- Title
-
Phytochemical and Safety Evaluations of Finger Lime, Mountain Pepper, and Tamarind in Zebrafish Embryos
- Authors
- Cáceres-Vélez, P.R., Ali, A., Fournier-Level, A., Dunshea, F.R., Jusuf, P.R.
- Source
- Full text @ Antioxidants (Basel)
|
Heatmap of the concentration of bioactive compounds (μg/g) in finger lime (FL), mountain pepper (MP), and tamarind (T). |
|
Heatmap of the alterations observed in zebrafish embryos exposed during 96 h to the plant extracts. The mean of three replicates ( |
|
Phenotypic assessment of zebrafish development for the whole organism exposed 96 h post-fertilization to different concentrations of finger lime ( |
|
Morbidity assessments of zebrafish development for the whole organism exposed at 96 h post-fertilization to different concentrations of finger lime ( |
|
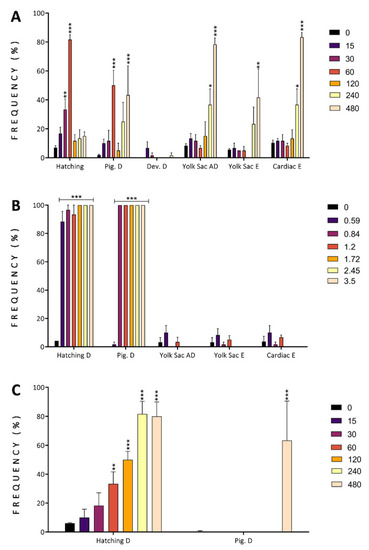
Developmental alterations observed in organisms exposed at 96 h post-fertilization to different concentrations of finger lime ( |
|
Malformations observed in zebrafish exposed at 96 h post-fertilization to different concentrations of finger lime and mountain pepper extracts. Each colour bar denotes the concentration tested in mg/L for finger lime ( |