- Title
-
Meis1 specifies positional information in the retina and tectum to organize the zebrafish visual system
- Authors
- Erickson, T., French, C.R., and Waskiewicz, A.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Neural Dev.
|
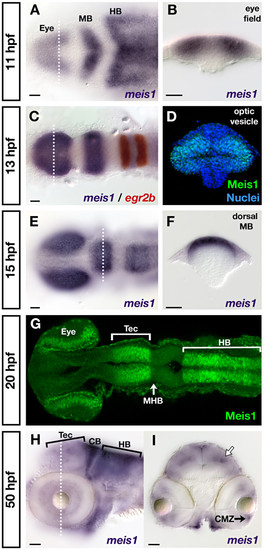
Developmental time course of meis1 mRNA and protein expression. (A, B) mRNA in situ hybridizations (ISHs) for meis1 at 11 hpf showing expression in the eye field, and in the presumptive midbrain (MB) and hindbrain (HB). The transverse section (B) shows meis1 expression in the eye field. (C) mRNA ISH showing meis1 expression at 13 hpf in the optic vesicles, midbrain and hindbrain. egr2b/krox20 expression (red) marks rhombomeres 3 and 5 of the hindbrain. (D) Transverse section of a whole mount immunostain for Meis1 showing protein in the dorsal and ventral leaflets of the 13 hpf optic vesicle. Hoechst 33258 stain marks the nuclei. (E, F) mRNA ISH at 15 hpf showing continued expression of meis1 in the optic vesicles, midbrain and hindbrain. The transverse section (F) shows meis1 expression in the dorsal midbrain. (G) Whole mount immunostain for Meis1 protein at 20 hpf. Meis1 protein is present in the eye, presumptive tectum (Tec), and in the hindbrain (HB) up to the r1-r2 boundary. Meis1 is excluded from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary (MHB). (H, I) mRNA ISH at 50 hpf showing meis1 expression in the hindbrain (HB) and cerebellum (CB) and tectum (Tec). The transverse section (I) shows meis1 expression in the ciliary marginal zone (CMZ) of the retina and in the dorsal midline and a deeper layer of the tectum (white arrow). Embryos in (A, C, E, G) are shown in dorsal view with anterior to the left. Embryo in (H) is shown in lateral view with anterior to the left. Transverse sections in (B, D, F, I) are oriented dorsal up. The dotted lines in (A, C, E, H) indicate the position of the corresponding transverse sections in (B, D, F, I). All scale bars = 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Meis1 positively regulates ephrin gene expression in the tectum. (A-H) mRNA in situ hybridizations (ISHs) for efna2 (A, B), efna3b (C, D), efna5a (E, F) and efnb3b (G, H) in 32-hpf wild-type (A, C, E, G) and meis1 morphant (meis1MO) (B, D, F, H) embryos. Meis1 knockdown leads to a downregulation in the tectal expression of these ephrin genes (arrows) (I-P) mRNA ISH for efna2 (I, J), efna3b (K, L), efna5a (M, N) and efnb3b (O, P) in 48-hpf wild-type (I, K, M, O) and meis1 morphant (J, L, N, P) embryos. The early defects in tectal ephrin gene expression remain in 48-hpf meis1 morphants (arrows). The dotted lines in (O, P) outline a single tectal lobe in each embryo. Embryos in (A-N) are shown in lateral view with anterior left, while embryos in (O, P) are shown in dorsal view with anterior left. |
|
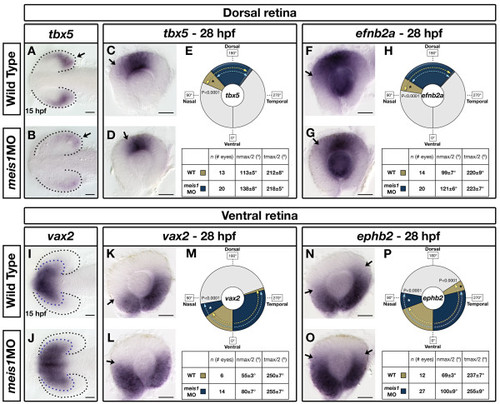
Meis1 contributes to dorsal-ventral patterning in the developing retina. (A, B, I, J) mRNA in situ hybridization (ISH) for the dorsal marker tbx5 (A, B) and the ventral marker vax2 (I, J) in 15-hpf wild-type and meis1 morphant (meis1MO) embryos. Black dotted lines outline the optic vesicle. Arrows indicate tbx5 expression in the presumptive dorsal retina. Purple dotted lines indicate the domain of vax2 expression. All views are dorsal with anterior left. (C, D, F, G, K, L, N, O) mRNA ISH for dorsal genes tbx5 (C, D) and efnb2a (F, G), and ventral genes vax2 (K, L) and ephb2 (N, O) in dissected, flat-mounted eyes from 28-hpf wild-type and meis1 morphant embryos. Arrows indicate the approximate limit of the gene expression domain. (E, H, M, P) The domains of gene expression were quantified by determining a 360° profile of in situ staining intensity and graphing the radial position at which gene expression intensity falls to the halfway point between its minimum and maximum values. The nmax/2 and tmax/2 values are given as the mean radial position in degrees ± one standard deviation. Asterisks indicate regions in which there are statistically significant differences in axial identity between wild type (WT) and meis1 morphants as determined by an unpaired, two-tailed t-test using a P-value of 0.01 as a cutoff for significance. Representative dissected eyes are shown. Scale bars = 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
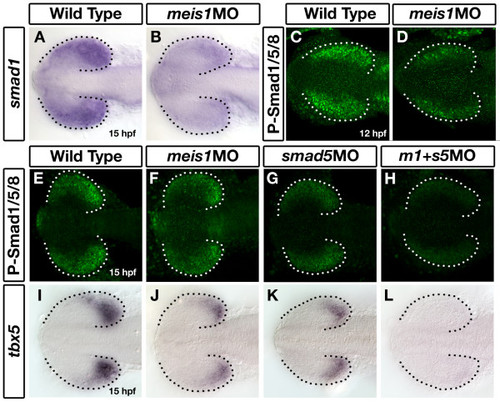
Meis1 positively regulates smad1 expression in the developing eye. (A, B) mRNA in situ hybridization (ISH) for smad1 in 15-hpf wild-type and meis1 morphant (meis1MO) embryos. (C, D) Whole mount immunostains for phosphorylated Smad1/5/8 on 12-hpf wild-type and meis1 morphant embryos. (E-H) Phospho-Smad1/5/8 immunostains on 15-hpf embryos treated with meis1 morpholino (F), smad5 morpholino (G) or a combination of both morpholinos (H). (I-L) mRNA ISH for tbx5 in 15-hpf wild-type (I), meis1 morphant (J), smad5 morphant (K), and meis1-smad5 double morphant (L) embryos. Dotted lines outline the optic vesicle. All views are dorsal with anterior to the left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
follistatin a is ectopically expressed in Meis1-depleted embryos and can inhibit Gdf6-mediated Bmp signalling. (A-D) mRNA in situ hybridizations for fsta on 13-hpf (A, B) and 19-hpf (C, D) wild-type and meis1 morphant (meis1MO) embryos. Dotted lines outline the optic vesicle. All views are dorsal with anterior to the left. (E) Results of the GDF6-Fsta interaction experiments. One-cell embryos were injected with either 200 pg of zebrafish fsta mRNA (bar 2), human GDF6 mRNA (bar 3), or both mRNAs (bar 4), raised until 28 hpf, and scored for dorsalized and ventralized phenotypes (see legend on the right for classification). (F, G) Confocal images of whole mount immunostains for phospho-Smad1/5/8 in wild-type and fsta mRNA-injected embryos at 14 hpf. Injection of fsta mRNA into one cell of a two-cell embryo causes a unilateral reduction in phospho-Smad1/5/8 staining (arrow in G). Dotted lines outline the optic vesicle. Views are dorsal with anterior to the left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
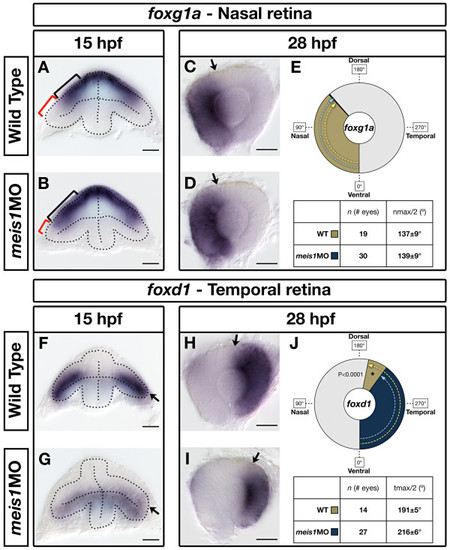
Meis1-depleted embryos exhibit a partial temporal-to-nasal shift in retinal identity. (A, B, F, G) mRNA in situ hybridization (ISH) for the nasal marker foxg1a (A, B) and the temporal marker foxd1 (F, G) in 15-hpf wild-type and meis1 morphant (meis1MO) embryos. Dotted lines outline the optic vesicle. The black brackets in (A, B) indicate the proximal-distal extent of foxg1a expression, while the red brackets indicate the foxg1a-free region. Arrows in (F, G) indicate the dorsal leaflet of the optic vesicle. Transverse sections are oriented dorsal up. (C, D, H, I) mRNA ISH for the nasal marker foxg1a (C, D) and the temporal marker foxd1 (H, I) in dissected, flat-mounted eyes from 28-hpf wild-type and meis1 morphant embryos. The arrows indicate the approximate limit of the gene expression domain. (E, J) The domains of gene expression were quantified by determining a 360° profile of in situ staining intensity and graphing the radial position at which gene expression intensity falls to the halfway point between its minimum and maximum values. The nmax/2 and tmax/2 values are given as the mean radial position in degrees ± one standard deviation. Asterisks indicate regions in which there are statistically significant differences in axial identity between wild type and meis1 morphants as determined by an unpaired, two-tailed t-test using a P-value of 0.01 as a cutoff for significance. Representative dissected eyes are shown. Scale bars = 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
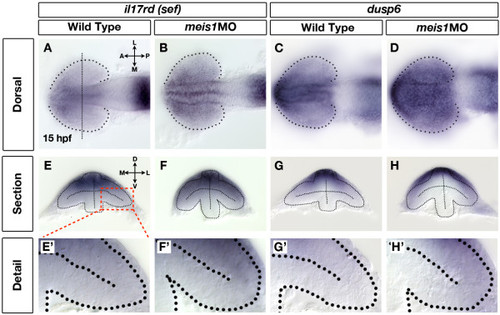
Retinal Fgf signalling is upregulated in Meis1-depleted embryos. (A-D) mRNA in situ hybridization (ISH) for the Fgf-responsive genes il17rd/sef (A, B) and dusp6 (C, D) in wild-type (A, C) and meis1 morphant (meis1MO) (B, D) embryos. Dotted lines outline the optic vesicle. The vertical dotted line in (A) indicates the estimated position of the transverse sections in (E-H). Views are dorsal with anterior left. (E-H) Transverse sections through the eyes of 15-hpf wild-type and meis1 morphant embryos stained for il17rd and dusp6. (E′-H′) Detailed views of the corresponding sections in (E-H). The region of interest is indicated by the red dashed-line box. Dotted lines outline the optic vesicles. All transverse sections are oriented with dorsal up. Legend for retinal axial position: D, dorsal; V, ventral; N, nasal; T, temporal; L, lateral; M, medial; A, anterior; P, posterior. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
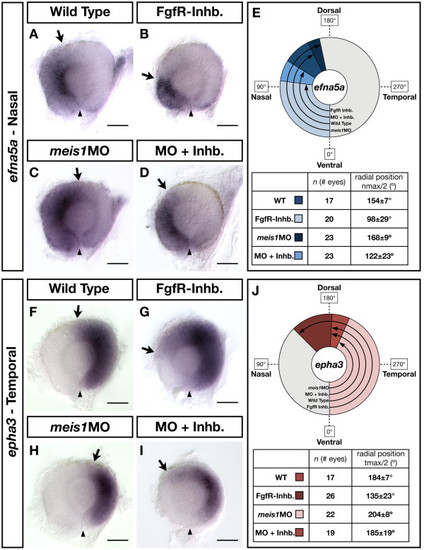
The contribution of Fgf signalling to the NT patterning defects in Meis1-depleted embryos. (A-D, F-I) mRNA in situ hybridizations for the NT markers efna5a (A-D) and epha3 (F-I) in wild type, Meis1-depleted (meis1MO), Fgf receptor-inhibitor treated (FgfR-Inhb.), and FgfR-inhibited/Meis1-depleted retinas (MO + Inhb.). Arrows indicate the extent of the gene expression domain, while the arrowheads indicate the position of the ventral choroid fissure. Representative dissected eyes are shown oriented with dorsal up and nasal to the left. Scale bars = 50 μm. (E, J) Quantification of the changes in efna5a and epha3 expression, as quantified by measuring a 360° profile of in situ staining intensity and graphing the mean radial position at which gene expression intensity falls to the halfway point between its minimum and maximum values. The nmax/2 and tmax/2 values are given as the mean radial position in degrees ± one standard deviation. WT, wild type |
|
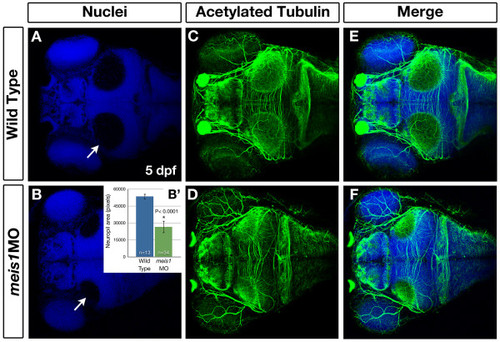
Meis1-depleted embryos have smaller tectal neuropil at 5 dpf. (A-F) Whole mount immunohistochemistry using anti-acetylated tubulin (axons - green) and Hoechst 33258 (nuclei - blue) to compare the size of the tectal neuropil in 5-dpf wild type (A, C, E) and meis1 morphant (meis1MO) (B, D, F) embryos. White arrows in (A, B) indicate the tectal neuropil. (B′) The area (in pixels) of the neuropil from wild type and meis1 morphant embryos was measured using ImageJ. The n values represent individual neuropil regions. The error bars show plus/minus one standard deviation. The asterisk indicates a statistically significant reduction the size of morphant neuropil as determined by an unpaired, two-tailed t-test. |
|
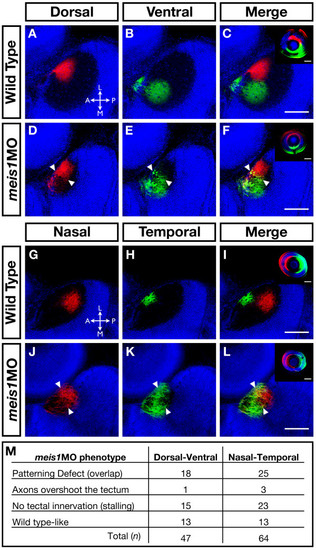
