Fig. 1
|
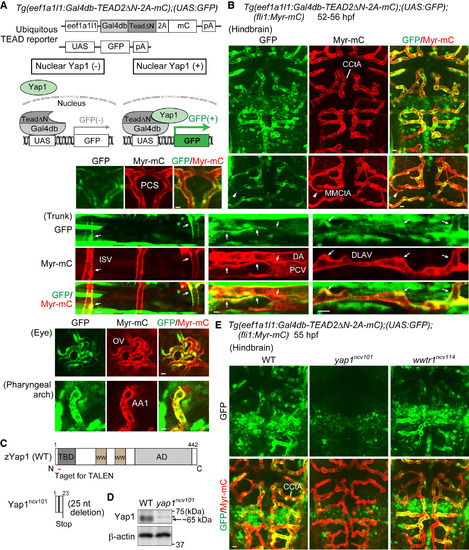
Monitoring Transcriptional Activity of Yap1 Indirectly in Endothelial Cells of Living Zebrafish (A) (Upper) The constructs used to monitor Yap1 responses ubiquitously by eef1a1l1 promoter (ubiquitous TEAD reporter). (Lower) Schematic illustration explains how the system works. In this Tg system, a fusion protein containing Gal4db-TEAD2ΔN, 2A peptide, and mCherry (mC) was ubiquitously expressed under the control of eef1a1l1 promoter. Gal4db-TEAD2ΔN is a Gal4 driver, in which a truncated form of human TEAD2 lacking the DNA-binding domain (TEAD2ΔN) is fused to the DNA-binding domain of Gal4 (Gal4db), whereas UAS-GFP is a responder transgene, in which GFP gene was placed downstream of UAS, the Gal4 recognition sequence. Upon nuclear translocation of Yap1, it binds to Gal4db-TEAD2ΔN in the nucleus, thereby inducing GFP expression via the Gal4-UAS system. This reporter reflects the interaction between endogenous Yap1 (or Wwtr1) and exogenously expressed Gal4db-TEAD2ΔN in the nucleus. pA, polyadenylation signal; UAS, upstream activation sequence. (B) Projection view of confocal stack fluorescence images of Tg(eef1a1l1:Gal4db-TEAD2ΔN-2A-mC);(UAS:GFP);(fli1:Myr-mC) embryos (52–56 hr post fertilization [hpf]). Images of hindbrain. Dorsal view, anterior to the top. Images of trunk, eye, and pharyngeal arch. Lateral view, anterior to the left. GFP images (green), mC images (red), and the merged images are shown. Arrows indicate GFP signal-positive ECs of lumenized blood vessels. Arrowheads indicate a vessel sprout showing GFP signals. (C) Schematic illustration of wild-type (WT) Yap1 and truncated Yap1ncv101 resulting from 25 nucleotides deletion in the exon1 of yap1ncv101 allele. TBD, TEAD-binding domain; WW, WW domain; AD, transcriptional activation domain. (D) Lysates from WT and homozygous yap1ncv101 mutant embryos were subjected to western blot analyses with anti-Yap1 and anti-β-actin antibodies. Arrow indicates Yap1. Asterisk indicates non-specific band. (E) Projection view of confocal stack fluorescence images of the hindbrain in Tg(eef1a1l1:Gal4db-TEAD2ΔN-2A-mC);(UAS:GFP);(fli1:Myr-mC) WT (left), homozygous yap1ncv101 mutant (middle), and wwtr1ncv114 mutant (right) embryos at 55 hpf. Upper panels, GFP images (green); lower panels, merged images (GFP, green; Myr-mC, red). Representative images of three independent experiments are shown. CCtA, cerebellar central artery; MMCtA, middle mesencephalic central artery; PCS, posterior communicating segment; ISV, intersomitic vessel; DA, dorsal aorta; PCV, posterior cardinal vein; DLAV, dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel; OV, optic vessel; AA1, mandibular arch. Scale bars, 10 μm. See also Figure S1; Movies S1 and S2. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 40, Nakajima, H., Yamamoto, K., Agarwala, S., Terai, K., Fukui, H., Fukuhara, S., Ando, K., Miyazaki, T., Yokota, Y., Schmelzer, E., Belting, H.G., Affolter, M., Lecaudey, V., Mochizuki, N., Flow-Dependent Endothelial YAP Regulation Contributes to Vessel Maintenance, 523-536.e6, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell