Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-171228-47
- Publication
- Rességuier et al., 2017 - Specific and Efficient Uptake of Surfactant-Free Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanovaccine Vehicles by Mucosal Dendritic Cells in Adult Zebrafish after Bath Immersion
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
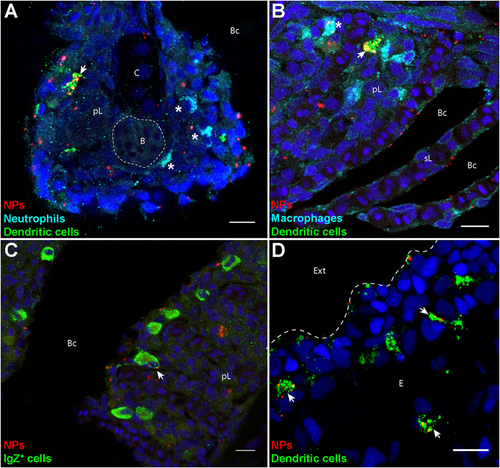
Poly(lactic acid) nanoparticles (PLA-NPs) are accumulated in mucosal antigen-presenting cells. (A–D) Representative confocal images of gills (A–C) and skin (D) of wild-type adults immersed for 24 h in 0.01% fluorescent PLA-NPs (red). Images were acquired from 40-μm-thick whole-body cryosections, stained for neutrophils (Mpx-positive, cyan) (A), macrophages (Mpeg1-positive, cyan) (B), IgZ+ B-cells (green) (C), and dendritic cells (DCs) (PNA, green) (A,B,D), in addition to nuclei (DAPI, blue). Maximal intensity projections from 3 (A–C) or 5 (D) optic sections acquired every micrometer. Nanoparticle (NP) accumulations are observed in gill DCs [(A,B), arrows], macrophages [(B), star], and IgZ+ cells [(C), arrow], while no NP are detected in neutrophils [(A), stars]. NPs are also taken up by a network of skin DCs [(D), arrows]. pL, primary lamellae; sL, secondary lamellae; Bc, branchial cavity; B, blood; C, cartilage; Ext, external environment; E, epidermis. Scale bar: 10 μm. |