The retinotectal map is disorganized in Meis1-depleted embryos. (A-L) Lipophilic fluorescent dyes DiI (red) and DiO (green) were injected into specific axial positions of the retina of fixed 5-dpf wild-type and meis1 morphant embryos and innervation patterns of the ganglion cell axons on the tectum were imaged by confocal microscopy. Nuclei are stained with Hoechst 33258 (blue). The wild-type (A-C) medial-lateral segregation of dorsal (red) and ventral (green) ganglion cell axons in the tectum is lost in meis1 morphants (white arrowheads in (D-F)). Similarly, the wild-type (G-I) anterior-posterior segregation of nasal (red) and temporal (green) ganglion cell axons in the tectum is disorganized in meis1 morphants (white arrowheads in (J-L)). The insets in (C, F, I, L) are lateral views of injected retinas from the embryos shown in the corresponding panels. Retinas are oriented with dorsal up and nasal to the left, while all tectal views are dorsal with anterior to the left. Legend for axial position in the tectum: L, lateral; M, medial; A, anterior; P, posterior. All scale bars = 75 μm. (M) Table describing the frequency of various retinotectal mapping phenotypes observed in meis1 morphants (meis1MO). No retinotectal mapping defects were observed in any wild-type embryos examined. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
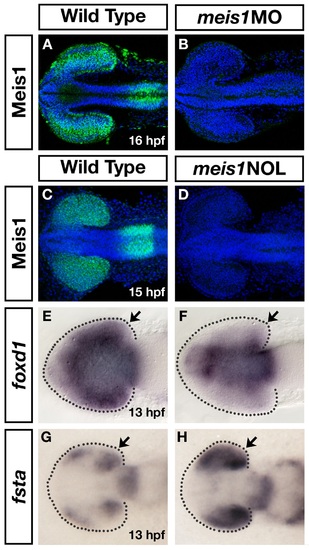
Two independent meis1 morpholinos result in similar phenotypes. (A-D) Two independent meis1 translation blocking morpholinos effectively knockdown Meis1 protein, as shown by whole mount immunohistochemistry using a Meis1 monoclonal antibody. Hoechst 33258 stain marks the nuclei. (E-H) The meis1 non-overlapping (NOL) morpholino gives similar phenotypes as the ATG-morpholino (compare with Figure 5A-D and Figure 6F, G). meis1NOL morphants exhibit reduced foxd1 expression in the presumptive temporal retina (n = 27/29) (E, F), and upregulated fsta expression in the eye at 13 hpf (n = 19/19) (G, H). Dotted lines outline the optic vesicle. Views are dorsal with anterior to the left. |
|
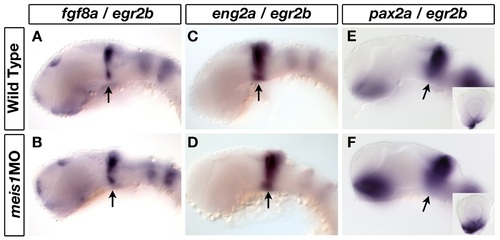
Meis1-knockdown does not affect patterning of the midbrain-hindbrain boundary. (A-F) mRNA in situ hybridization for midbrain-hindbrain boundary (MHB) markers fgf8a (A, B), eng2a (C, D) and pax2a (E, F) in 32-hpf wild-type and meis1 morphant embryos. Arrows indicate the relevant gene expression domain at the MHB. The insets in (E, F) are representative dissected eyes showing an upregulation of pax2a staining in the optic stalk of meis1 morphants (n = 18/18). Embryos are co-stained with the hindbrain r3 and r5 marker egr2b. Embryos are shown in lateral view with dorsal up and anterior to the left, and the dissected retinas are oriented with dorsal up and nasal to the left. |
