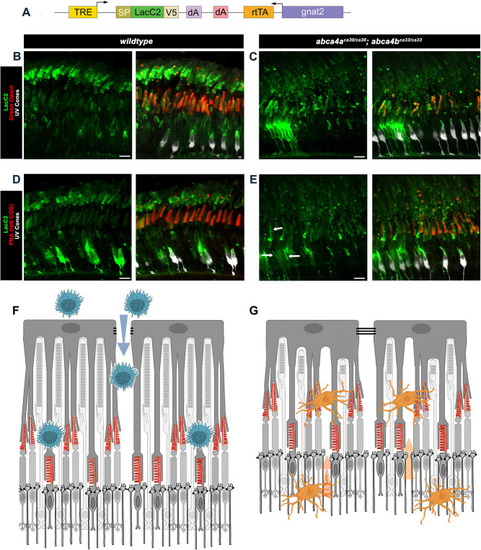
In vivo labeling of externalized phosphatidylserine. (A) Schematic of the doxycycline (DOX)-responsive V5-epitope-tagged LacC2V5 phosphatidylserine (PS)-sensitive DNA construct that was injected into single-cell wild-type or abca4ca30/ca30;abca4bca33/ca33 embryos. TRE, tetracycline response element; SP, signal peptide; gnat2, gnat2 promoter sequence; rtTA, reverse tetracycline-controlled transactivator; dA, polyA sequence. (B-E) Confocal z-projection (z=4.4 µm) images showing the photoreceptor layer in 4-month-old wild-type (B,D) or abca4ca30/ca30;abca4bca33/ca33 mutant (C,E) fish that had been treated with doxycycline for 7 days, and co-labeled for V5 (LacC2, green) and Green Opsin (red) or V5 (LacC2, green) and PNA (red) as indicated. EGFP-expressing UV cones are shown in white. (A-E) Very brightly labeled cells have incorporated the transgene, and make and secrete LacC2 protein. In the wild-type retina, LacC2 labeling smoothly coats the surface of COS and in ROS forms distinct stripes beginning at the ROS base. In the abca4a−/−;abca4b−/− double mutant retina, LacC2 labeling in COS is disrupted, with the appearance of puncti and stripes of LacC2 labeling (examples indicated by arrows in E), and ROS labeling appears less intense. Scale bars: 10 µm. (F) Schematic of how loss of RPE tight-junction (TJ) integrity in retinal degeneration diseases, like AMD, might allow macrophage (blue) infiltration, and how recognition of COS-externalized PS (indicated in red) could result in COS attack. (G) Schematic of how disruption of the outer limiting membrane (OLM) − which is formed by adherens junctions between Müller glia and photoreceptors, in retinal rod degeneration diseases, like retinitis pigmentosa − could allow microglial (orange) infiltration and recognition of the phagocytic ‘eat-me’ signal of externalized PS on COS, resulting in COS attack.
|