- Title
-
Egfl7 knockdown causes defects in the extension and junctional arrangements of endothelial cells during zebrafish vasculogenesis
- Authors
- De Mazière, A., Parker, L., Van Dijk, S., Ye, W., and Klumperman, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
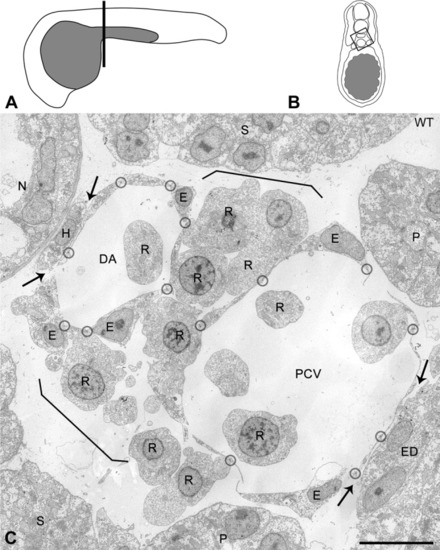
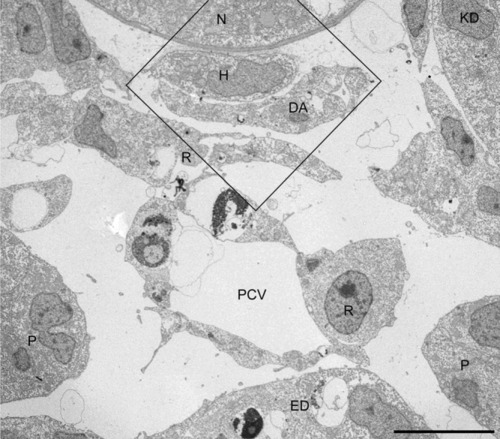
Cellular organization of the axial vascular area in the trunk of a 24 hours postfertilization (hpf) control embryo, viewed in cross-section. A: Scheme of a 24 hpf embryo with the position (line) of cross-sections. B: Scheme of a cross-section. Box: area analyzed by electron microscopy (EM). C: Axial vascular area of control (WT) embryo. Characteristically, the most dorsal endothelial cells (ECs) of the dorsal aorta (DA) are intimately associated with the hypochord (H), whereas the ventral part of the posterior cardinal vein (PCV) is associated with the endoderm (ED; arrows). Note that the extremely flattened ECs of the DA and PCV are connected by tiny contact zones (encircled), containing tight junctions and sometimes a desmosome or gap junction (see higher magnification in Fig. 2). Cells with morphological characteristics of red blood cell precursors (R) are observed in the vessel lumens and form a layer (between brackets) in between DA and PCV. E, nucleus of EC; N, notochord; P, pronephric duct; S, somite. Scale bar = 10 μm. |
|
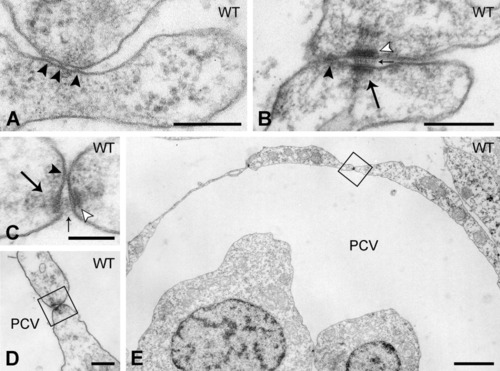
Endothelial cell-cell interactions in the axial vessels in the trunk of control embryos. A,B: Representative high magnification images of endothelial cell-endothelial cell (EC-EC) contact zones containing (A) only a tight junction consisting of a few plasma membrane fusion points (arrowhead), or (B) a tight junction (arrowhead) flanked by a desmosome (arrow). Note the tiny densities on the intercellular filamentous material at the central plane (small arrows) and the well-delineated dense plaques apposed to the plasma membranes (open arrowheads). C-E: EC-EC contact zone with tight junction (arrowhead) and desmosome (arrow), enlarged from boxed areas in D and E, showing the location of the desmosome between posterior cardinal vein (PCV) -ECs at a position luminal from the tight junction. Scale bars = 200 nm in A,B,D; 100 nm in C; 2 μm in E. |
|
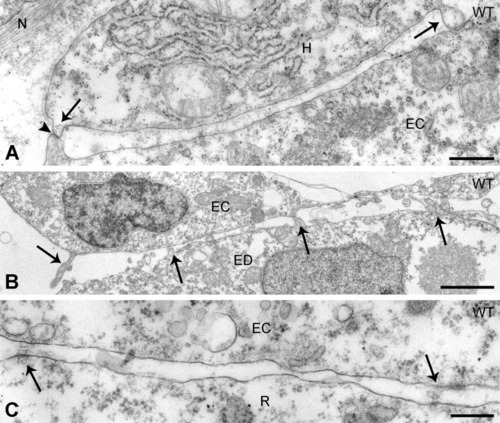