|
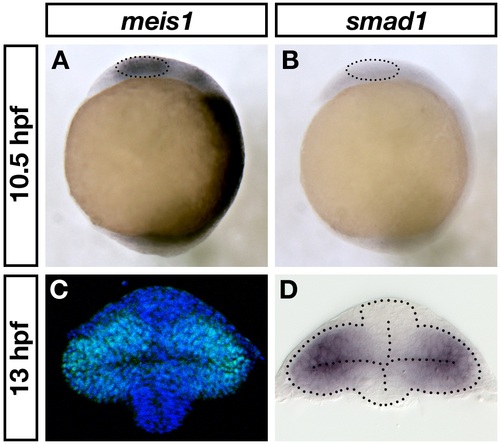
meis1 and smad1 expression in the early optic vesicle. (A, B) mRNA in situ hybridizations for meis1 (A) and smad1 (B) in 10.5-hpf wild-type embryos. The dotted circles indicate the eye fields. Views are lateral with anterior on the top. (C, D) Transverse sections of wild-type 13-hpf optic vesicles stained for Meis1 protein (C) and smad1 mRNA (D). Note that (C) is the same as shown in Figure 1D. The dotted lines outline the optic vesicle and neural tube. Sections are oriented with dorsal at the top. |
|
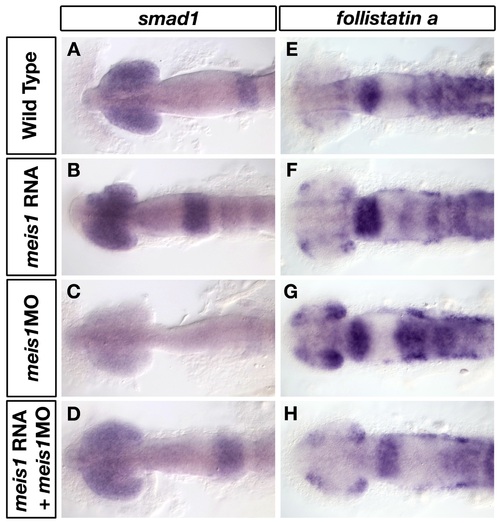
Morpholino-insensitive myc-meis1 RNA can rescue the smad1 and fsta expression defects in meis1 morphants. (A-H) mRNA in situ hybridizations for smad1 (A-D) and fsta (E-H) in wild-type (A, E), myc-meis1 RNA (B, F), meis1 morphant (C, G) and myc-meis1 RNA/meis1 morphant embryos at 14 hpf. All embryos are shown in dorsal view with anterior to the left. |
|
gdf6a morphants have normal smad1 and fsta expression at 13 hpf. (A-D) mRNA in situ hybridizations for smad1 (A, B) and fsta (C, D) in wild-type (A, C) and gdf6a morphant (B, D) embryos at 13 hpf. Dotted lines outline the optic vesicle. Views are dorsal with anterior to the left. |
|
smad5 expression is normal in meis1 morphants. (A-D) mRNA in situ hybridization for smad5 on wild-type (A, B) and meis1 morphant (C, D) embryos at 15 hpf. (A, C) Lateral views with anterior up; (B, D) dorsal views with anterior to the left. |
|
The temporal expression domains of epha7 and epha4b are reduced in meis1 morphants. (A, B) mRNA in situ hybridization (ISH) for epha7 on wild-type (A) and ,i>meis1 morphant (B) embryos at 16 hpf. Arrows indicate the expression of epha7 in the presumptive temporal retina. Embryos are shown in dorsal view with anterior to the left. (C-F) mRNA ISH for the temporal markers epha7 (C, D) and epha4b (E, F) in dissected, flat-mounted eyes from 26- to 28-hpf wild-type and meis1 morphant embryos. Arrows indicate the dorsal extent of gene expression. Representative dissected eyes are shown. Legend for retinal axial orientation: D, dorsal; V, ventral; N, nasal; T, temporal. |
|
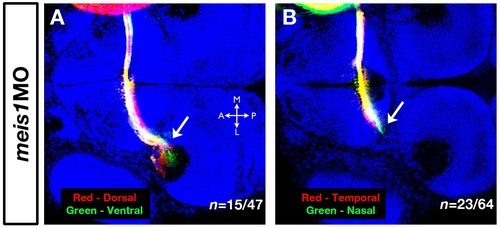
The RGC axon stalling phenotype in meis1 morphants. (A, B) Dorsal-ventral (A) and nasal-temporal (B) RGC axon stalling phenotypes in meis1 morphants. Arrows indicate the stalled RGC axons labelled with fluorescent lipophilic dyes DiI (red) and DiO (green). Hoechst 33258 (blue) marks nuclei. All views are dorsal with anterior to the left. Legend for axial position in the tectum: M, medial; L, lateral; A, anterior; P, posterior. |