Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250410-27
- Publication
- Rajeswari et al., 2025 - Brain monoamine changes modulate the corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1-mediated behavioural response to acute thermal stress in zebrafish larvae
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
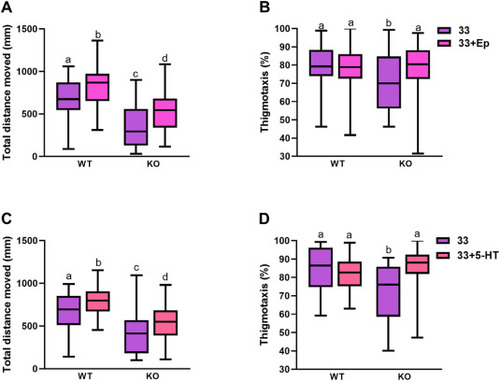
Epinephrine and 5-HT rescues the thermal stressor-mediated behavioral response in the crhr1−/− larvae: The box plots represent the total distance moved in light (A and C) and percent thigmotaxis (B and D) exhibited by the wildtype (WT) and crhr1−/− larvae (KO) at 33 °C without (33) and with either epinephrine (33+Ep) or serotonin (33+5-HT) at 60 min. Both epinephrine (Ep, Fig. A, significant interaction and no main effect, P = 0.00008) and serotonin (5-HT, Fig. C, significant interaction and no main effect, P = 0.00002) rescued the hypoactivity and the lower % thigmotaxis (Fig. B, significant interaction, P = 0.007 for Ep and Fig. D for 5-HT, significant interaction, P = 0.04) seen in fish lacking Crhr1 at 60 min (See Fig. 2, Fig. 3 for more details). Boxes represent 1 SD above and below the mean of the data (n = 40–120, 2–5 trials with 24 larvae each), the line inside the box shows the median of the data, and the whiskers indicate the minimum and maximum of all the data; boxes with different letters are significantly different (nonparametric Two-way ANOVA). |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Conditions: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 6 |
Reprinted from Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, , Rajeswari, J.J., Gilbert, G.N.Y., Khalid, E., Vijayan, M.M., Brain monoamine changes modulate the corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1-mediated behavioural response to acute thermal stress in zebrafish larvae, 112494112494, Copyright (2025) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.