Heterologous cell interactions in the axial vascular area in the trunk of control embryos. A,B: Contact zone of dorsal aorta-endothelial cells (ECs) with the hypochord (A) and (B) of posterior cardinal vein-ECs with the endoderm. In both A and B, the cells contact each other by means of cellular extensions (arrows) approaching the opposed cell to a minimal distance. Arrowhead in A, gap junction. C: Between ECs and red blood cell precursors, deposits of extracellular material (arrows) are present at irregular distances. ED, endoderm; H, hypochord; N, notochord sheath; R, red blood cell precursor. Scale bars = 500 nm in A, 2 μm in B, 200 nm in C. |
|
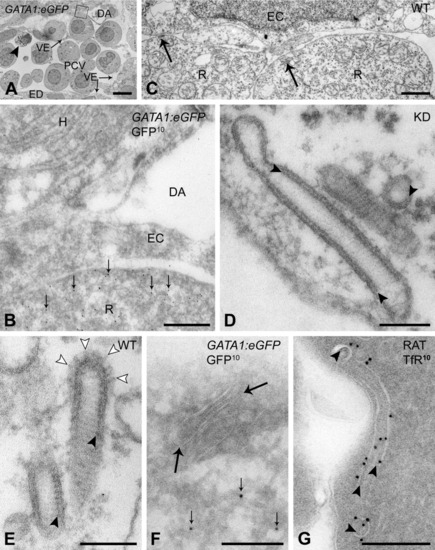
Characteristic striated tubules are exclusively found in red blood cell precursors. A,B,F,G: Ultrathin cryosections. C-E: Epon sections. A: Axial vascular area of 24 hours postfertilization (hpf) GATA1:eGFP transgenic embryo, labeled for green fluorescent protein (GFP). Arrowhead, apoptotic cell. B: Higher magnification of area boxed in A. Red blood cell precursor located between dorsal aorta (DA) and posterior cardinal vein (PCV), and identified by labeling with anti-GFP antibodies (10-nm gold particles, GFP10, small arrows). C-E: Characteristic tubules (arrows) near the plasma membrane of red blood cell precursors in control (C,E) and Egfl7 knockdown (D) embryos display regular cross-striations and an inner coating (arrowheads) of the limiting membrane. Open arrowheads, clathrin coat. F: Striated tubules (arrows) with electron-dense inner coating inside the electron-lucent limiting membrane colocalize with GFP label (10-nm gold particles, GFP10, small arrows) in red blood cell precursors of GATA1:eEGFP transgenic embryos. G: Rat bone marrow erythroblast. Intracellular tubules with inner coating (arrowheads), resembling zebrafish striated tubules, are labeled with 10-nm gold particles for transferrin receptor (TfR10). EC, endothelial cell; ED, endoderm; H, hypochord; R, red blood cell precursor; VE, venous endothelium. Scale bars = 5 μm in A, 0.5 μm in B, 1 μm in C, 100 nm in D,E, 200 nm in F,G. |
|
Altered positions of endothelial cells (ECs) in the axial vascular area of the trunk of Egfl7 KD embryos at 24 hours postfertilization (hpf). Cross-section of the vascular area. Dorsal aorta (DA), without lumen, and irregularly shaped posterior cardinal vein (PCV) are still associated with hypochord and endoderm, respectively. The box is enlarged in Figure 6. ED, endoderm; H, hypochord; N, notochord; P, pronephric duct; R, red blood cell precursor. Scale bar = 10 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
