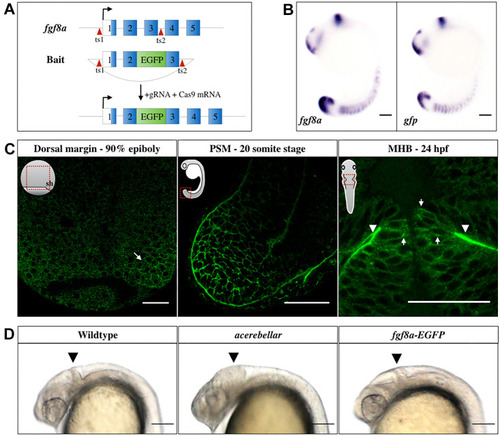
Generation and characterization of the Tg(fgf8a:fgf8a-EGFP) fish line. (A) Knock-in strategy: EGFP was inserted between exons 2 and 3 of the endogenous Fgf8a locus using CRISPR/Cas9. Exon sequences are shown as numbered blocks, separated by introns. The open reading frame sequence is in blue. Red arrowheads indicate the sgRNA target sites (ts). (B) In situ hybridization against fgf8a and gfp in 16-somite stage (ss) embryos. Scale bars: 100 μm. (C) Fgf8a-EGFP fluorescence in the dorsal embryonic margin (arrow) at late gastrula, PSM at 20 ss, as well as at the basal (arrowheads) and lateral (arrows) sides of the MHB neuroepithelia 24 h post fertilization (hpf). Orientations of embryos are shown schematically in insets. Red rectangles outline the locations imaged. sh, shield. Scale bars: 50 μm. (D) Comparison of homozygous fgf8a-EGFP with wild type and homozygous ace mutants at 24 hpf. Homozygous viability and normal structure of the MHB (arrowhead) in the fgf8a-EGFP transgenics confirms the functionality of the fgf8a-EGFP knock-in line. Lateral views are shown. Scale bars: 100 μm.
|

