- Title
-
Functional Analysis of Zebrafish socs4a: Impacts on the Notochord and Sensory Function
- Authors
- Trengove, M., Wyett, R., Liongue, C., Ward, A.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Brain Sci
|
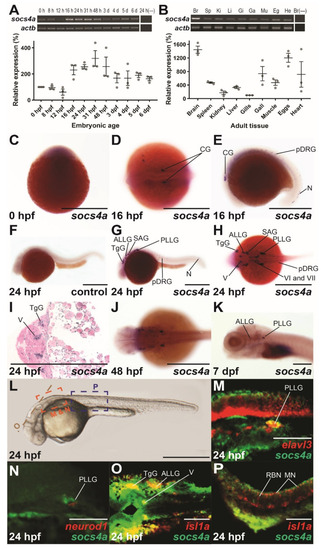
Spatio-temporal expression profile of socs4a. RT-PCR analysis of socs4a and control actb (β-actin) from total RNA extracted from embryos at the indicated times post fertilization ((A), upper panel) or from the indicated adult tissues ((B), upper panel), with a no RT control included (−). Levels of socs4a were quantified using densitometry and standardized to the actb gene with the embryonic expression profile shown relative to expression at 0 hpf ((A), lower panel) and the adult profile relative to expression in the gills ((B), lower panel). Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of socs4a on embryos at 0 hpf (C), 16 hpf (D,E), 24 hpf (F–I), 48 hpf (J), and 7 dpf (K) using either sense (control) or anti-sense (socs4a) probes, as indicated. Expression is demonstrated by the presence of blue/purple staining. dFISH on 24 hpf embryos with anti-sense probes for socs4a and either elavl3 (M), neurod1 (N) or isl1a (O,P), with the regions of the embryo imaged displayed in panel L. Expression is demonstrated by red or green fluorescence for each marker, as indicated, with areas of co-expression being yellow. The embryo in panel C is upright and imaged laterally. All other embryos are positioned with their anterior to the left and imaged laterally (E–G,K–N,P), dorsally (D,H,J,O) or represent a cross-section (I). Scale bars = 0.5 mm (C–L) or 0.1 mm (M–P). Abbreviations: ALLG, anterior lateral line ganglion; Br, brain; CG, cranial ganglion; Eg, eggs; Ga, gall bladder; Gi, gills; He, heart; Ki, kidney; Li, liver; MN, motor neuron; Mu, muscle; N, neuron; pDRG, precursor dorsal root ganglion; PLLG, posterior lateral line ganglion; RBN, Rohan–Beard neuron; SAG, statoacoustic ganglion; Sp, spleen; TgG, trigeminal ganglion; V, fifth cranial nerve; VI, sixth cranial nerve; VII, seventh cranial nerve. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Phenotypic consequences of socs4a knockdown. Schematic of socs4a mRNA schematic showing exons boxed and joined by a thin line, with non-coding sequence in blue and coding in grey. Sequences targeted by ATG MO (purple) and UTR MO (pink) are indicated (A). Confirmation of ATG MO efficacy by in vitro transcription and translation of socs4a in the presence of control (Ctl) or ATG MO with the arrow indicating the position of the Socs4a protein at ~44 kDa and the asterisk a non-specific protein (B). Analysis of embryos injected with Ctl (C,F,K,N,P), ATG (D,E,L,O,Q) or UTR (G) MO, or combined UTR MO with MO-resistant socs4a mRNA (UTR/RNA, (H)) or with p53 MO (UTR/p53, (I)) by either light microscopy (C–I,K,L,N,O) or fluorescence microscopy of phalloidin (Ph) staining of muscle fibers (P,Q). All embryos are positioned with their anterior to the left and images are lateral view. Scale bars = 0.5 mm (C–I) or 0.1 mm (K,L,N,Q). The ventral curl phenotype in Ctl, ATG, UTR, UTR/RNA and UTR/p53 MO was quantified, and shown as mean ± SEM, with statistical significance versus Ctl (p < 0.05: *; p < 0.01: **) or UTR (p < 0.05: #) shown (J). Embryo length (anterior–posterior) at 4 dpf is provided for individual embryos, with mean ± SEM and statistical significance versus Ctl indicated (p < 0.05: *) (M). Abbreviations: fp, floor plate; hc, hypochord; sb, somite boundary. |
|
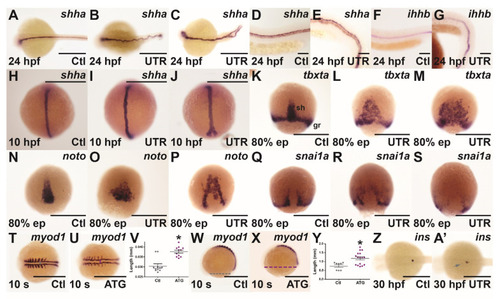
Effect of socs4a knockdown on convergence and extension. Embryos injected with either Ctl (A,D,F,H,K,N,Q,T,W,Z), UTR (B,C,E,G,I,J,L,M,O,P,R,S,A’) or ATG (U,X) MO were subjected to WISH at 24 hpf (A–G), 10 hpf (H–J), 80% epiboly (ep) (K–S), 10 somites (s) (T,U,W,X) and 30 hpf (Z,A’) for shha (A–E,H–J), ihhb (F,G), tbxta (K–M), noto (N–P), snai1a (Q–S), myod1 (T,U,W,X) and ins (Z,A’). Both mild (B,I,L,O,R) and more severe (C,J,M,P,S) phenotypes are shown. Scale bars = 0.5 mm (A–C,H–U,W,X,Z,A’) or 0.1 mm (D–G). The distance between parallel paraxial mesoderm structures (V) and across yolk from anterior to posterior for 10 somite embryos was measured (Y). Results are shown for individual embryos, along with mean ± SEM, with statistical significance relative to Ctl indicated (p < 0.05: *). Abbreviations: gr, germ ring; sh, shield. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
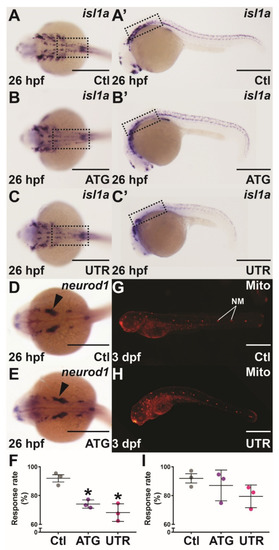
Mechanosensory analysis in socs4a knockdown embryos. Embryos injected with Ctl (A,A’,D,G), ATG (B,B’,E) or UTR (C,C’,H) MO were subjected to WISH with isl1a (A–C’) or neurod1 (D,E) at 26 hpf, or Mitotracker red (Mito) staining at 3 dpf (G,H) and imaged dorsally (A–E) and laterally (A’–C’,G,H), with the boxed areas highlighting the equivalent areas in the alternative images (A–C,A’–C’). Scale bars = 0.5 mm. Alternatively, the responsiveness to touch at 24 hpf (F) and water movement at 3 dpf (I) was quantified, with results presented for 3 independent experiments (n > 30 embryos in each group) along with mean ± SEM and statistical significance relative to Ctl (p < 0.05: *). Abbreviation: NM, neuromast. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|