Figure 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210708-60
- Publication
- Salam et al., 2021 - Identification of a novel interaction of FUS and syntaphilin may explain synaptic and mitochondrial abnormalities caused by ALS mutations
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
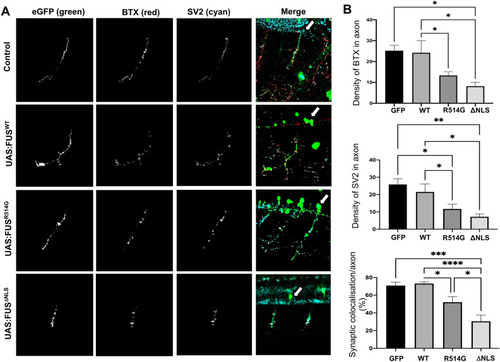
Zebrafish expressing mutant FUS show abnormal neuromuscular junctions and orphaned pre-synaptic endings. ( |