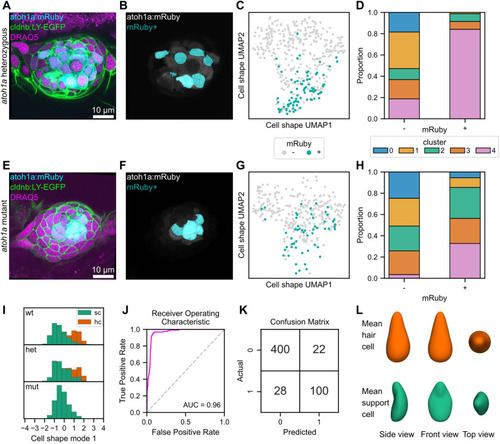
Shape characteristics of atoh1a:mRuby heterozygotes and mutants, and logistic classifier for hair cells based on cell shape features. (A-G) Analysis of cell shape distributions in atoh1a:mRuby heterozygotes (A-D) and mutants (E-H). (A,E) Single confocal slice of a neuromast from an atoh1a:mRuby heterozygote (A) and mutant (E) also expressing Tg(-8.0cldnb:LY-EGFP) and stained with DRAQ5. Image contrast was adjusted for visibility. (B,F) The same slices as in A and E, with the atoh1a:mRuby channel (gray) overlaid with a mask indicating cells classified as mRuby+ (cyan) for a atoh1a:mRuby heterozygote (B) and mutant (F). (C,G) UMAP of mRuby+ (cyan) and mRuby− (gray) cells from atoh1a:mRuby heterozygotes (C) and mutants (F). (D,H) Proportions of mRuby− cells (left bar) and mRuby+ cells (right bar) from atoh1a:mRuby heterozygotes (D) and mutants (H) in each cell shape cluster. (I) Distributions of cell shape mode 1 scores, separated by genotype (top row, wild type; middle row, atoh1a heterozygous; bottom row, atoh1a mutant). Hair cells (hc, green); support cells (sc, orange). (J) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (fuchsia) for a logistic regression classifier trained to detect hair cells based on cell shape mode 1-8. The area under the curve (AUC) score is shown (0.96). Gray dashed line, performance of a random classifier. (K) Confusion matrix for the cell shape-based hair cell classifier. 0, support cells; 1, hair cells. Top left, true negatives; top right, false positives; bottom left, false negatives; bottom right, true positives. (L) The idealized mean cell shape for hair cells (top, orange) and support cells (bottom, green).
|