Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150824-6
- Publication
- Crucke et al., 2015 - The innervation of the zebrafish pharyngeal jaws and teeth
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
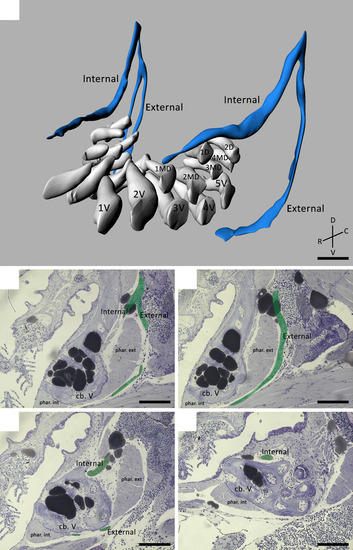
(A) 3D visualization of a 9.5 mm SL zebrafish dentition demonstrating the main nerve branches (blue) in the vicinity of the developing teeth (white). The internal and external branches emerge from a common stem on the postero-dorsal side of the dentition. Note that the internal branch is split up in two bundles on one body side. The teeth are organized in a ventral (1V–5V), mediodorsal (1MD–4MD) and dorsal (1D–2D) row. (B–E) Consecutive sagittal toluidine blue-stained sections of a wild-type zebrafish (SL = 8.3 mm) showing how the internal and external branch (pseudocoloured green) course in relation to both internal and external pharyngoclavicularis muscles (phar. int./ phar. ext.), and the fifth ceratobranchials (cb. V). The external branch extends ventrally and bends in a medial direction along the ventral side of the dentition. The internal branch on the other hand, bends medially almost instantly thus running along the dorsal side of the dorsal tooth row. C, caudal; D, dorsal; R, rostral; V, ventral. Scale bars: 50 µm (A); 100 µm (B–E). |