Figure 1—figure supplement 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-231116-86
- Publication
- Shrestha et al., 2023 - The myocardium utilizes a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (Pdgfra) - phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade to steer towards the midline during zebrafish heart tube formation
- Other Figures
-
- Figure 1
- Figure 1—figure supplement 1
- Figure 1—figure supplement 2
- Figure 1—figure supplement 3
- Figure 1—figure supplement 4
- Figure 1—figure supplement 5
- Figure 1—figure supplement 6
- Figure 2
- Figure 2—figure supplement 1
- Figure 2—figure supplement 2
- Figure 3
- Figure 3—figure supplement 1
- Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
- Figure 4
- Figure 4—figure supplement 1
- Figure 5
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
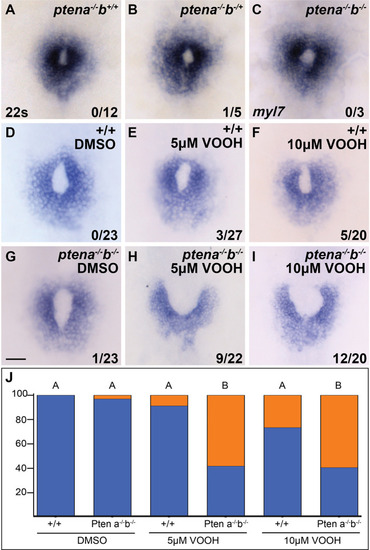
Loss of Pten, an antagonist of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) activity, causes cardiac fusion defects. ( |