Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-231121-49
- Publication
- Ketkar et al., 2023 - Conservation of the insert-2 motif confers Rev1 from different species with an ability to disrupt G-quadruplexes and stimulate translesion DNA synthesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
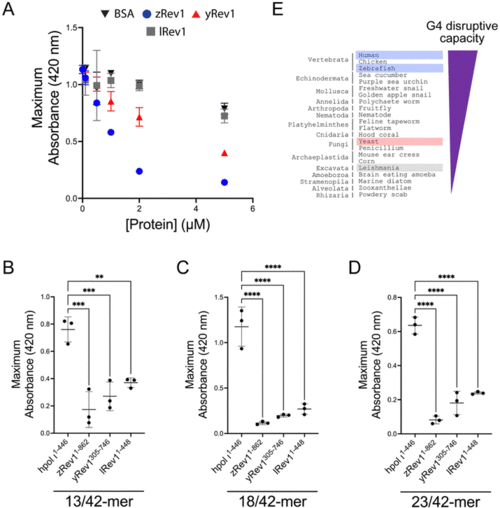
The presence of insert-2 increases the G4 disruptive capacity of Rev1. (A) The maximum absorbance at 420 nm was plotted as a function of protein concentration for reactions where G4-forming Myc 14/23 ss-DNA (1 μM) oligonucleotide was incubated with either BSA (black inverted triangles), zRev11-862 (blue circles), yRev1305-746 (red triangles), or lRev11-448 (gray squares). (B) The maximum absorbance at 420 nm was measured for reactions where 13/42-mer DNA with the Myc 14/23 G4 motif in the template strand (1 μM) was incubated with 5 μM of the indicated proteins. (C) The maximum absorbance at 420 nm was measured for reactions where 18/42-mer DNA with the Myc 14/23 G4 motif in the template strand (1 μM) was incubated with 5 μM of the indicated proteins. (D) The maximum absorbance at 420 nm was measured for reactions where 23/42-mer DNA with the Myc 14/23 G4 motif in the template strand (1 μM) was incubated with 5 μM of the indicated proteins. (E) Based on the results of the G4 hemin DNAzyme assay, the relative G4 disruptive capacity increased when moving across the tree of life from excavata through fungi to vertebrates. Results shown in panels (A–D) represent the mean (± std. dev.) for three replicates. p-Values in panels (B–D) were calculated using an ordinary one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett's multiple comparisons test where ** = p-value < 0.01, *** = p-value < 0.001, and **** = p-value < 0.0001. |