Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250410-26
- Publication
- Rajeswari et al., 2025 - Brain monoamine changes modulate the corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1-mediated behavioural response to acute thermal stress in zebrafish larvae
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
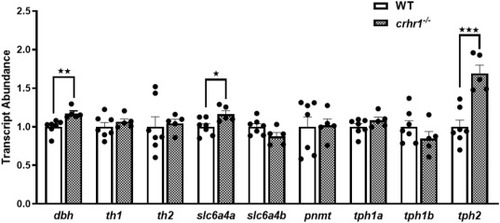
Relative transcript abundance of monoamine system genes: Graphs represent changes in transcript abundance of genes involved in monoamine biosynthesis and transport at 6 dpf in the wildtype (WT) and crhr1−/− larvae. Bars represent means + SEM (n = 5–7), with the individual data points shown. An asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference between genotypes (Student's t-test; ∗: P < 0.05, ∗∗: P < 0.01, ∗∗∗: P < 0.001); dbh: dopamine beta-hydroxylase; th1 and th2: tyrosine hydroxylase 1 and 2; slc6a4a and slc6a4b: serotonin transporter a and b; tph1a, tph1b, and tph2: tryptophan hydroxylase 1a, 1b and 2. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Day 6 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 6 |
Reprinted from Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, , Rajeswari, J.J., Gilbert, G.N.Y., Khalid, E., Vijayan, M.M., Brain monoamine changes modulate the corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1-mediated behavioural response to acute thermal stress in zebrafish larvae, 112494112494, Copyright (2025) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.