- Title
-
TBK1 is involved in programmed cell death and ALS-related pathways in novel zebrafish models
- Authors
- Raas, Q., Haouy, G., de Calbiac, H., Pasho, E., Marian, A., Guerrera, I.C., Rosello, M., Oeckl, P., Del Bene, F., Catanese, A., Ciura, S., Kabashi, E.
- Source
- Full text @ Cell Death Discov
|
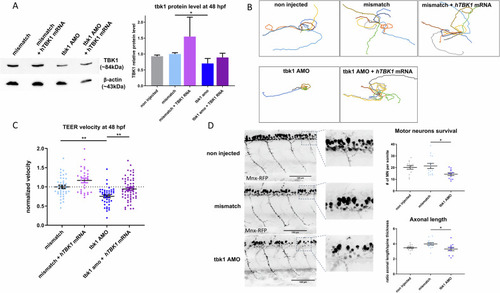
Motor behavior and motor neuron phenotype induced by tbk1 knockdown in zebrafish larvae. |
|
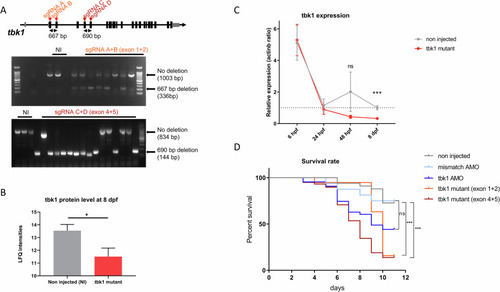
Tbk1 expression and survival in zebrafish larvae with CRISPR-induced deletion of the tbk1 gene. |
|
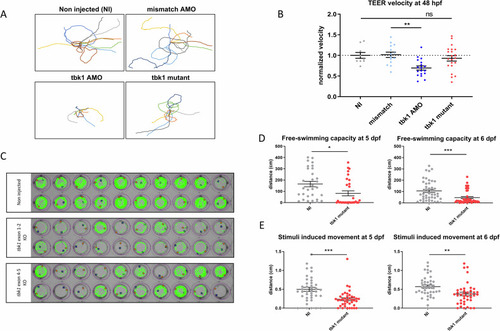
Motor behavior of tbk1 mutant zebrafish larvae. |
|
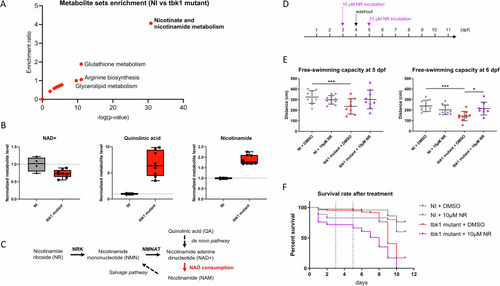
Metabolomic analysis and nicotinamide riboside treatment of tbk1 mutant zebrafish. |
|
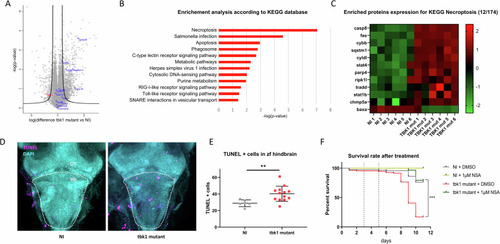
Proteomic profile and markers of programmed cell death in tbk1 mutant zebrafish. |
|
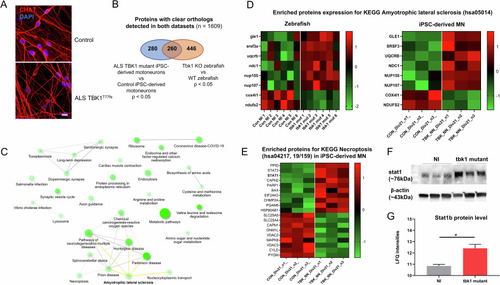
Joint proteomic analysis of tbk1 mutants zebrafish and iMNs from ALS patients with TBK1 mutations. |