|
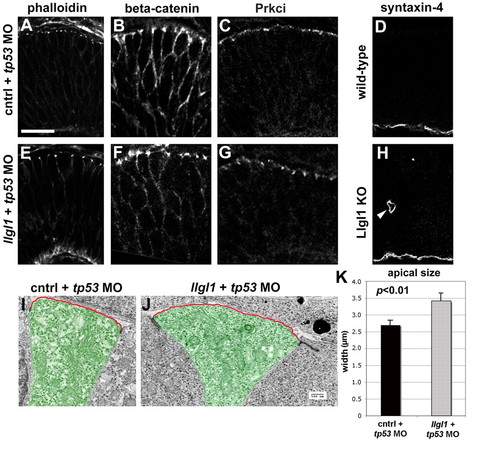
Apicobasal polarity is maintained in Llgl1-deficient retinal neuroepithelia. (A-C,E-G) Immunostaining for apical junction markers in 36 hpf zebrafish retina: (A,E) rhodamine-phalloidin; (B,F) β-catenin; (C,G) Prkci. For the apical markers, zebrafish were injected with either 8 ng control+ 8ng tp53 MO (A-C) or 8 ng tp53 + 8ng llgl1 ATG MO (E-G). (D,H) Immunostaining for the basal marker syntaxin 4 in wild-type (D) or Lgl1 mutant (H) E15.5 mouse retina. Note the basal staining in a rosette in H (arrowhead). (I,J) Transmission electron micrographs of zebrafish retinal neuroepithelial cells injected with either 8 ng control+ 8ng tp53 MO (I) or 8 ng tp53 + 8ng llgl1 ATG MO (J). The apical membrane above the electron-dense adherens junctions is highlighted (red outline). Individual cells are pseudo-colored green for contrast. (K) Comparison of the average length of apical membrane between control (black bar) and llgl1 morphant (gray bar) cells. Scale bars: 25 μm in A-H; 500 nm in I,J.
|