a3/dat (M–P) and ddc (Q–T) are also reduced in morphant embryos when compared to controls (arrows point to the prethalamus). U: Evaluation of the effect of Arx knockdown on th expression for each DA cluster. Both ATG (left) and splice (right) targeting morpholinos affected DC1 and PO groups development, also when co-injected with the p53-MO (+). The groups of the arx morphant larvae were compared with those of control MO injected larvae, which all developed normally and are summarized here in the left-most lanes (ctr). A–C,M,N,Q,R are lateral views; D–L, O, P, S, T are dorsal views; anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 100 μm. Abbreviations: AC, amacrine cells; DC1-6, diencephalic groups 1–6; LC, locus coeruleus; MO, medulla oblongata; OB, olfactory bulb; PO, preoptic area; poc, postoptic commissure; Pr, pretectum; SP, subpallium; TC, telencephalic cluster; vDC, ventral diencephalic cluster. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
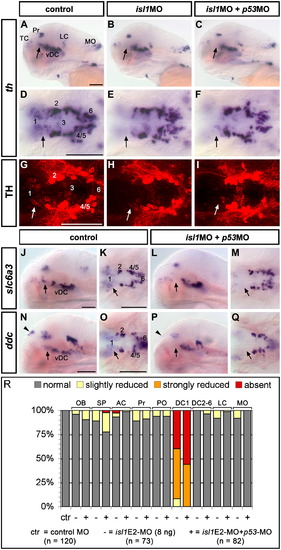
Knockdown of Isl1 leads to a reduction of prethalamic DA neurons. The analyses of th expression (A–F) and of TH protein distribution (G–I) show a significant reduction in the number of prethalamic group 1 DA neurons (arrows) in the morphant embryos (B, C, E, F, H, I) compared to the controls (A, D, G). Similarly, slc6a3/dat (J–M) and ddc (N–Q) display a reduction of their prethalamic expression domains in Isl1 morphants (arrows, compare J with L and K with M for slc6a3/dat; N with P and O with Q for ddc), arguing for a role of isl1 in the specification of group 1 DA neurons. In addition, ddc expression in the epiphysis is lost in the morphants (arrowheads, compare N with P). The embryos were analyzed at 96 hpf. R: Evaluation of the effect of Isl1 knockdown on th expression for each DA cluster. The groups of the isl1 morphant larvae were compared with those of control MO injected larvae, which all developed normally and are summarized here in the left-most lanes (ctr). A–C, J, L, N, P are lateral views; D–I, K, M, O, Q are dorsal views, anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 100 μm. Abbreviations are like in Fig. 5. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
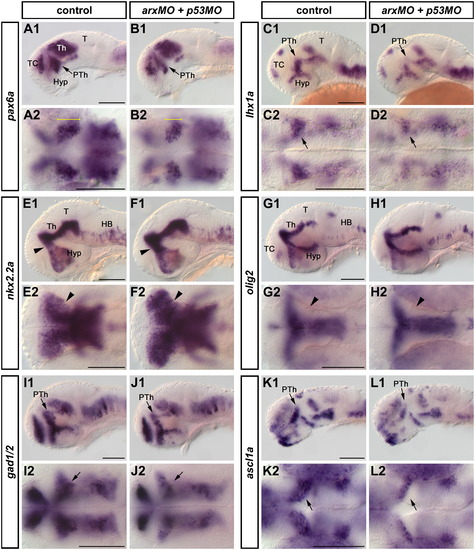
