Fig. S2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180906-18
- Publication
- Mochizuki et al., 2017 - Cell division and cadherin-mediated adhesion regulate lens epithelial cell movement in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
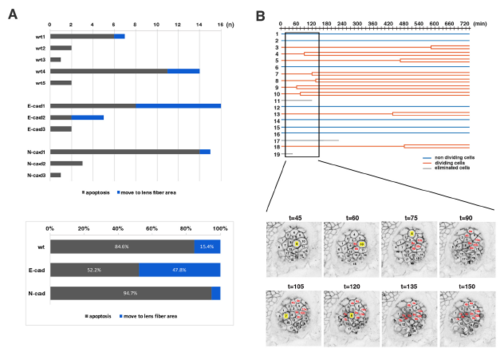
Analyses of the eliminated cell population and clustered cell divisions of wild-type lenses (A) (Upper panel) Number of two types of eliminated cell population, which underwent apoptosis (grey) and moved into the lens fiber area (blue), respectively, in individual wild-type, E-cadherin mutant, and N-cadherin morphant lenses. The number of eliminated cells were varied depending on individual lenses. Eliminated cells that moved into the lens fiber area were generally observed in lenses with a high number of eliminated cells. (Lower panel) Histogram of the percentages of two types of eliminated cell population, which underwent apoptosis (grey) and moved into the lens fiber area (blue), respectively, relative to the total number of eliminated cells observed in five wild-type, three E-cadherin mutant, and three N-cadherin morphant lenses. The fraction of eliminated cells that moved into the lens fiber area was higher in E-cadherin mutant lenses (47.8%) than in wild-type lenses (15.4%), suggesting that E-cadherin suppresses cell movement from lens epithelium into the lens fiber area. In N-cadherin morphant lenses, this fraction was only 5.3%, much less than in wild-type lenses (15.4%). (B) (Upper panel) Lineages of lens epithelial cells from zebrafish transgenic line, Tg(h2afva:GFP; EF1α:mCherry-CAAX) from 33 to 45 hpf, also shown in Movie2. Red, blue, and grey lines indicate dividing, non-dividing, and eliminated cell populations, respectively. (Lower panel) Confocal images for 135 min shown as squares in the upper panel. Only mCherry-CAAX fluorescence is shown. Numbers on individual cells correspond to cell numbers in the upper panel. Yellow squares and red numbers indicate mitotic cells and their daughter cells, respectively. |