Fig. 9
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080417-29
- Publication
- Kotani et al., 2008 - misty somites, a maternal effect gene identified by transposon-mediated insertional mutagenesis in zebrafish that is essential for the somite boundary maintenance
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
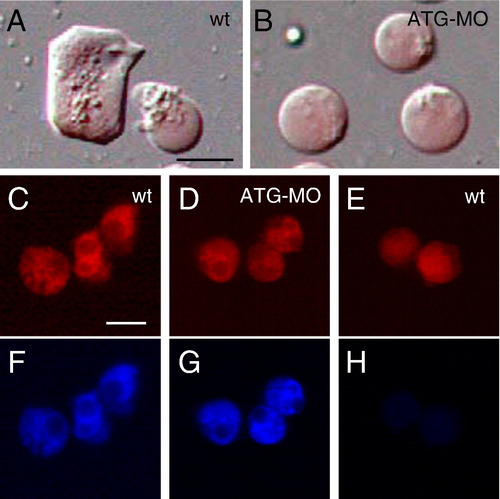
The mys-deficient cells decreased lamellipodia formation on Fibronectin. (A, B) The morphology of cells dissociated from 4 hpf embryos and incubated on Fibronectin for overnight. (A) Cells dissociated from wild type embryos. (B) Cells dissociated from the ATG-MO injected embryos. The embryos were injected with rhodamine-dextran (red). Lamellipodia formation is impaired in the ATG-MO injected cells. (C–H) Analysis of FAK activation. Wild type cells (C, F) and the ATG-MO injected cells (D, G) incubated on Fibronectin for overnight. (E, H) Wild type cells immediately after placed on Fibronectin. (C, D, E) Images of rhodamine-dextran. (F, G, H) Immunostaining using the anti-phosphorylated FAK antibody. FAK is activated in the ATG-MO injected cells. Scale bars show 20 μm. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Sphere |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 316(2), Kotani, T., and Kawakami, K., misty somites, a maternal effect gene identified by transposon-mediated insertional mutagenesis in zebrafish that is essential for the somite boundary maintenance, 383-396, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.