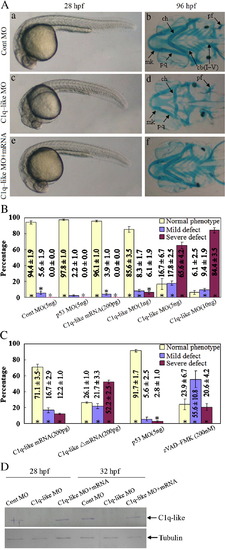
Effect of the C1q-like knockdown on embryo development. (A) Embryo phenotypes observed under the microscope (a, c, e) and the head phenotypes stained with Alcian Blue (b, d, f). The arrows show the defected craniofacial phenotypes in the C1q-like morphant. Abbreviations: cb(I–V), first to fifth ceratobranchial; ch, ceratohyal; mk, Meckel's cartilage; pf, pectoral fin; pq, palatoquandrate. Each picture represents typical results out of three separate experiments (30 embryos in each experiment). (B, C) The statistical data of three independent experiments on C1q-like knockdown and C1q-like over-expression (B), as well as C1q-like mRNA rescue and p53 MO co-injection (B). Results are represented as mean ± SD of three separate experiments (60 embryos in each experiment). *p < 0.05. (D) Western blot detection of C1q-like knockdown during embryogenesis. The protein extracts from 30 embryos (28 hpf and 32 hpf) were analyzed by Western blot using the polyclonal anti-C1q-like antibody. A band of about 24 KD was not detected in C1q-like morphants. The picture represents typical result from three separate experiments.
|

