- Title
-
The mineralocorticoid receptor plays a crucial role in macrophage development and function
- Authors
- Faught, E., Schaaf, M.J.M.
- Source
- Full text @ Endocrinology
|
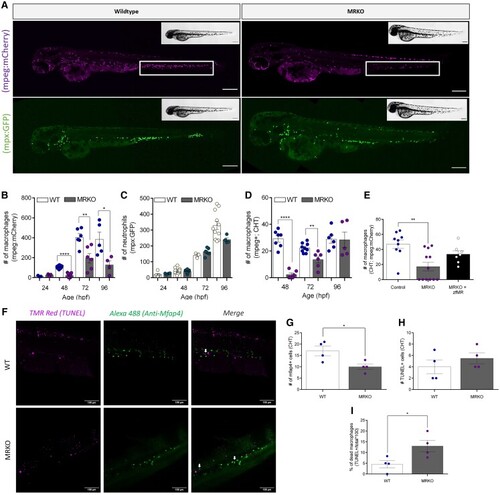
A loss of MR results in global macrophage depletion throughout development. (A) Representative images of either |
|
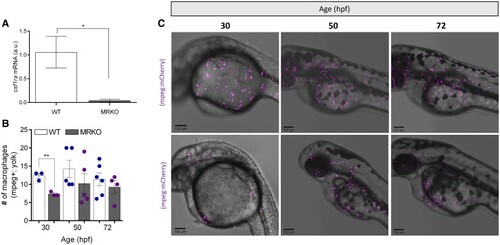
A loss of MR impacts macrophage production and distribution during development. (A) Transcript abundance of |
|
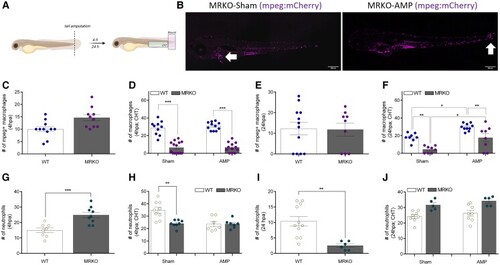
Macrophages lacking MR are still responsive to an inflammatory stimulus. (A) Schematic diagram of tail fin amputation. Distinct areas of quantification are indicated. (B) Representative images of sham and amputated (AMP) |
|
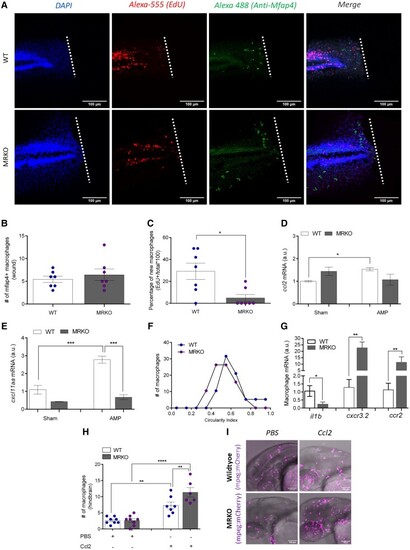
The generation of new macrophages is reduced in MRKO larvae, and macrophages migrating toward the wound exhibit a less inflammatory phenotype. (A) Representative images of macrophage proliferation at 48 hours postfertilization (hpf), 4 hours postamputation (hpa), where the nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue), new cells have incorporated the thymidine nucleoside analogue EdU (red), and macrophages are visualized by immunohistochemistry using a Mfap4 antibody (green). White dotted lines denote the location of amputation. (B) Number of Mfap4+ macrophages localized to the wound site at 4 hpa (n = 7). (C) The percentage of new (EdU+) macrophages localized to the wound site at 4 hpa (n = 7). (D and E) Transcript abundance of macrophage-specific chemokines |
|
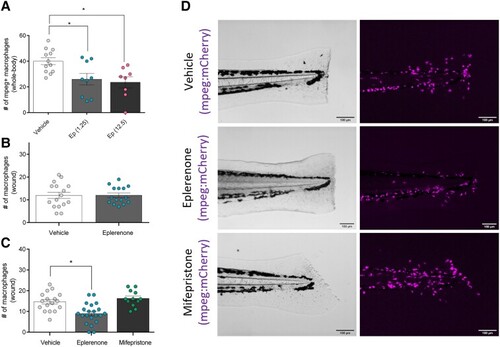
Pharmacological blockade of MR results in a reduced macrophage migration toward a wound. (A) Number of mpeg+ macrophages in the whole body of zebrafish at 52 hpf after incubation with either 1.25 μM or 12.5 μM eplerenone for 50 hours ( |
