- Title
-
Ras-Related Nuclear Protein is required for late developmental stages of retinal cells in zebrafish eyes
- Authors
- Lin, C.Y., Huang, H.Y., Lu, P.N., Lin, C.W., Lu, K.M., Tsai, H.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Dev. Biol.
|
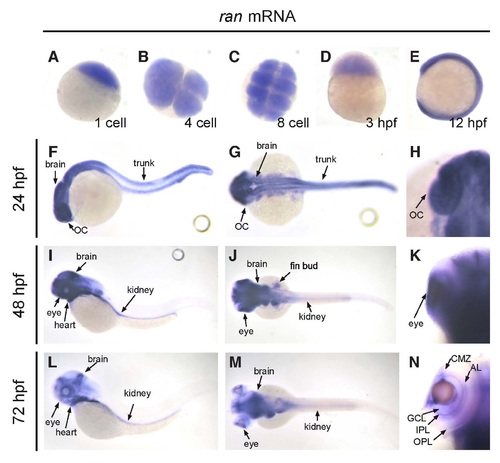
The spatiotemporal expression pattern of ran mRNA in developing zebrafish embryo. (A-E) From one-cell stage up to 12 hpf, ran mRNA was detected on the whole embryo. (A,D,E) Lateral view; (B,C) animal polar view. (F-H) At 24 hpf, while ran mRNA can still be detected in brain and optic cup, the level of ran mRNA started to decrease at the trunk area. (I-K) At 48 hpf, ran mRNA was highly expressed in brain, eyes, heart, fin buds and kidney, but not in trunk. (L-N) At 72 hpf, ran mRNA was expressed in brain, heart and kidney. In the eye, ran mRNA was detected on CMZ, GCL, IPL, AL and OPL. (F,I,L) Lateral view with anterior to the left; (G,J,M) dorsal view with anterior to the left; (H,K,N) dorsal view with anterior to the top, focused on the optic cup area, and only the left eyes are presented to show better detail. AL, amacrine layer; CMZ, ciliary marginal zone; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; OC, optic cup; OPL, outer plexiform layer. All images are representative of at least three repeats with n>25 for each repeat. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
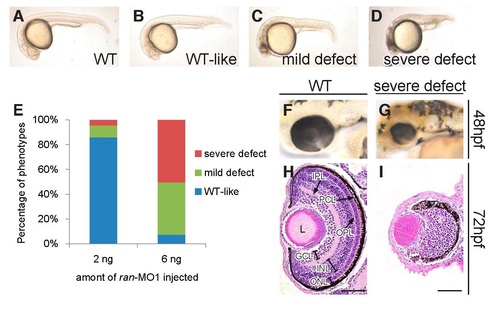
The phenotypes of ran deficiency. (A-D) Typical phenotypes of live WT and ran-deficient embryos at 24 hpf. (E) The distribution of phenotypes when 2 ng and 6 ng of ran-MO1 were injected. The injection experiment was repeated three times with pooled n = 411 and 627 for 2 ng and 6 ng injection groups, respectively. (F-G) Typical images of live WT eye and the eye with severe ran-deficient phenotype at 48 hpf. All live embryo images are lateral view with anterior to the left. (H-I) H&E staining of WT eye and the eye with severe ran-deficient phenotype at 72 hpf. All H&E staining images are coronal sections with anterior to the top. GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; PCL, pigment cell layer. Scale bars, 50 µm. All images of ran-deficient embryos were injected with 6 ng of ran-MO1. All images are representative of at least three repeats with pooled n>400. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
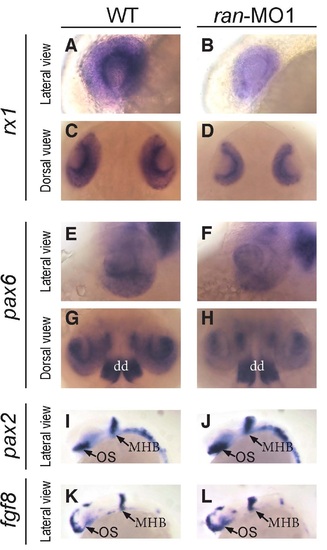
