Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210210-1
- Publication
- Cambier et al., 2020 - Spreading of a mycobacterial cell surface lipid into host epithelial membranes promotes infectivity
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
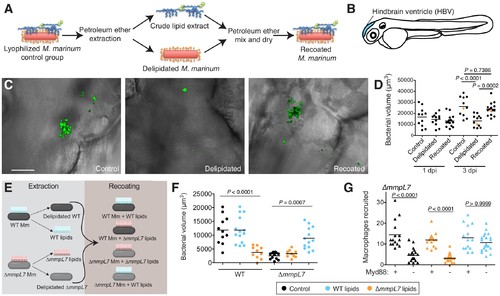
Lipid removal and recoating reveals that pre-infection PDIM reservoirs are required for M.marinum infection of zebrafish. (A) Model of lipid removal and recoating of M. marinum. (B) Model of zebrafish larva showing the hindbrain ventricle (HBV) injection site. (C) Representative images of the experiment in D (orange dots), wasabi (green) fluorescent protein expressing M. marinum in the HBV at 3 dpi are shown, scale bar = 50 μm. (D) Mean bacterial volume after HBV infection of wildtype fish with ~100 control, delipidated, or recoated M. marinum. (E) Model of lipid-swap experiment. (F) Mean bacterial volume at 3 dpi after HBV infection of wildtype fish with ~100 WT or ∆mmpL7 M. marinum treated as follows: non-extracted control (black), extracted and recoated with WT lipids (blue), or extracted and recoated with ∆mmpL7 lipids (orange). (G) Mean macrophage recruitment at 3 hpi of the HBV of wildtype or Myd88-depleted fish with ~100 ∆mmpL7 M. marinum as treated in F. (D), (F), and (G) representative of at least three separate experiments. Ordinary one-way ANOVA with (D) Sidak's multiple comparisons test for the comparison’s shown and (F) Tukey’s multiple comparisons test with selected adjusted P values shown. (G) Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA for unequal variances with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test with selected adjusted P values shown. |