- Title
-
Functional divergence of zebrafish keap1 paralogs revealed by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing: a specialized role for keap1b in inflammation
- Authors
- Nguyen, V.T., Van, B.T.T., Uyen, T.N., Tong, N.X., Pham, T.L., Vy, N.H.T., Thuy, D.T., Thuy, N.P., Kobayashi, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Transgenic. Res.
|
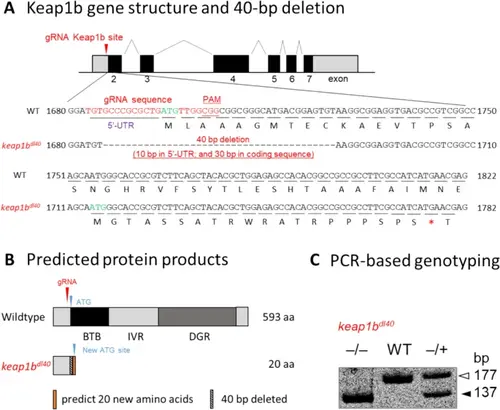
Generation and molecular characterization of the keap1bdl40 knockout allele using CRISPR/Cas9. A Gene structure and deletion. Zebrafish keap1b gene showing gRNA target site (red arrow) at the 5’-UTR/exon 2 boundary. The 40-bp deletion removes 10 bp from 5’-UTR, the ATG start codon (3 bp), and 27 bp from exon 2. Translation initiates from a downstream out-of-frame ATG (green), producing a 20-amino-acid peptide (MGTASSATRWRATRPPPSPS*) terminated by a premature stop codon (asterisk). B Protein products. Wild-type: 593-aa protein with BTB, IVR, and DGR domains. Mutant: 20-aa non-functional peptide (orange) lacking all domains. C PCR genotyping. Gel electrophoresis showing wild-type (177 bp), mutant (137 bp), and heterozygous (both bands) genotypes |
|
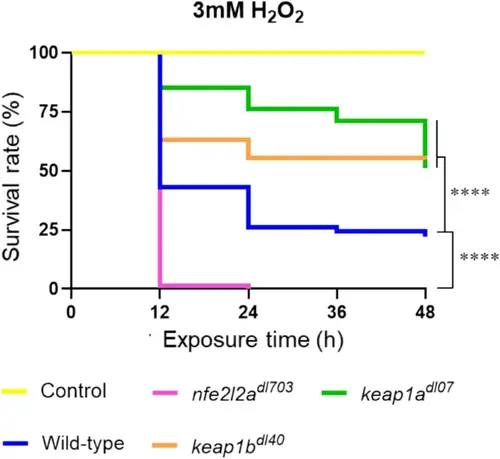
Keap1 paralogs differentially regulate survival under oxidative stress. Survival curves of WT, nfe2l2a−/−, keap1a−/−, and keap1b−/− larvae exposed to 3 mM H2O2 for 48 h. Loss of either Keap1a or Keap1b confers significant protection against oxidative stress compared to wild-type. Conversely, loss of Nrf2a (nfe2l2a−/−) results in extreme hypersensitivity, confirming the essential protective role of this transcription factor. Data are representative results from n = 3 biological replicates. ****p < 0.0001 vs. control |
|
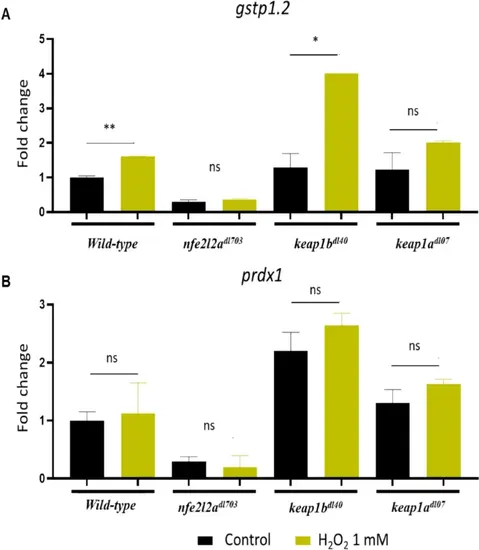
Constitutive activation of Nrf2 target genes in keap1 mutants. Relative mRNA expression of A gstp1.2 and B prdx1 in 4 dpf larvae of different genotypes, with or without H₂O₂ treatment. In the absence of oxidative stress, both keap1a−/− and keap1b−/− mutants show significantly elevated basal expression of these Nrf2 target genes, indicating constitutive pathway activation due to loss of Keap1-mediated Nrf2 repression. This constitutive activation is completely abolished in nfe2l2a−/− larvae, confirming these genes are bona fide Nrf2 targets. Expression is normalized to ef1a and relative to the untreated WT group. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 |
|
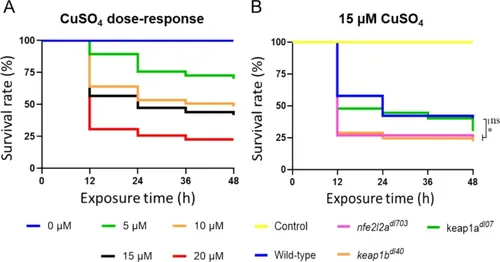
Keap1b is critical for survival during CuSO₄-induced inflammation. A Dose–response curve for wild-type larvae exposed to different concentrations of CuSO4 (0, 5, 10, 15, 20 µM) for 48 h, used to determine the LC50 value of approximately 15 µM. B Survival curves of WT, nfe2l2a−/−, keap1a−/−, and keap1b−/− larvae exposed to 15 µM CuSO4 for 48 h. Note the extreme hypersensitivity of keap1b−/− and nfe2l2a−/− larvae, with survival rates plummeting to ~ 25%, indicating a specialized, non-redundant role for Keap1b in orchestrating a viable inflammatory response. In stark contrast, keap1a−/− larvae show survival rates comparable to wild-type, demonstrating functional divergence between the paralogs. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3) |
|
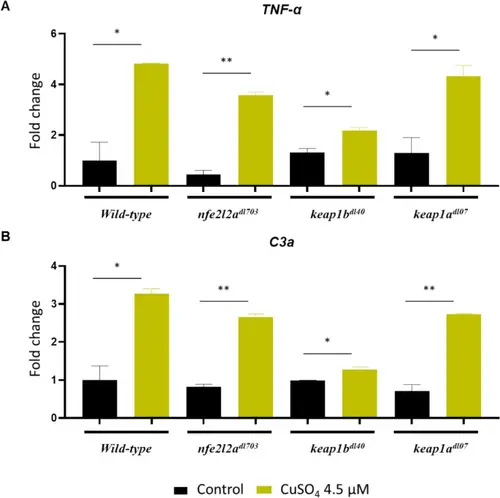
Dysregulated inflammatory gene expression in keap1b mutants. Relative mRNA expression of A TNF-α and B c3a in larvae after 12-h exposure to a sub-lethal concentration of 4.5 μM CuSO4 (to analyze the transcriptional inflammatory response prior to the onset of significant mortality). The lethal phenotype of keap1b−/− larvae observed at higher concentrations (Fig. 4B) is associated with a significantly blunted transcriptional induction of these key pro-inflammatory cytokines compared to wild-type, suggesting that the hypersensitivity is due to an inadequate, rather than excessive, inflammatory response. This indicates that Keap1b plays a critical role in facilitating proper inflammatory gene expression through an Nrf2-mediated response mechanism. Expression is normalized to ef1a and relative to the untreated WT group. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05 |