Patterning defects in the prethalamus of arx morphants. Embryos were analyzed by WISH at 30 (A1–D2, K1–L2) or 48 (E1–J2) hpf. The prethalamic expression domains of pax6a (A1–B2, arrows) and lhx1a (C1–D2, arrows) were significantly reduced in arx morphant embryos (B1, B2, D1, D2) compared to controls (A1, A2, C1, C2), whereas an increase in nkx2.2a (E1–F2) expression could be observed at 48 hpf in the prethalamus of arx morphants (F1, F2, arrowhead) compared to controls (E1, E2). olig2 (G1-H2) expression was not perturbed by Arx knockdown at 48 hpf. A specific reduction of gad1/2 (I1–J2) and ascl1a (K1–L2) expression was observed in the prethalamus of the morphants at 48 and 30 hpf, respectively. Abbreviations: HB, hindbrain; Hyp, hypothalamus; PTh, prethalamus; T, tectum, Th, Thalamus; TC, telencephalon. A1-L1 are lateral views; A2-L2 are dorsal views. Anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
|
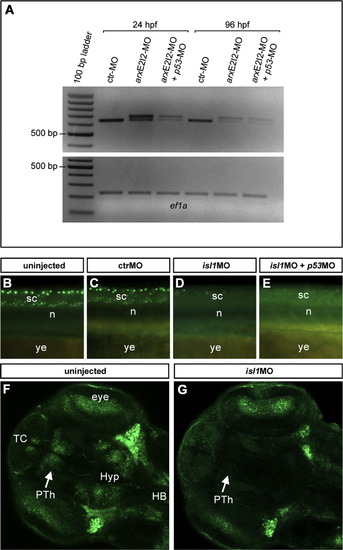
Assessment of arxE2I2-MO (A) and isl1E2-MO (B-G) efficiency. (A) PCR on cDNA synthesized from 24 and 96 hpf embryos injected with 8 ng of arxE2I2-MO. This morpholino blocks the splice donor site at the exon2-intron2 boundary, giving rise to a longer mature mRNA. We amplified elongation factor 1-alpha (ef1a) as a positive control. |
|
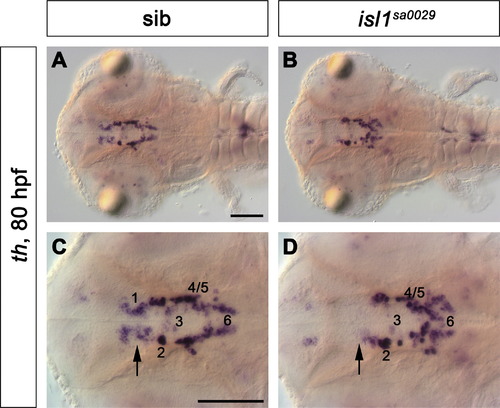
th expression was analysed at 80 hpf by WISH in the isl1sa0029 mutant line, recently isolated by target-selected mutagenesis. Mutant larvae displayed a specific reduction of group 1 DA neurons (B,D, arrow) when compared to WT siblings (A,C, arrow). Dorsal views of the whole head (A,B) and higher magnifications of the diencephalic groups (C,D) are shown. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
|
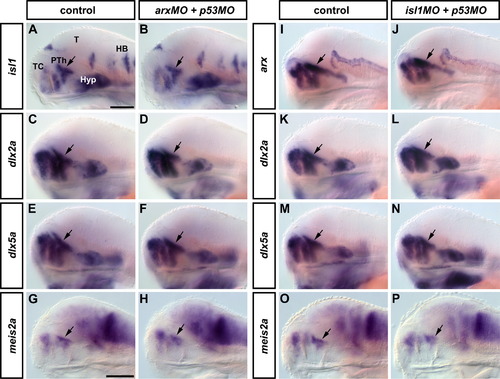
Patterning is normal in arx and isl1 morphant embryos. Whole mount in situ hybridizations were performed on arx (A-H) and isl1 (I-P) morphants at 72 and 96 hpf, respectively. Lateral views of the head are shown, anterior is to the left. The arrows point to the prethalamus. The analyzed genes are indicated at the left side of each row. Abbreviations: HB, hindbrain; Hyp, hypothalamus; PTh, prethalamus; T, tectum; TC, telencephalon. Scale bars in A (applies to A-F and I-N) and in G (applies to G,H,O,P) = 100 μm. |
|
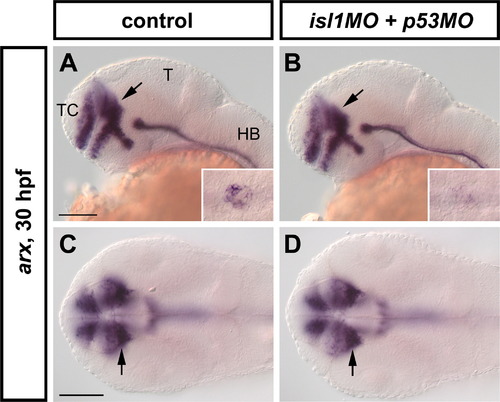
