Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100730-6
- Publication
- Eberhart et al., 2006 - Early Hedgehog signaling from neural to oral epithelium organizes anterior craniofacial development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
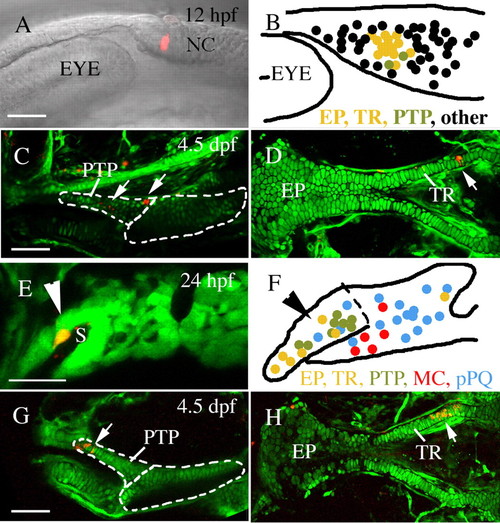
Pre- and postmigratory anterior neurocranium and upper jaw precursors co-localize. Single or two adjacent neural crest cells were labeled via microelectroporation at 12 hpf (A-D) or 24 hpf (E-H, Meckel′s cartilage and palatoquadrate data reanalyzed from Crump et al. unpublished). (A-D) At 12 hpf, pterygoid process (C, arrows, n=2) and anterior neurocranium (D, arrow, n=14) precursors are localized to a discrete cluster postoptically (B). (E-H) Within the first arch, at 24 hpf, pterygoid process (G, arrow, n=8) and anterior neurocranium (H, arrow, n=7) progenitors co-mingle on the stomodeal roof, away from Meckel′s cartilage (n=5) and palatoquadrate (n=16) precursors. The condensed anterior craniofacial neural crest precursor domain is indicated by arrowheads in E and F. (B,F) Schematic enlargements of A and E showing compiled fate mapping data for 12 hpf (B) and 24 hpf (F). Anterior neurocranium, yellow; pterygoid process, olive; non-pterygoid palatoquadrate, blue; Meckel′s cartilage, red. Black dots in B represent fates other than 4.5 dpf skeletal elements. EP, ethmoid plate; MC, Meckel′s cartilage; NC, neural crest; pPQ, non-pterygoid palatoquadrate; PTP, pterygoid process of the palatoquadrate; TR, trabeculae. Anterior is leftwards in all panels. (A,B,D-F,H) Dorsal is upwards. (C,G) Dorsal views. Scale bar: 50 μm. |