|
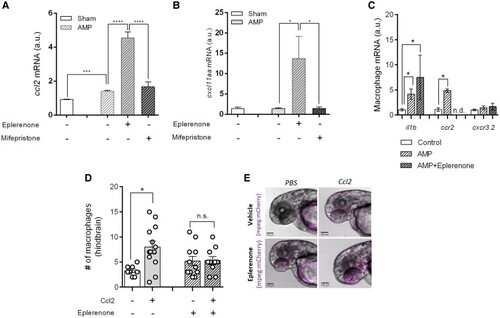
The anti-inflammatory effect of eplerenone is due to altered responsivity at the level of the macrophage. (A and B) Transcript abundance (determined by qPCR) of genes encoding the macrophage-specific chemo-attractants |
|
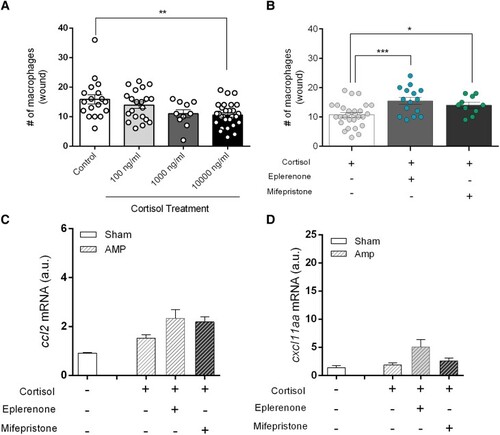
MR modulates the cortisol-induced reduction in macrophage migration toward a wound site. (A) Number of mpeg+ macrophages that have migrated toward the wound site (200 µm from amputation site), at 4 hours after amputation, in larvae exposed to different levels of cortisol ranging from doses that reflect physiological stress levels (100 ng/mL) to a pharmacological dose (10 μg/mL) (n = 11-30). (B) The number of mpeg+ macrophages that have migrated toward the wound site in the presence of cortisol (10 µg/mL), in combination with either eplerenone (1.25 µM) or mifepristone (1.25 µM) (n = 10-28). (C and D) Transcript abundance of genes encoding the macrophage-specific chemoattractants |
|
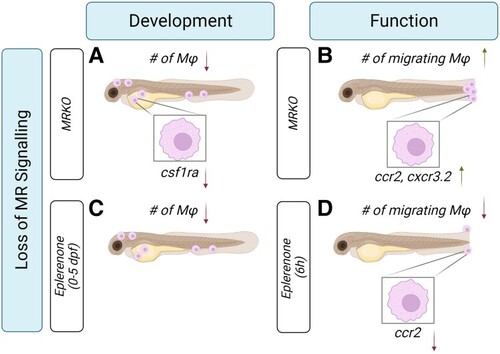
Summary schematic of the different roles of mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) in modulating the development and function of macrophages in zebrafish. A reduction in MR signalling in zebrafish, either through genetic perturbations or pharmacological antagonism, leads to altered macrophage responsivity to developmental and inflammatory signals, showing that MR is crucial for macrophage development and function. (A) During a key developmental period (0-120 hours postfertilization [hpf]), larvae lacking MR (MRKO) experience a global reduction in whole-body macrophage numbers. This is associated with a lack of production in the yolk and distribution out of the yolk, and these macrophages show reduced transcript abundance of the colony-stimulating factor receptor 1 ( |