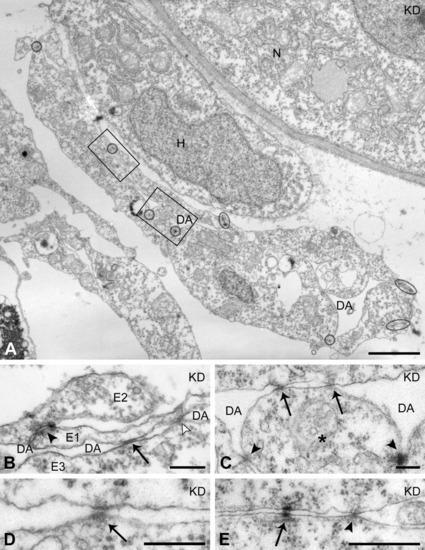
Altered positions of endothelial cell-endothelial cell (EC-EC) cell junctions in the axial vascular area of the trunk of Egfl7 knockdown (KD) embryos at 24 hours postfertilization (hpf). A: Higher magnification of dorsal aorta (DA) boxed in Figure 5. ECs are linked by tight junctions (encircled) and form a flattened, ring-like endothelium. Ectopic cell-cell junctions (boxes) are positioned within the luminal EC plasma membranes, crossing the obliterated vessel lumen. B,C: Higher magnifications of the ectopic cell junctions in the boxed areas of A. B: From a section consecutive to the section shown in A. A dorsally located EC (E1) is connected to another dorsal EC (E2) by a regular tight junction (arrowhead), and across the collapsed vessel lumen (DA) to a ventrally located EC (E3) by an aberrantly positioned gap junction (arrow) and a tight junction (open arrowhead). C: An EC (*) is linked by regular tight junctions to its lateral neighbors (arrowheads) and by two aberrantly positioned tight junctions (arrows) to an EC at the opposite side of the vessel. D: Example of an ectopic adherens junction (arrow) linking the luminal plasma membrane domains of opposed ECs in the DA. E: Tight junction (arrowhead) and desmosome (arrow) linking the basal plasma membrane domains of ECs. H, hypochord; N, notochord. Scale bars = 2 μm in A, 200 nm in B-D; 500 nm in E. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
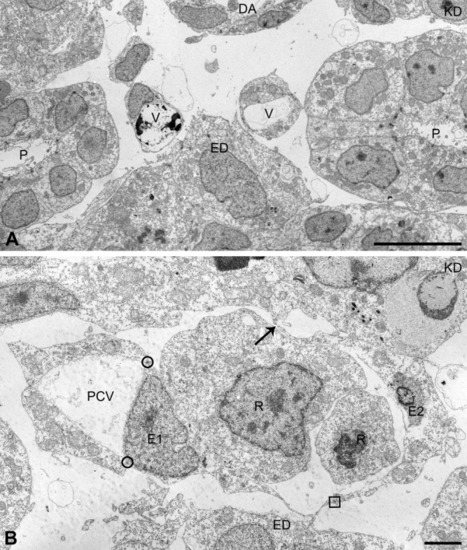
Aberrant endothelial cell (EC) arrangements, different from vessel lumen obliteration, in the axial vascular area of the trunk of Egfl7 KD embryos at 24 hours postfertilization (hpf). In addition to reduced vessel lumens caused by cross-luminal EC-EC junctions, other types of structural defects were found in Egfl7 knockdown (KD) embryos. A: Example of a posterior cardinal vein (PCV) that splits into two small vessels, each associated with the endoderm. B: Example of a PCV with a small lumen and attached loose-ending (arrow) EC sheet. The EC denoted as E1 is arranged in the PCV endothelium by means of two normally positioned tight junctions (circles), and attached to the loose EC sheet (E2) by means of an aberrantly positioned tight junction (square) within the basal plasma membrane of E1. ED, endoderm; P, pronephric duct; R, red blood cell precursor; V, vein. Scale bars = 10 μm in A, 2 μm in B. PHENOTYPE:
|

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|