Analysis of arx expression in isl1-MO injected embryos at 30 hpf. At this stage, no differences in arx expression could be observed in the prethalamus of Isl1 morphant embryos (B,D, arrows) when compared to the controls (A,C, arrows). Conversely, arx transcription was strongly downregulated in the pancreatic anlage of the morphants (inset in B) compared to the controls (inset in A). Abbreviations: HB, hindbrain; T, tectum; TC, telencephalon. A,B are lateral views; C,D are dorsal views. Anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
|
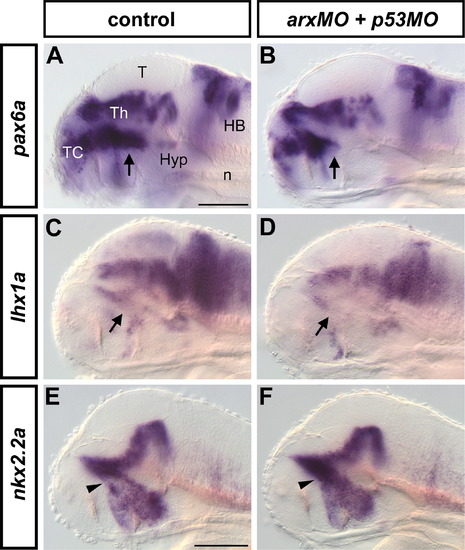
Dorso/ventral patterning defects in the prethalamus of arx morphants. WISH was performed to detect pax6a (A,B), lhx1a (C,D) and nkx2.2a (E,F) expression in arx morphants at 72 hpf. Arx knock-down results in the specific reduction of pax6a and lhx1a prethalamic domains (arrows in B and D, respectively), and in the increase of prethalamic nkx2.2a expression (arrowhead in E). Lateral views of the heads are shown, anterior is to the left. Abbreviations: HB, hindbrain; Hyp, hypothalamus; n, notochord; T, tectum; TC, telencephalon; Th, thalamus. Scale bars in A (applies to A-D) and in E (applies to E,F) = 100 μm. |
|
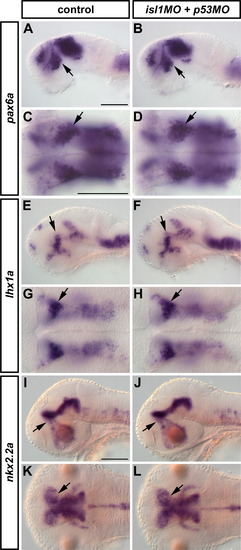
WISH was performed to detect pax6a (A-D, 30 hpf), lhx1a (E-H, 30 hpf) and nkx2.2a (I-L, 48 hpf) in isl1 morphant embryos. No differences in their expression patterns were observed between control and morphant embryos. A,B,E,F,I,J are lateral views; C,D,G,H,K,L are dorsal views. Anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
|
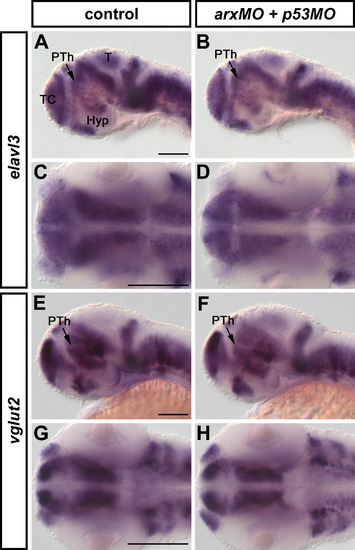
Expression of elavl3 (A-D, 48 hpf) and vglut2 (E-H, 48 hpf) in arx morphant embryos was analyzed by WISH. No significant differences in their expression patterns were observed between control (A,C,E,G) and arx morphant embryos (B,D,F,H). A,B,E,F are lateral views; C,D,G,H are dorsal views. Anterior is to the left. Abbreviations: Hyp, hypothalamus; T, tectum; TC, telencephalon; PTh, prethalamus. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 369(1), Filippi, A., Jainok, C., and Driever, W., Analysis of transcriptional codes for zebrafish dopaminergic neurons reveals essential functions of Arx and Isl1 in prethalamic dopaminergic neuron development, 133-149, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.