- Title
-
Rnf111 has a pivotal role in regulating development of definitive hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells through the Smad2/3-Gcsfr/NO axis in zebrafish
- Authors
- Liu, X., Sha, J., Wang, L., Wang, Z., Fang, Z., Han, X., Tan, S., Chen, Y., Yuan, H., De The, H., Zhou, J., Zhu, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Haematologica
|
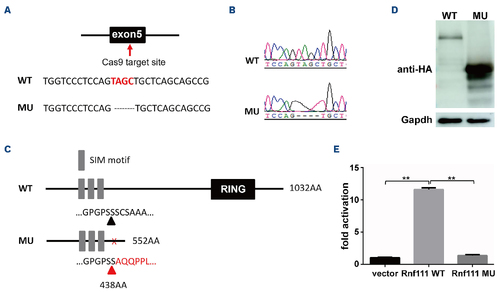
Generation of the Rnf111 mutant line. (A) The Cas9 target site was in the fifth exon; 4 base pair (bp) nucleotides were deleted. (B) The wild-type and mutant sequencing peak maps. (C) Schematic representation of wild-type and mutant Rnf111 proteins. (D) Western blot of HA-tagged wild-type and mutant Rnf111 proteins expressed in HEK293T cells. (E) CAGA12-luciferase transcriptional reporter assay of wild-type and mutant Rnf111. The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation with **P<0.01. WT: wild-type; MU: Rnf111 mutants with deletion of 4 bp; SIM: SUMO-interacting motifs. |
|
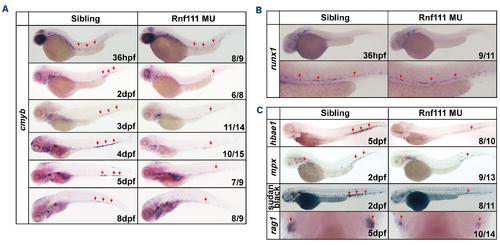
Impairment of definitive hematopoiesis in Rnf111 mutants. (A) Whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) analysis of cmyb expression from 36 hpf to 8 dpf. (B) WISH assay of runx1 in mutants at 36 hpf. (C) WISH analysis of key hematopoietic markers and Sudan black analysis. All experiments were independently replicated at least three times. MU: Rnf111 mutants with deletion of 4 base pair nucleotides; hpf: hours post-fertilization; dpf: days post-fertilization. |
|
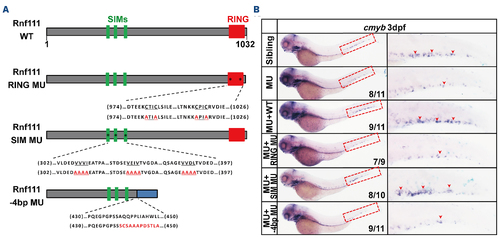
Schematic representation and rescue assay of the four Rnf111 constructs. (A) Schematic diagram of the Rnf111 wild-type, Rnf111 RING mutant, Rnf111 SIM mutant and -4 base pair (bp) mutant proteins. (B) Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of the rescue efficiency of Rnf111 wild-type, Rnf111 RING mutant, Rnf111 SIM mutant and Rnf111-4 bp mutant RNA. Red arrows indicate cmyb-positive hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. All experiments were independently replicated at least three times. WT: wild-type; RING MU: Rnf111 RING mutant with the RING domain mutated; SIM MU: Rnf111 SIM mutant with three SUMO-interacting motifs all mutated; SIM: SUMO-interacting motifs; -4bp MU: Rnf111-4 bp mutant with deletion of 4 bp nucleotides; dpf: days post-fertilization; MU: Rnf111 mutants with deletion of 4 bp nucleotides. |
|
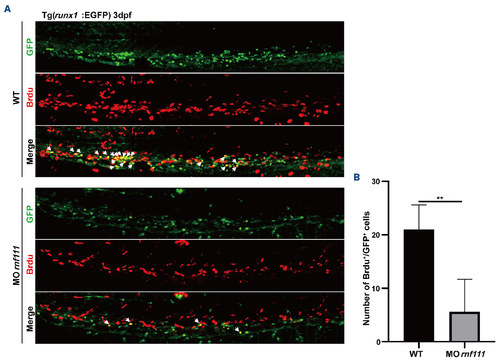
Bromodeoxyuridine incorporation assay. (A) Double immunostaining of runx1-EGFP with green fluorescent protein (GFP) and anti-bromodeoxyuridine (Brdu) in the caudal hematopoietic tissue of the transgenic Tg (runx1-EGFP) line at 3 dpf. White arrows indicate Brdu and runx1-EGFP double-positive cells. (B) Statistics of Brdu and runx1-GFP double-positive cells. The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. with **P<0.01. dpf: days post-fertilization; WT: wild-type; MO rnf111: rnf111 morphants. |
|
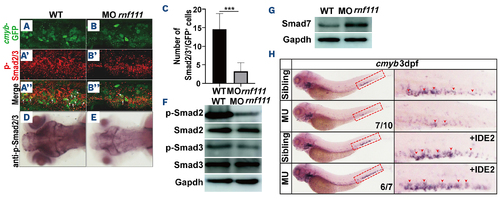
Analysis of p-Smad2/3, Smad7 and IDE2 rescue assay in Rnf111-deficient embryos. (A, A’, A’’, B, B’, B’’) Double immunostaining of anti-GFP (A, B) and anti-p-Smad2/3 (A’, B’) in the caudal hematopoietic tissue of the transgenic Tg (cmyb-EGFP) line at 3 dpf. The bottom panel shows merged images (A’’, B’’). White arrows indicate p-Smad2/3 and cmyb-EGFP double-positive cells. (C) Statistics of p-Smad2/3 and cmyb-EGFP double-positive cells. The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation with ***P<0.001. (D, E) Immunohistochemistry of p-Smad2/3. (F) Western blot analysis of p-Smad2, Smad2, p-Smad3 and Smad3. (G) Western blot analysis of Smad7. (H) Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of rescue efficiency of IDE2. Red arrows indicate cmyb-positive hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the caudal hematopoietic tissue. All experiments were independently replicated at least three times. WT: wild-type; MO rnf111: rnf111 morphants; GFP: green fluorescent protein; MU: Rnf111 mutants with deletion of 4 base pair nucleotides; IDE2: definitive endoderm 2 inducer; EGFP: enhanced green fluorescent protein; dpf: days post-fertilization. |
