- Title
-
A Novel Class of Norovirus Inhibitors Targeting the Viral Protease with Potent Antiviral Activity In Vitro and In Vivo
- Authors
- Van Dycke, J., Dai, W., Stylianidou, Z., Li, J., Cuvry, A., Roux, E., Li, B., Rymenants, J., Bervoets, L., de Witte, P., Liu, H., Neyts, J., Rocha-Pereira, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Viruses
|
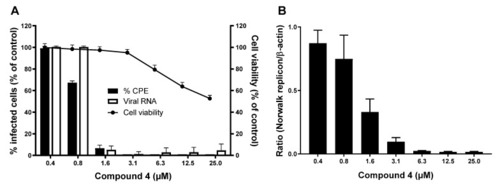
The antiviral effect of compound 4 against MNV and the HuNoV GI.1 replicon. (A) The antiviral activity of compound 4 against MNV was quantified by (i) virus-induced CPE reduction and (ii) reduction in viral RNA levels. Cellular toxicity was assessed in parallel. n = 3–4 (±SEM). (B) The antiviral activity of compound 4 against the HuNoV GI.1 replicon. Intracellular RNA loads are represented by relative genome quantification of the HuNoV GI.1 replicon versus β-actin. n = 5 (±SEM). |
|
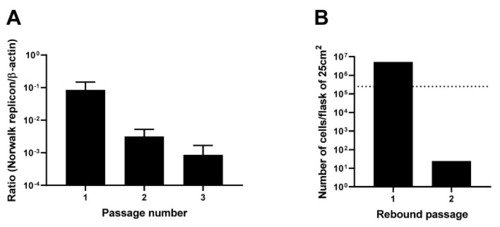
Clearance of the HuNoV GI.1 replicon from HGT cells by compound 4. (A) Clearance phase: cells were treated for three consecutive passages with compound 4 (10 µM) without G418. (B) Rebound phase: cells from the clearance phase were placed under selective pressure with G418, without compound 4. The dotted line represents the minimum number of HGT cells required for the next passage. |
|
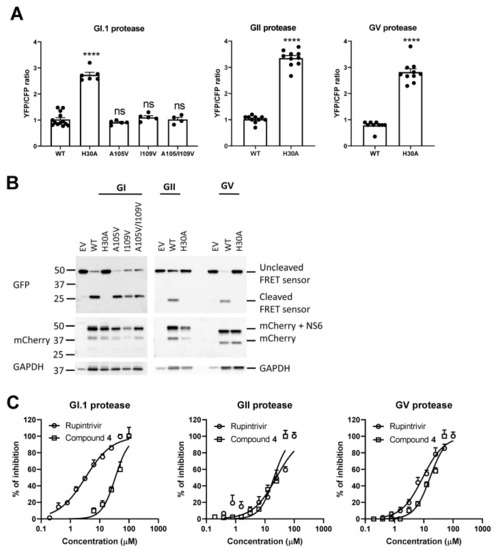
Compound 4 and rupintrivir block the norovirus protease. (A) The FRET signal was lost upon co-transfection with the wild-type (WT) or a mutated protease (A105V, I109V, A105V/I109V). The signal remained upon co-transfection with the inactive (H30A) protease. (B) Western blot of HEK293T cells co-transfected with the GI, GII or GV WT or mutant proteases along with the FRET construct. Cleavage was observed in the WT and mutant proteases in all genogroups. EV: empty vector. (C) Dose–response curves of compound 4 and rupintrivir on the WT proteases. Mean values ±SEM are presented, Mann–Whitney test **** p < 0.0001, ns: not significant. |
|
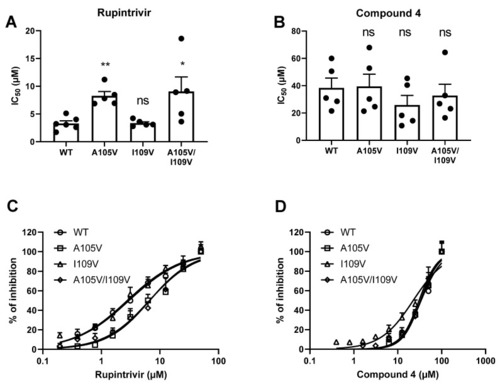
The susceptibility of mutated GI.1 proteases to rupintrivir and compound 4. IC50 values of rupintrivir (A) and compound 4 (B) on the WT or mutant GI proteases. Dose–response inhibition curves of rupintrivir (C) and compound 4 (D) on the WT or mutant GI proteases. Mean values ±SEM are presented, Mann–Whitney test ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, ns: not significant. |
