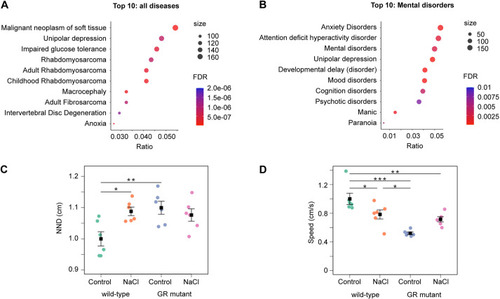
The glucocorticoid receptor regulates depression-associated genes in adult zebrafish brain and stress-responsive locomotor behaviour in zebrafish larvae. (A) Enrichment analysis to identify diseases associated with human orthologues of GR-regulated genes by using the disgenet2r package to search the DisGeNET database. Human orthologues of zebrafish genes exhibiting significant differential expression in wild-type and GR-mutant adult brain samples were analysed using all data available in this database. A total of 678 diseases, symptoms and syndromes are significantly associated with orthologues of GR-regulated zebrafish genes; an adjusted false discovery rate (FDR) cut-off of P<0.05 was used (Table S6). The top ten diseases were selected based on FDR and then ranked according to the gene ratio. Unipolar depression ranked second after malignant neoplasm of soft tissue. (B) The top ten diseases within the Mental Disorders category of the DisGeNET database were identified using the disgenet2r package, selected based on FDR and then ranked according to the gene ratio. Anxiety disorders ranked first and unipolar depression fourth. (C,D) Group swimming analysis of zebrafish larvae at 5 days post fertilization under baseline and stressed conditions for nearest neighbour distance (NND) and swim speed. Panel C shows that the NND of wild-type groups increases under stress, whereas mutant groups have a higher NND than wild-type groups under baseline conditions and their NND is not affected by stress [two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc test; genotype: treatment interaction, F=8.09, d.f.=1, 20 (P=0.01)]. Panel D shows that the swimming speed of wild-type groups is reduced under saline stress (NaCl), whereas GR-mutant groups swim slower than wild-type fish under baseline conditions and their swim speed is not affected by NaCl-induced stress [two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc test; genotype: treatment interaction, F=14.41; d.f.=1, 20 (P=0.001)]. Wild-type and GR-mutant groups (both n=12) across two independent experiments. Plots show the mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
|