- Title
-
Comparative analysis between zebrafish and an automated live-cell assay to classify developmental neurotoxicant chemicals
- Authors
- St Mary, L., Truong, L., Bieberich, A.A., Fatig, R.O., Rajwa, B., Tanguay, R.L.
- Source
- Full text @ Tox. App. Pharmacol.
|
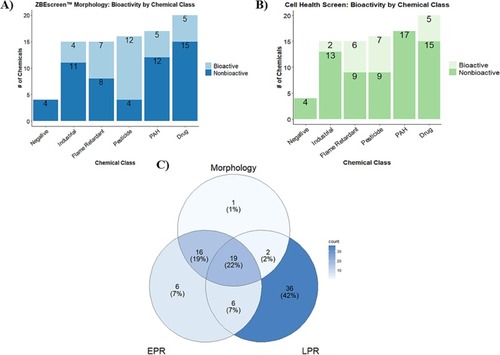
Bioactivity across the SYSTEMETRIC® Cell Health Screen and the ZBEscreen™. Bar plots of DNT chemical library bioactivity as identified by A) ZBEscreen™ mortality/morphological assessments and B) CHI™ categorized by chemical class C) Venn diagram of bioactivity across the morphological and behavioral (EPR and LPR) assessments of the DNT chemical library in the ZBEscreen™. |
|
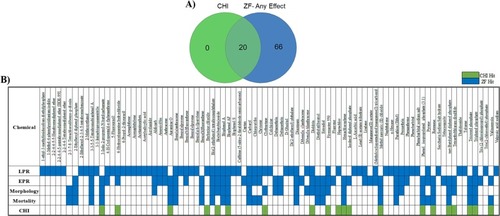
Concordance between the SYSTEMETRIC® Cell Health Screen and ZBEscreen™. A) Venn diagram showing the number of bioactive chemicals between the ZBEscreen™ and SYSTEMETRIC® CHS B) Distribution of CHI™ bioactives and ZBEscreen™ endpoints across the 87 DNT chemical library where the zebrafish endpoints were separated by mortality, morphology, and the behavioral assessments EPR and LPR (green indicates bioactivity identified by CHI, blue indicates bioactivity identified by any of the 4 zebrafish readouts). Likewise, DNT chemicals not identified through the CHI™ classification were detected by the ZBEscreen™, demonstrating the complementarity between the systems used in tandem. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) |
|
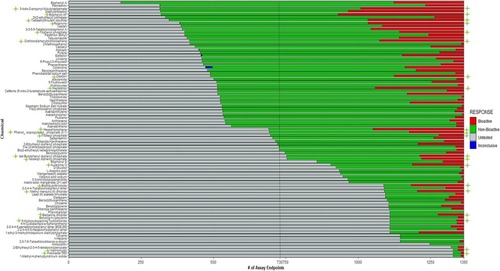
Hit call distribution of 87-DNT chemical library among 1365 in vitro assays from the EPA CompTox Dashboard. The black dashed line indicates the average number of untested assays across all 87 chemicals, and the green stars indicate CHI™ bioactive chemicals. Among available in vitro data, 9 CHI™ chemicals were undertested (49 of the chemical library), and 11 CHI™ chemicals were thoroughly tested (36 of the chemical library). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) |
|
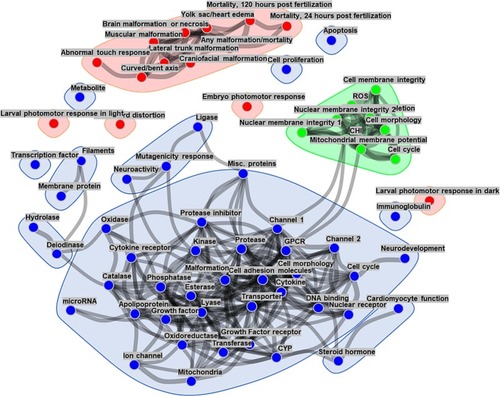
Correlation network representation of assay endpoints from CHS, ZBEscreen™, and the EPA's CompTOX dashboard. Correlation analyses and clustering of the network vertices showed the formation of distinct groups of assay endpoints. Blue points are assay endpoints curated within CompTOX, red and green points represent endpoint readouts from the ZBEscreen™ and CHS, respectively. The edges indicating correlations with absolute value <0.5 are not shown. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) |
|
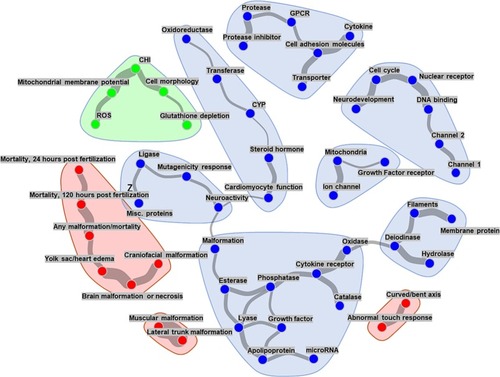
Links between the distinct physiological subsystems tested. The graphical network model shows each assay readout as a node in a graph, and edges between nodes represent conditional dependencies between assays' endpoints. The presence and line thickness show the strength of these dependencies (a thicker line indicates stronger association). For the sake of clarity, readouts without corresponding edges are omitted from the network. The blue points indicate CompTOX-curated assay endpoints, whereas the red and green points represent ZBEscreen™️ and CHS endpoint readouts, respectively. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) |