- Title
-
Retinal neurogenesis: the formation of the initial central patch of postmitotic cells
- Authors
- Hu, M. and Easter, Jr., S.S.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
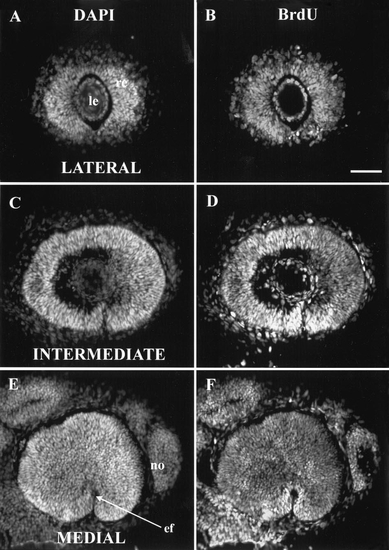
At 27 hpf, all retinal cells were synthesizing DNA. 27 hpf injection of BrdU, 41 hpf sacrifice. Three sagittal sections at the levels (lateral, intermediate, and medial) described in the text. In this and subsequent figures, all eyes are shown as right eyes viewed laterally; that is, dorsal is up and nasal (anterior) is to the right. (A, C, E) All stained with DAPI to show all nuclei; (B, D, F) all stained with anti-BrdU to show those nuclei synthesizing DNA between 27 and 41 hpf. In both the lens and the nose, some nuclei are labeled with DAPI but not BrdU, so they had ceased DNA synthesis prior to 27 hpf. No such cells were found in the retina. Abbreviations: ef, embryonic fissure; le, lens; no, nose. Calibration: 40 μm. |
|
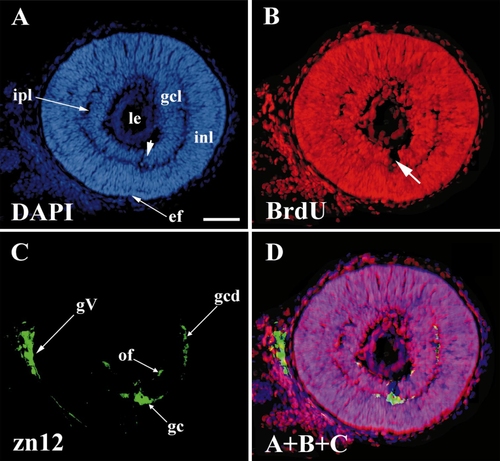
The first postmitotic retinal cells appeared at 28 hpf in ventronasal retina, and included the first ganglion cells. 28 hpf BrdU, 42 hpf sacrifice. All panels show the same (intermediate) section, stained as indicated. (A) DAPI staining shows all nuclei. (B) BrdU staining shows those (unlabeled) nuclei that had ceased DNA synthesis before 28 hpf. (C) zn12 stain shows early neurons in the retina and the trigeminal ganglion. (D) A merger of A, B, and C to show that the early ganglion cells (zn12-positive) lie in the BrdU-negative cells adjacent to the embryonic fissure. Abbreviations: as in Fig. 1, gc, ganglion cells; gcd, ganglion cell dendrites; gcl, ganglion cell layer; gV, trigeminal ganglion; inl, inner nuclear layer; ipl, inner plexiform layer; of, optic fibers. Calibration: 40 μm. |
|
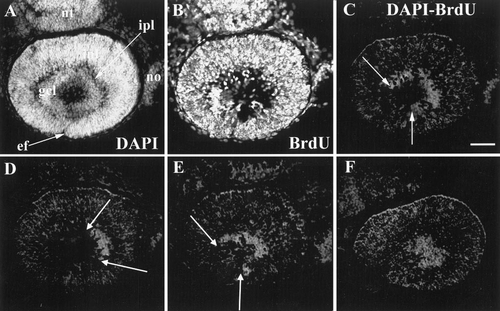
The patch of ganglion cells advanced around the embryonic fissure in an arc, beginning in ventronasal retina. 31 hpf BrdU, 41 hpf sacrifice. A and B are the same section, stained as indicated. (C) Difference image of A and B, showing the arc of unlabeled cells in the ganglion cell layer, the two borders indicated by arrows. (D, E, and F) Similar difference images (DAPI and BrdU) from adjacent sections from this same retina to show that the unlabeled cells extend into lateral (D) and more medial (E, F) sections to form a disk of unlabeled cells. Abbreviations: as in Figs 1 and 2; nt, neural tube. Calibration: 40 μm. |
|
A circle of ganglion cells. 37 hpf BrdU, 51 hpf sacrifice. A and B stained as indicated. (C) Difference image shows a nearly complete circle of BrdU-negative cells with the ventronasal and ventrotemporal edges separated by a thin row of proliferative (BrdU-positive) cells that mark the embryonic fissure. Abbreviations: as in Figs 1–3. Calibration: 40 μm. |
|
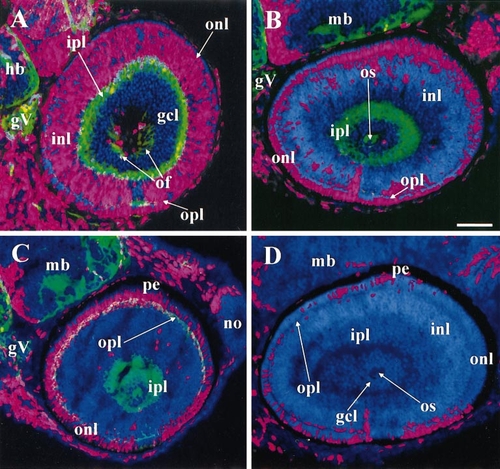
The ventronasal retina was the most precocious region for both inner and outer nuclear layers as well as the ganglion cell layer. All panels labeled with DAPI (blue), BrdU (red), and (except for D) zn12 (green). (A) 38 hpf BrdU, 52 hpf sacrifice. A patch of BrdU-negative cells appears in ventronasal retina with abundant zn12 labeling in the adjacent outer plexiform layer, evidence for precocious birthdates and differentiation. (B) 43 hpf BrdU, 57 hpf sacrifice. Most of the inner nuclear layer is BrdU-negative. (C) 48 hpf BrdU, 62 hpf sacrifice. A patch of BrdU-negative cells has now appeared in ventronasal retina adjacent to the most heavily zn12-positive patch of the outer plexiform layer, evidence for precocious birthdates and differentiation. (D) 54 hpf BrdU, 68 hpf sacrifice. No zn12 staining. The outer nuclear layer contains BrdU-negative cells everywhere, but small patches of BrdU-positive cells remain, disconnected with one another. For this reason, a summary drawing, such as the one in Fig. 6, cannot be made for the INL and ONL. Abbreviations: as in Figs. 1–6, hb, hindbrain; mb, midbrain; pe, pigmented epithelium. Calibration: 40 μm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 207, Hu, M. and Easter, Jr., S.S., Retinal neurogenesis: the formation of the initial central patch of postmitotic cells, 309-321, Copyright (1999) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.