Figure 6.
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230916-75
- Publication
- Faught et al., 2023 - The mineralocorticoid receptor plays a crucial role in macrophage development and function
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
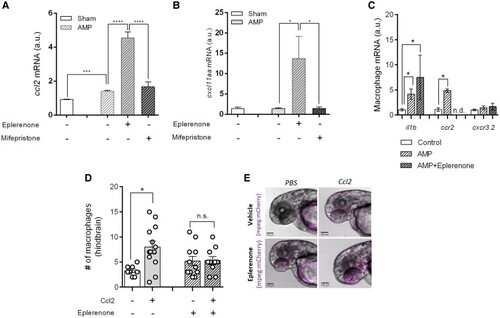
The anti-inflammatory effect of eplerenone is due to altered responsivity at the level of the macrophage. (A and B) Transcript abundance (determined by qPCR) of genes encoding the macrophage-specific chemo-attractants |