Figure 2.
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-231002-64
- Publication
- Gao et al., 2023 - Sensory deficit screen identifies nsf mutation that differentially affects SNARE recycling and quality control
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
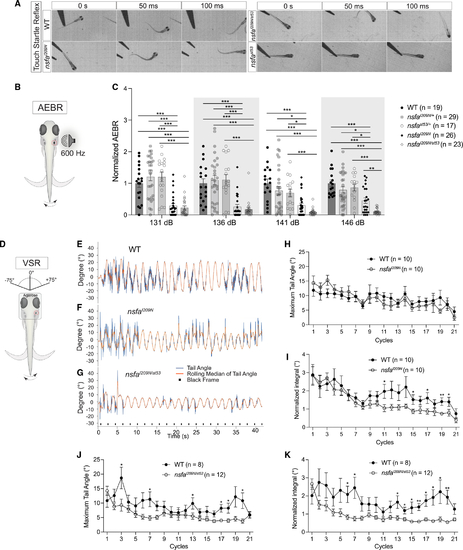
The I209N mutation in Nsfa selectively affects hearing and vestibular function without causing paralysis (A) Still frames from high-speed videos of larvae. (B) (B and C) Acoustic evoked behavioral responses of larvae exposed to a 600-Hz stimulus at the intensities indicated normalized to homozygous WT siblings. n indicates number of fish tested. (D–K) Vestibulospinal reflexes are reduced in Mean ± SEM and two-way ANOVA with Benjamini-Hochberg correction for each dataset were performed. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 5 |