Fig. 9
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100730-11
- Publication
- Eberhart et al., 2006 - Early Hedgehog signaling from neural to oral epithelium organizes anterior craniofacial development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
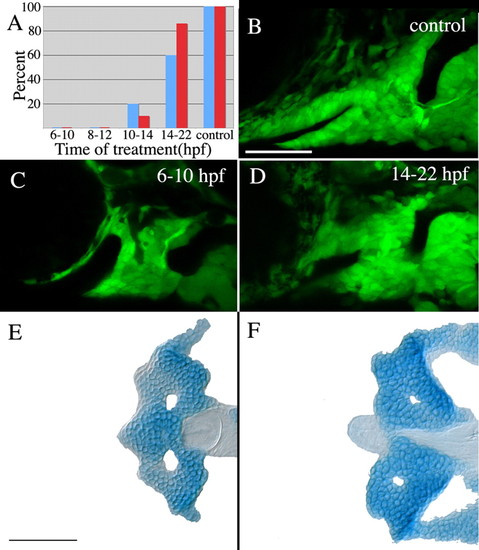
Hh signaling is required at the end of gastrulation for stomodeum expression ofpitx2and proper crest cell condensation. (A) No embryos treated with cyclopamine from 6-10 hpf or 8-12 hpf express stomodeal pitx2 (blue bars) or condense crest on the stomodeal roof (red bars). A small number of embryos treated with cyclopamine from 10-14 hpf express pitx2 in the stomodeum and exhibit condensation of anterior craniofacial crest cells, whereas the majority of embryos treated between 14-22 hpf do express pitx2 in the stomodeum and condense crest cells on the roof of the stomodeum. Control DMSO-treated embryos all expressed pitx2 and undergo crest cell condensation normally. (B-D) Effects of cyclopamine treatment on the condensation of neural crest cells. Anterior craniofacial crest cells condense on the stomodeal roof in control embryos (B) and embryos treated from 14-22 hpf (D); however, this crest cell subpopulation fails to condense in embryos treated from 6-10 hpf (C). (E,F) The anterior neurocranium is deleted in all cyclopamine-treated embryos. n=10 in each treatment group for pitx2 expression. Crest cell condensation and neurocranial cartilage analysis: 6-10 hpf, n=25; 8-12 hpf, n=16; 10-14 hpf, n=20; 14-22 hpf, n=21; control, n=14. Scale bars: 50 μm. |