|
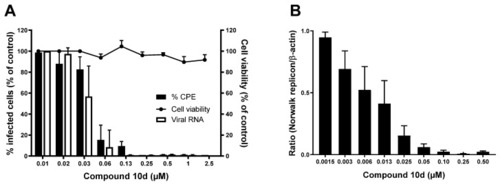
The antiviral effect of compound 10d against MNV and the HuNoV GI.1 replicon. (A) The antiviral activity of compound 10d against MNV was quantified by (i) virus-induced CPE reduction and (ii) reduction in viral RNA levels. Cellular toxicity was assessed in parallel. n = 3–4 (±SEM). (B) The antiviral activity of compound 10d against the HuNoV GI.1 replicon. Intracellular RNA loads are represented by relative genome quantification of the HuNoV GI.1 replicon versus β-actin. n = 3 (±SEM). |
|
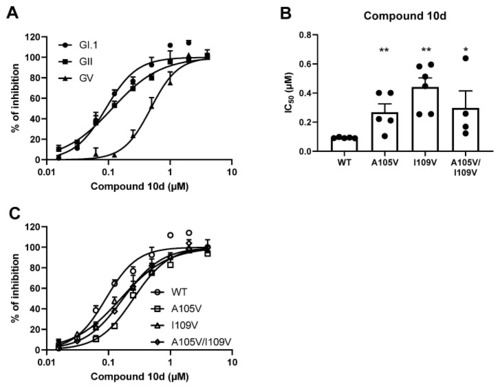
The susceptibility of mutated GI.1 proteases to compound 10d. (A) Dose–response inhibition curves showing the effect of compound 10d on the WT proteases. (B) IC50 values of compound 10d on the WT or mutant GI.1 proteases. (C) Dose–response inhibition curves showing the effect of compound 10d on the WT or mutant GI proteases. Mean values ±SEM are presented, Mann–Whitney test, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05. |
|
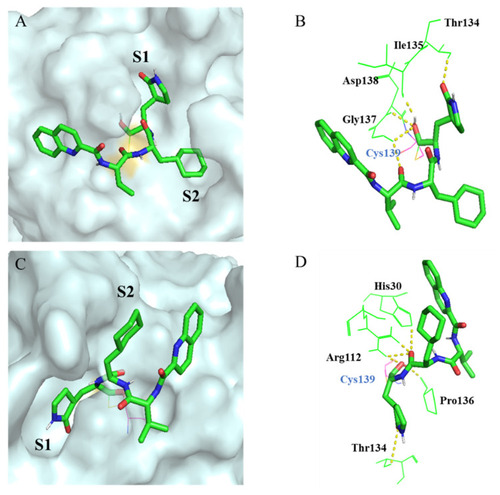
Molecular docking of compound 10d in the GI.1 and GII.4 norovirus 3CL protease. (A) The binding mode of 10d at the substrate-binding site of the GI.1 norovirus 3CLpro (PDB code: 3UR9). The GI.1 norovirus 3CLpro was shown as molecular surface and 10d was shown by green sticks. (B) Interactions of 10d with the surrounding residues. Residues are shown as light green lines, and H-bonds are represented by yellow dashed lines. (C) The binding mode of 10d at the substrate-binding site of the GII.4 norovirus 3CLpro (PDB code: 6NIR). (D) Interactions of 10d with the surrounding residues. The Schrödinger program (Maestro covalent docking) was used for calculations and PyMOL program for visualizations. |
|
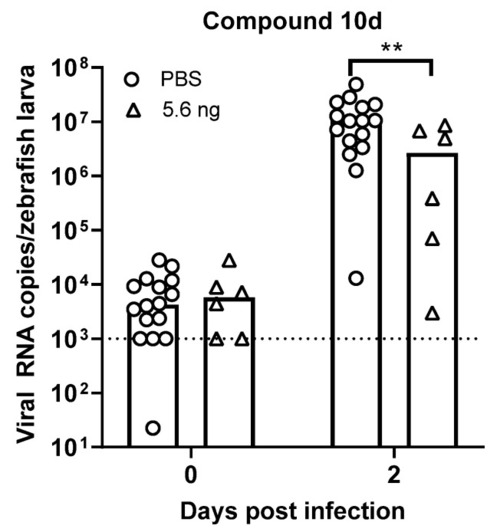
Compound 10d reduces HuNoV GII.4 replication in zebrafish larvae. Single treatment of zebrafish infected with HuNoV GII.P4-GII.4 with compound 10d (n = 6–11). The dotted line represents the limit of detection (LOD), mean values ±SEM, Mann–Whitney test, ** p < 0.01. |