- Title
-
Cytoneme-mediated transport of active Wnt5b-Ror2 complexes in zebrafish
- Authors
- Zhang, C., Brunt, L., Ono, Y., Rogers, S., Scholpp, S.
- Source
- Full text @ Nature
|
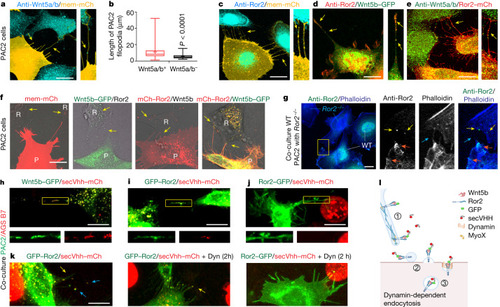
Wnt5b–Ror2 complexes are transported from the producing cells to the receiving cells via cytonemes. |
|
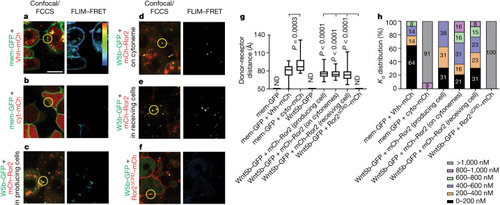
In vivo FLIM–FRET and FCCS imaging reveal maintenance of Wnt5b–Ror2 complex cohesiveness during transport. |
|
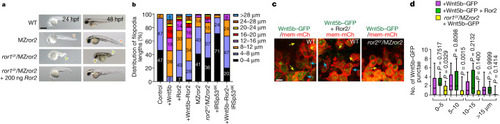
Wnt5b–Ror2–JNK signalling promotes the formation of long cytonemes. |
|
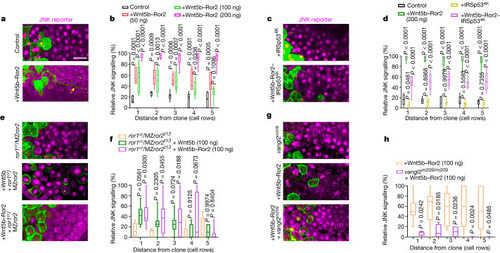
Wnt5b–Ror2-expressing clones activate paracrine JNK signalling. |
|
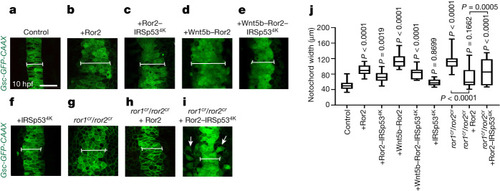
Alterations of cytoneme-mediated dissemination of Wnt5b–Ror2 complexes affect convergence and extension in the zebrafish embryo. |