- Title
-
Hepatocyte growth factor mimetic confers protection from aminoglycoside-induced hair cell death in vitro
- Authors
- Uribe, P.M., Hudson, A.M., Lockard, G., Jiang, M., Harding, J., Steyger, P.S., Coffin, A.B.
- Source
- Full text @ Hear. Res.
|
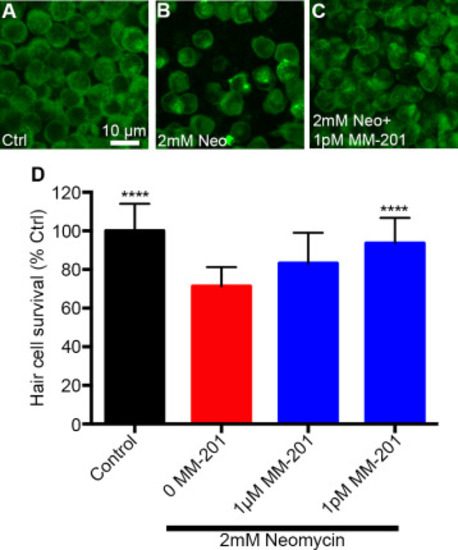
MM-201 protects mouse utricular hair cells from neomycin exposure in vitro. (A-C) Representative images of utricular extrastriolar hair cell densities from explants treated with (A) control culture medium, (B) 2 mM neomycin, or (C) 2 mM neomycin plus 1 pM MM-201. Scale bar applies to all three images. (D) 1 pM of MM-201 robustly protects utricular hair cells from neomycin exposure whereas 1 µM does not exhibit significant protection (One-way ANOVA: F3,38=10.68 p<0.0001). Asterisks indicate significant difference from 2 mM neomycin treated group (****p<0.001). N = 4–6 utricular explants per treatment, error bars represent + s.d. |
|
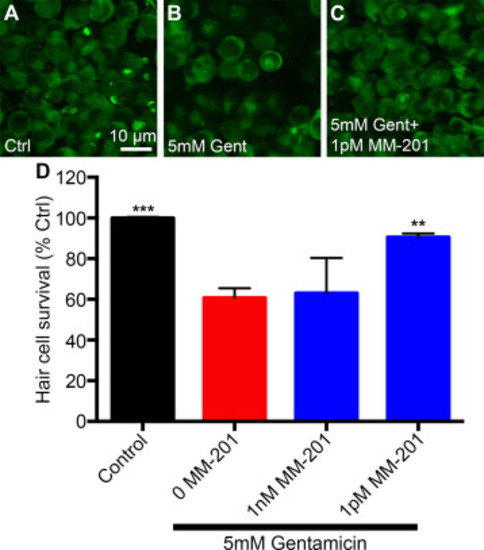
Co-treatment with MM-201 protects utricular hair cells from gentamicin exposure in vitro. (A-C) Representative extrastriolar images of (A) untreated, (B) 5 mM gentamicin, or (C) 5 mM gentamicin plus 1 pM MM-201 treated utricles. (D) 1 pM MM-201 robustly protects utricular explant hair cells from gentamicin exposure (One-way ANOVA: F3,7 = 19.38 p = 0.0009). Asterisks indicate significant difference from gentamicin-exposed group (**p<0.01). N = 2–4 utricular explants per treatment, error bars represent + s.d. |
|
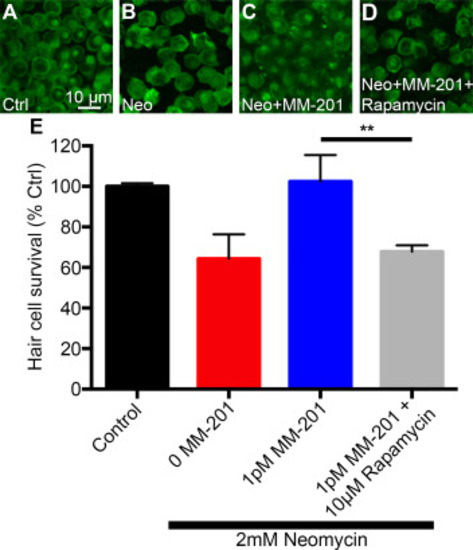
MM-201 mediated protection is dependent on mTOR signaling. (A-D) Representative images of (A) untreated, (B) 2 mM neomycin, (C) 2 mM neomycin plus 1 pM MM-201, or (D) 2 mM neomycin plus 1 pM MM-201 and 10 µM rapamycin-treated utricles. (E) Protection from neomycin conferred by 1 pM MM-201 is attenuated with co-treatment of the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (One-way ANOVA: F3,7 = 12.56 p = 0.0033). Asterisks indicate significant difference between the 2 mM neomycin plus 1 pM MM-201 group and the 2 mM neomycin plus 1 pM MM-201 and 10 µM rapamycin group (**p<0.01). N = 2–3 utricular explants per treatment and error bars represent + s.d. |
