FIGURE
Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150413-6
- Publication
- Banerjee et al., 2015 - Zebrafish foxc1a drives appendage-specific neural circuit development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. 6
|
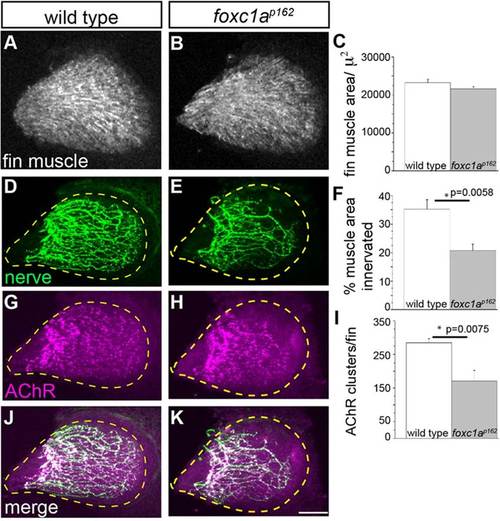
foxc1a mutants display reduced fin nerve arborization and synaptic contacts. (A-C) At 96hpf, fin muscle differentiation and surface area are unaffected in foxc1a mutants compared with wild type. (D-K) By contrast, the area of the fin muscle covered by presynaptic nerve branches (D-F) and the density of postsynaptic AChR clusters is significantly reduced in foxc1a mutants. All images are maximum projection views. The fin is outlined using a dashed yellow line. Scale bar: 50µm. (C,F,I) Asterisks indicate P<0.05 (Student′s t-test). Data are mean±s.e.m. |
Expression Data
| Antibody: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Day 4 |
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 4 |
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development