Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-171228-50
- Publication
- Rességuier et al., 2017 - Specific and Efficient Uptake of Surfactant-Free Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanovaccine Vehicles by Mucosal Dendritic Cells in Adult Zebrafish after Bath Immersion
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
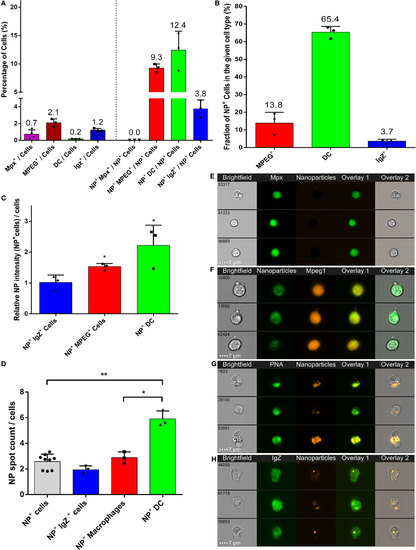
High uptake of poly(lactic acid) nanoparticles (PLA-NPs) by mucosal dendritic cells (DCs). (A–D) Quantification by imaging flow cytometry of the nanoparticle (NP) uptake by gill phagocytes from adult zebrafish, previously immersed for 24 h in 0.05% NPs. For each cell type, results from at least three independent acquisitions are represented as dots; histograms indicate the mean. Neutrophils and macrophages were labeled by GFP and mCherry expression in transgenic mpx:GFP and mpeg1:mCherry fish, respectively (one fish per acquisition). DCs and IgZ+ B-cells were identified based on high intracellular and granular FITC-PNA staining and intracellular IgZ staining, respectively (two fishes per acquisition). (A) Percentage of NP-positive cells, for each phagocyte type, relative to the total number of cells (left) or of NP-positive cells (right). APCs, which represent less than 4% of total cells in gills, represent over 25% of NP-positive cells altogether, among which DCs show the most important enrichment. (B) Percentage of NP-positive cells within each cell type. A high majority of DCs are positive to PLA-NPs. (C) NP signal intensity per cell relative to the mean fluorescence of all NP-positive cells. DCs and macrophages internalize more NPs than average. (D) NP signal spot count per cell. DCs display more signal foci than average. (E–H) Representative images of neutrophils (E), NP-positive macrophages (F), DCs (G), and IgZ+ cells (H). Error bars: SD. Significance level is indicated as: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. |