|
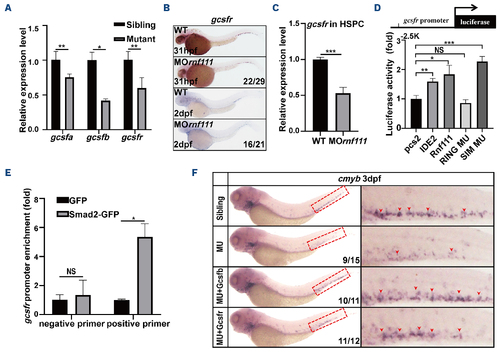
Gcsf signaling was the downstream target of Rnf111-Smad2/3. (A) Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) of gcsfa, gcsfb and gcsfr in siblings and mutants at 3 dpf. The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) with *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (B) Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of gcsfr. (C) Real-time qPCR of gcsfr in HSPC of rnf111 morphants. The data are presented as mean ± SD with ***P<0.01. (D) Luciferase assay of gcsfr promotor in HEK293T cells. The data are presented as mean ± SD with *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, NS: no significant difference. (E) Chromatin immunoprecipitation qPCR assay of Smad2-GFP binding to gcsfr promotor at 2 dpf. The data are presented as mean ± SD with *P<0.05, NS: no significant difference. (F) Rescue assay of gcsfb and gcsfr RNA in Rnf111 mutants. Red arrows indicate cmyb-positive hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the caudal hematopoietic tissue. All experiments were independently replicated at least three times. WT: wild-type; MO rnf111: rnf111 morphants; HSPC: hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell; IDE2: definitive endoderm 2 inducer; RING MU: Rnf111 RING mutant with the RING domain mutated; SIM MU: Rnf111 SIM mutant with three SUMO-interacting motifs all mutated; GFP: green fluorescent protein; MU: Rnf111 mutants with deletion of 4 base pair nucleotides; hpf: hours post-fertilization; dpf: days post-fertilization. |
|
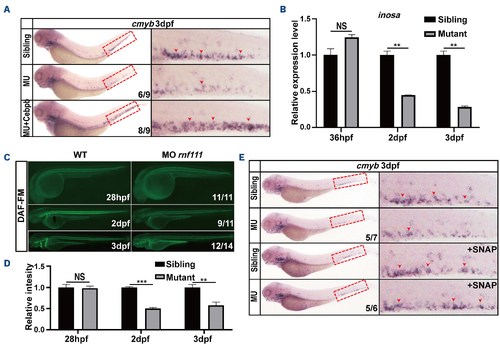
Cebpb-Nos2a acts downstream of Gcsf signaling. (A) Rescue assay of cebpb RNA. (B) Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction results for inosa in Rnf111 mutants compared with wild-type embryos at 36 hpf, 2 dpf and 3 dpf. The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) with **P<0.01, NS: no significant difference. (C) DAF-FM assay showed the decreased production of nitric oxide (NO) morphants at 2 dpf and 3 dpf. (D) Statistics of NO fluorescence intensity. The data are presented as mean ± SD with **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, NS: no significant difference. (E) A rescue effect of the NO agonist S nitroso N-acetylpenicillamine (SNAP) on cmyb expression was observed in Rnf111 mutants. Red arrows indicate cmyb-positive hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in caudal hematopoietic tissue. All experiments were independently replicated at least three times. dpf: days post-fertilization; MU: Rnf111 mutants with deletion of 4 base pair nucleotides; hpf: hours post-fertilization; WT: wild-type; MO rnf111: rnf111 morphants; DAF-FM: 4-amino-5-methylamino-2′,7′-difluorofluorescein diacetate. |
|
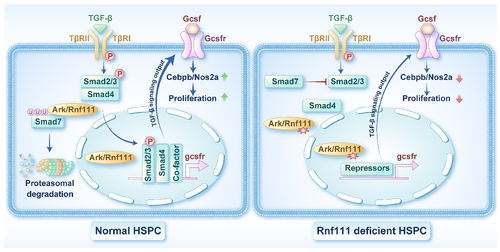
Schema of Rnf111 regulating the development of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells by maintaining Smad2/3 phosphorylation and activating the Gcsfr/NO signaling pathway. Left. At a physiological concentration of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), ARK/Rnf111 maintains Smad2/3 phosphorylation by promoting the degradation of Smad7 and further facilitates activation of the Gcsfr/NO signaling pathway to ensure the proliferative response of HSPC to TGF-β. Right. Deletion of ARK/Rnf111 in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC) leads to a weakening of TGF-β signaling output, which is manifested by a decrease in the Gcsfr/NO signal, resulting in an attenuated proliferative response of HSPC to TGF-β. |