Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100616-33
- Publication
- Ito et al., 2010 - Characterization of neural stem cells and their progeny in the adult zebrafish optic tectum
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
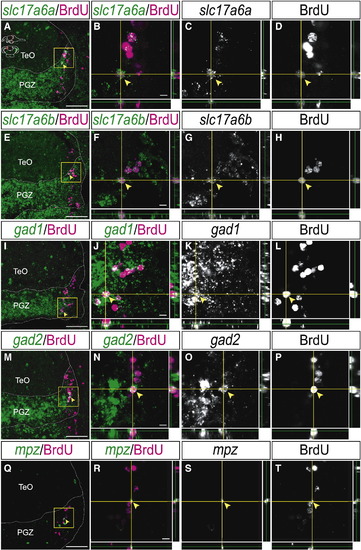
Neural stem/progenitor cells in the mitotic region of the PGZ differentiate into the glutamatergic or GABAergic neurons and oligodendrocytes. (A–P) Expression of glutamatergic and GABAergic neuronal markers in the BrdU-positive cells in the PGZ of the adult zebrafish optic tectum at 1 month post-BrdU administration (14 μm transverse sections, stacked images, dorsal top). (A–H) Some of the BrdU-positive cells express glutamatergic neuronal markers, slc17a6a (A–D, arrowheads) and slc17a6b (E–H, arrowheads) (B–D: high magnification of yellow-boxed area in A, F–H: high magnification of yellow-boxed area in E). (I–P) Some of the BrdU-positive cells express GABAergic neuronal markers, gad1 (I–L, arrowheads) and gad2 (M–P, arrowheads) (J–L: high magnification of yellow-boxed area in I, N–P: high magnification of yellow-boxed area in M). (Q–T) Expression of oligodendrocyte marker, mpz in the BrdU-positive cells in the PGZ of the adult zebrafish optic tectum at 1 month post-BrdU administration (arrowheads) (14 μm transverse sections, stacked images, dorsal top) (R–T: high magnification of the yellow-boxed area in Q). CCe, corpus cerebelli; PGZ, periventricular gray zone; TeO, tectum opticum. Scale bars: 50 μm in A, E, I, M, Q; 5 μm in B, F, J, N, R. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 342(1), Ito, Y., Tanaka, H., Okamoto, H., and Ohshima, T., Characterization of neural stem cells and their progeny in the adult zebrafish optic tectum, 26-38, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.