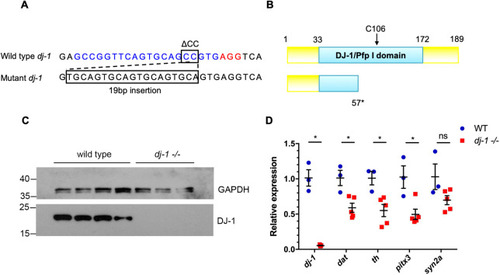
The zebrafishdj-1−/− mutation is a genetic null. (A) Wild-type dj-1 target sequence in the zebrafish genome (top). The 20 bp target sequence (blue) is directly upstream of a 3 bp protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) site (red). A 2 bp deletion (ΔCC) followed by a 19 bp insertion in the target sequence causes a frameshift mutation in dj-1 (bottom). (B) Comparison of the protein structure for wild-type Dj-1 (top), with essential residue C106 indicated, and the predicted mutant protein truncated at residue 57 (bottom). (C) Western blot analysis of Dj-1 protein expression in the brains of wild-type adult zebrafish (lanes 1-4) and their dj-1−/− mutant siblings (lanes 5-7). Gapdh was used as a loading control. (D) qRT-PCR analysis (single replicate) comparing gene expression in brains extracted from wild-type adult zebrafish (n=3, biological replicates) and their dj-1−/− mutant siblings (n=5) at 16 weeks post-fertilisation (wpf). Target gene dj-1 was analysed alongside DA neuron markers dopamine transporter (dat), tyrosine hydroxylase (th) and pituitary homeobox 3 (pitx3); synapsin IIa (syn2a) acted as a general synapse marker. Student’s t-tests (two-tailed, unpaired) were used to compare the dCt values for dj-1−/− and wild-type samples. Data are mean±s.e.m., *P<0.05; ns, not significant.
|

