Fig. EV1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250131-1
- Publication
- Ten Martin et al., 2024 - Tubulin glutamylation regulates axon guidance via the selective tuning of microtubule-severing enzymes
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
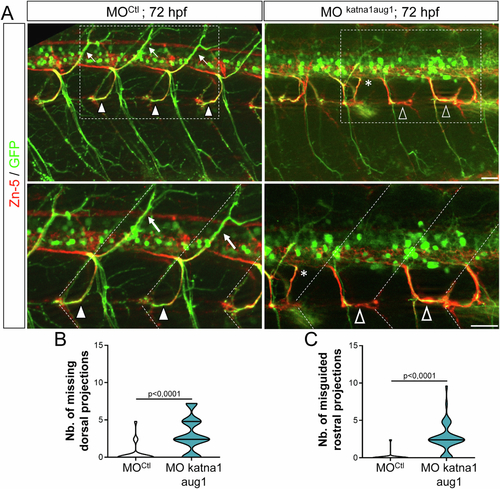
p60-katanin knockdown with MOkatna1aug1 morpholino induces similar spinal motor axon defects to MOp60Kat morpholino. (A) Immunolabelling of secondary motoneuron (sMN) axon tracts in 72 h post-fertilisation (hpf) transgenic Tg(Hb9:GFP) larvae injected with control (n = 40) or MOkatna1aug1 (n = 40) morpholinos, using Zn-5 and GFP antibodies. Lateral views of the trunk, anterior to the left. Bottom panels represent higher magnifications of the boxed region in the corresponding top panels. Dotted lines delineate lateral myosepta. Full arrowheads and full arrows point at normal rostral and dorsal nerves, respectively. Empty arrowheads show misguided rostral nerves. Asterisks indicate ectopic sorting points of sMN axons from the spinal cord. (B, C) Quantifications of sMN defects in larvae analysed in panel A and pooled from three independent experiments. Mean number of missing dorsal nerves (B) and misguided rostral nerves (C) per larva. Non-blind quantifications were performed on 24 spinal hemisegments located around the yolk tube per larva. Violin Plots; horizontal bars indicate the median ± the 1st and 3rd quartiles. Mann–Whitney test. P values are displayed on graphs. Source data are available online for this figure. |