Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080514-1
- Publication
- Kondo et al., 2001 - Dispersion of cyclin B mRNA aggregation is coupled with translational activation of the mRNA during zebrafish oocyte maturation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
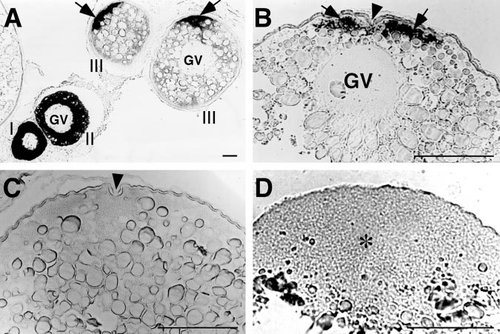
Localization of cyclin B mRNA (arrows) during zebrafish oocyte growth and maturation. GV, germinal vesicle. Scale, 100 μm. (A) Cyclin B mRNA during oocyte growth. Roman numerals show the stages of oocytes. Cyclin B mRNA is initially distributed throughout the cytoplasm of previtellogenic oocytes but translocated during oocyte growth to the future animal pole. (B) A full-grown immature oocyte showing localization of cyclin B mRNA along the cytoplasm at the animal pole identified by the presence of micropyle (indicated by arrowhead). (C) A mature oocyte treated with 17α,20β-DP showing the absence of cyclin B mRNA along the cytoplasm at the animal pole (arrowhead indicates the micropyle as a marker of the animal pole.). (D) A fertilized egg (30 min after spawning) showing the uniform distribution of cyclin B mRNA in the blastodisc (indicated by asterisk). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 229(2), Kondo, T., Kotani, T., and Yamashita, M., Dispersion of cyclin B mRNA aggregation is coupled with translational activation of the mRNA during zebrafish oocyte maturation, 421-431, Copyright (2001) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.