|
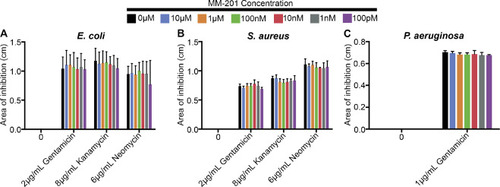
MM-201 does not alter the bactericidal activity of gentamicin, kanamycin, or neomycin as measured by the Kirby-Bauer Assay. (A) Co-treatment with one of a range of MM-201 concentrations (100 pM-10 µM) does not alter the area of inhibited E. coli growth surrounding the treatment-soaked disk (Two-way ANOVA; MM-201: F6, 139=0.7523 p = 0.6086). (B) MM-201 does not alter bactericidal activity of gentamicin, kanamycin, or neomycin against S. aureus (Two-way ANOVA; MM-201: F6,56=0.5474 p = 0.7699). (C) MM-201 does not alter bactericidal activity of gentamicin against P. aeruginosa (Two-way ANOVA; MM-201: F6,28=0.7975 p = 0.5800). N = 6 disks per treatment, and error bars represent + s.d. |
|
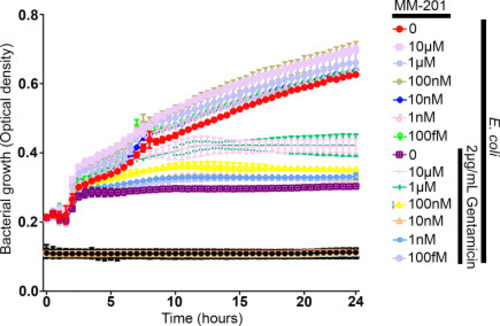
MM-201 does not alter bacterial liquid growth curves at therapeutically relevant concentrations of MM-201. Co-treatment with one of a range of MM-201 concentrations (100 fM-100 nM) plus 2 µg/mL gentamicin exhibit similar bacterial growth curves as 2 µg/mL gentamicin alone. MM-201 concentrations of 1 µM and 10 µM exhibit modest attenuation of gentamicin bactericidal activity. N = 3 replicates per treatment. |
|
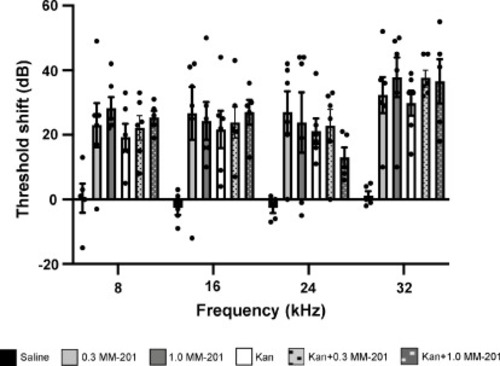
MM-201 does not alter aminoglycoside-induced threshold shifts in mice. Animals were treated with 0, 0.3, or 1 µg/ml MM-201 with or without kanamycin. Threshold shift was calculated as the post-treatment minus the pre-treatment threshold for each animal. There is a significant effect of both treatment (F5,112=16.77, p<0.0001) and frequency (F3,112=5.847, p = 0.001) (2-way ANOVA), but this effect manifests as differences between saline-treated controls and each of the other groups. Each black dot denotes the threshold shift for each individual animal. N = 5–6 animals/group (2–3 per sex) and error bars represent ± s.e.m. |
Reprinted from Hearing Research, 434, Uribe, P.M., Hudson, A.M., Lockard, G., Jiang, M., Harding, J., Steyger, P.S., Coffin, A.B., Hepatocyte growth factor mimetic confers protection from aminoglycoside-induced hair cell death in vitro, 108786108786, Copyright (2023) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Hear. Res.