The effects of Ran deficiency on the expression of early eye differentiation markers. (A-D) Typical expression patterns of rx1 mRNA on the eyes of WT and Ran-deficient embryos. While sizes are different, note that the patterns of pax6 were not significantly changed. (E-H) Typical expression patterns of pax6 mRNA on the eyes of WT and ran-deficient embryos. dd: dorsal diencephalon. (I,J) The expression patterns of pax2 mRNA on the eyes of WT and ran-deficient embryos. (K,L) The expression patterns of fgf8 mRNA on the eyes of WT and Ran-deficient embryos. (A, B, E, F, I - L) Lateral view with anterior to the left; (C,D,G,H) dorsal view with anterior to the top. MHB, midbrain/hindbrain boundary; OS, optic stalk. All images are representative of at least three repeats with n>25 for each repeat. |
|
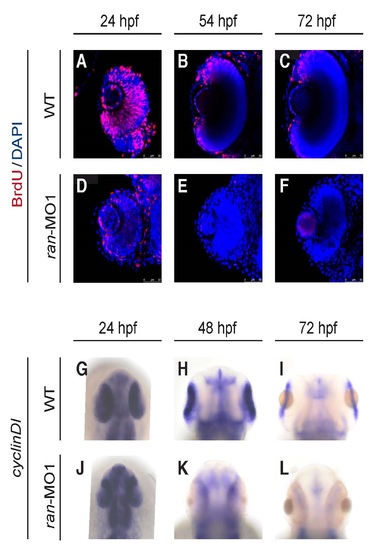
Ran deficiency impaired eye cell proliferation. (A-F) Temporal dynamics of cell proliferation on the eyes of WT and ran-deficient embryos. All images are coronal sections with anterior to the top. Red, BrdU; Blue, DAPI. Scale bars indicate 50 µm. (G-L) Temporal dynamics of cell proliferation marker cyclinD1 mRNA on the eyes of WT and ran-deficient embryos. All images are dorsal view with anterior to the top. All images are representative of at least three repeats with n>25 for each repeat. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
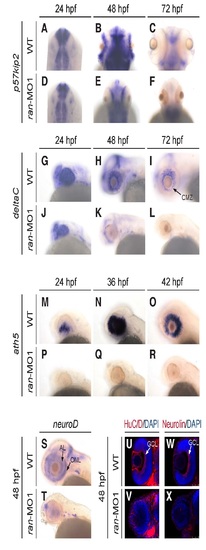
Ran deficiency impaired eye cell differentiation. (A-R) Temporal dynamics of the expression of cell differentiation marker (A-F) p57kip2, (G-L) deltaC and (M-R) ath5 on the eyes of WT and ran-deficient embryos. (S, T) Expression of cell differentiation marker neuroD on the eyes of WT and ran-deficient embryos. (U-X) Expression of the cell differentiation marker (U,V) HuC/D protein and (W,X) Neurolin protein on the eyes of WT and ran-deficient embryos. (A-F) Dorsal view with anterior to the top; (G-T) lateral view with anterior to the left; (U-X) dorsal view with anterior to the top, and only the left eyes are presented to show better detail. AL, amacrine layer; CMZ, ciliary marginal zone; GCL, ganglion cell layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer. All images are representative of at least three repeats with n>25 for each repeat. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
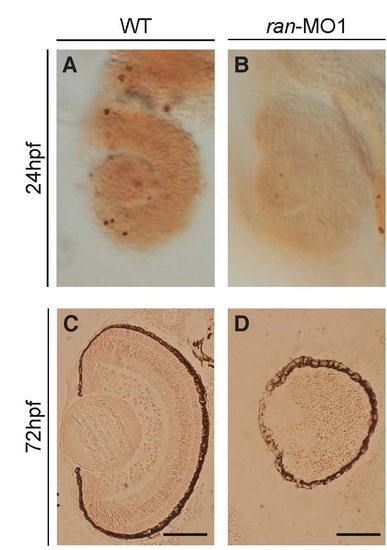
Ran-deficient embryos did not exhibit a significant change in the apoptosis of retinal cells. (A,B) Lateral views of 24 hpf eyes. (C,D) coronal sections of 72 hpf eyes. The apoptosis signals in the embryonic ocular section were detected by TUNEL assay. A small amount of apoptosis signals was detected in both wild-type embryos and ran-deficient embryos at 24 hpf, in which there was not much differences. Additionally, few apoptosis signals were also detected in both wild-type embryos and ran-morphants at 72 hpf, indicating that apoptosis would not be caused by the loss of Ran at both early and late developmental stages of retinal cells. Scale bars, 50 µm. PHENOTYPE:
|