Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-231121-46
- Publication
- Ketkar et al., 2023 - Conservation of the insert-2 motif confers Rev1 from different species with an ability to disrupt G-quadruplexes and stimulate translesion DNA synthesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
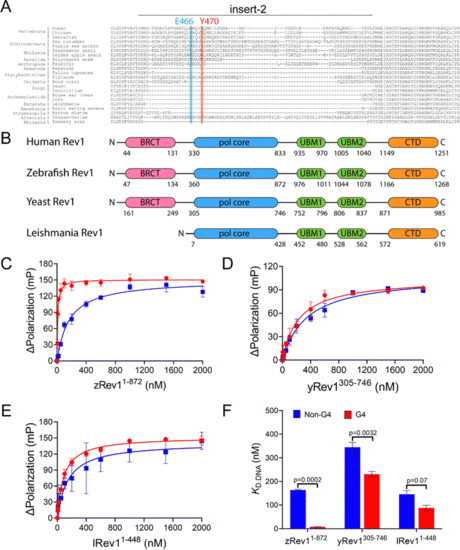
Comparison of G4 binding properties for Rev1 proteins from different species. (A) The sequence alignment of the insert-2 region for Rev1 proteins ranging from the SAR supergroup through vertebrata is shown. (B) A schematic illustration of domain arrangement and conservation is shown for the four Rev1 proteins used in this study. Binding curves for (C) zRev11-872 (D) yRev1305-746, and (E) lRev11-448 proteins with either the Myc 14/23 G4 DNA substrate (red circles) or non-G4 DNA control (blue squares) are shown. Protein was titrated into a solution containing either single-stranded (ss)-G4 DNA or ss-non-G4 DNA substrates at a concentration of 2 nM. The range of concentrations for the protein is indicated on the X-axis. The change in fluorescence polarization at each concentration was measured and plotted as a function of the protein concentration. (F) The changes in fluorescence polarization were fit to a quadratic equation to yield binding dissociation constants. The actual KD,DNA estimates are reported in Table 2. Values reported here represent the mean (± std. dev.) for three independent replicates. The reported p-values were calculated by using an unpaired Student's t-test with Welch's correction. |